|
Peak Expiratory Flow Rate
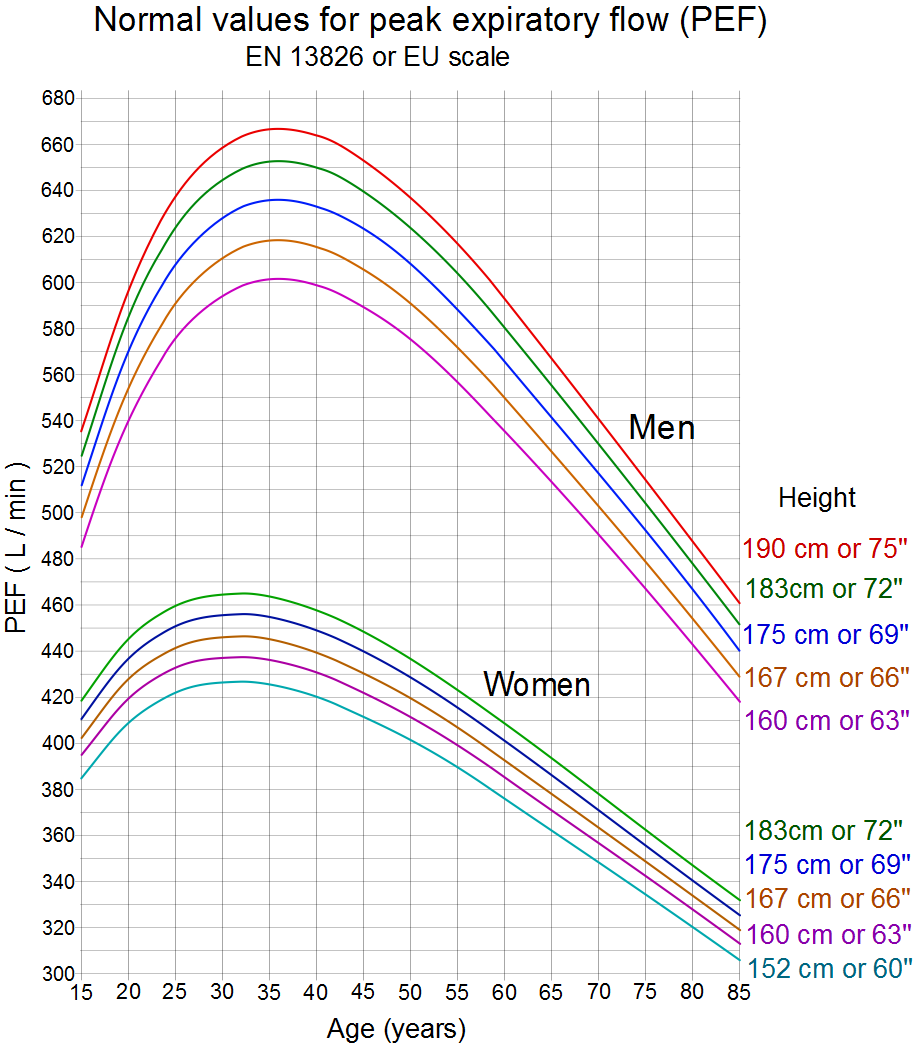
The peak expiratory flow (PEF), also called peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR), is a person's maximum speed of expiration, as measured with a peak flow meter, a small, hand-held device used to monitor a person's ability to breathe out air. It measures the airflow through the bronchi and thus the degree of obstruction in the airways. Peak expiratory flow is typically measured in units of liters per minute (L/min). Function Peak flow readings are higher when patients are well, and lower when the airways are constricted. From changes in recorded values, patients and doctors may determine lung functionality, the severity of asthma symptoms, and treatment. Measurement of PEFR requires training to correctly use a meter and the normal expected value depends on the patient's sex, age, and height. It is classically reduced in obstructive lung disorders such as asthma. Due to the wide range of 'normal' values and the high degree of variability, peak flow is not the recommended test to ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronchus
A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi pronounced (BRAN-KAI) to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. These are the widest bronchi, and enter the right lung, and the left lung at each hilum. The main bronchi branch into narrower secondary bronchi or lobar bronchi, and these branch into narrower tertiary bronchi or segmental bronchi. Further divisions of the segmental bronchi are known as 4th order, 5th order, and 6th order segmental bronchi, or grouped together as subsegmental bronchi. The bronchi, when too narrow to be supported by cartilage, are known as bronchioles. No gas exchange takes place in the bronchi. Structure The trachea (windpipe) divides at the carina into two main or primary bronchi, the left bronchus and the right bronchus. The carina of the trachea is located at the level of the sternal angle and the fifth thoracic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. These may occur a few times a day or a few times per week. Depending on the person, asthma symptoms may become worse at night or with exercise. Asthma is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Environmental factors include exposure to air pollution and allergens. Other potential triggers include medications such as aspirin and beta blockers. Diagnosis is usually based on the pattern of symptoms, response to therapy over time, and spirometry lung function testing. Asthma is classified according to the frequency of symptoms, forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), and peak expiratory flow rate. It may also be classified as atopic or non-atop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Equipment
A medical device is any device intended to be used for medical purposes. Significant potential for hazards are inherent when using a device for medical purposes and thus medical devices must be proved safe and effective with reasonable assurance before regulating governments allow marketing of the device in their country. As a general rule, as the associated risk of the device increases the amount of testing required to establish safety and efficacy also increases. Further, as associated risk increases the potential benefit to the patient must also increase. Discovery of what would be considered a medical device by modern standards dates as far back as c. 7000 BC in Baluchistan where Neolithic dentists used flint-tipped drills and bowstrings. Study of archeology and Roman medical literature also indicate that many types of medical devices were in widespread use during the time of ancient Rome. In the United States it wasn't until the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flow Meters
Flow may refer to: Science and technology * Fluid flow, the motion of a gas or liquid * Flow (geomorphology), a type of mass wasting or slope movement in geomorphology * Flow (mathematics), a group action of the real numbers on a set * Flow (psychology), a mental state of being fully immersed and focused * Flow, a spacecraft of NASA's GRAIL program Computing * Flow network, graph-theoretic version of a mathematical flow * Flow analysis * Calligra Flow, free diagramming software * Dataflow, a broad concept in computer systems with many different meanings * Microsoft Flow (renamed to Power Automate in 2019), a workflow toolkit in Microsoft Dynamics * Neos Flow, a free and open source web application framework written in PHP * webMethods Flow, a graphical programming language * FLOW (programming language), an educational programming language from the 1970s * Flow (web browser), a web browser with a proprietary rendering engine Arts, entertainment and media * ''Flow'' (journal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Inventions ...
The following articles cover the timeline of United States inventions: * Timeline of United States inventions (before 1890), before the turn of the century * Timeline of United States inventions (1890–1945), before World War II * Timeline of United States inventions (1946–1991), for the post-war era * Timeline of United States inventions (after 1991), after the Fall of the Soviet Union {{DEFAULTSORT:Timeline of United States Inventions United States inventions United States The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirometry
Spirometry (meaning ''the measuring of breath'') is the most common of the pulmonary function tests (PFTs). It measures lung function, specifically the amount (volume) and/or speed (flow) of air that can be inhaled and exhaled. Spirometry is helpful in assessing breathing patterns that identify conditions such as asthma, pulmonary fibrosis, cystic fibrosis, and COPD. It is also helpful as part of a system of health surveillance, in which breathing patterns are measured over time. Spirometry generates pneumotachographs, which are charts that plot the volume and flow of air coming in and out of the lungs from one inhalation and one exhalation. Indications Spirometry is indicated for the following reasons: * to diagnose or manage asthma * to detect respiratory disease in patients presenting with symptoms of breathlessness, and to distinguish respiratory from cardiac disease as the cause * to measure bronchial responsiveness in patients suspected of having asthma * to diagn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salbutamol
Salbutamol, also known as albuterol and sold under the brand name Ventolin among others, is a medication that opens up the medium and large airways in the lungs. It is a short-acting β2 adrenergic receptor agonist which works by causing relaxation of airway smooth muscle. It is used to treat asthma, including asthma attacks, exercise-induced bronchoconstriction, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It may also be used to treat high blood potassium levels. Salbutamol is usually used with an inhaler or nebulizer, but it is also available in a pill, liquid, and intravenous solution. Onset of action of the inhaled version is typically within 15 minutes and lasts for two to six hours. Common side effects include shakiness, headache, fast heart rate, dizziness, and feeling anxious. Serious side effects may include worsening bronchospasm, irregular heartbeat, and low blood potassium levels. It can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but safety is not en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory Monitoring
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, with the main goal of helping the delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide. Mechanical ventilation is used for many reasons, including to protect the airway due to mechanical or neurologic cause, to ensure adequate oxygenation, or to remove excess carbon dioxide from the lungs. Various healthcare providers are involved with the use of mechanical ventilation and people who require ventilators are typically monitored in an intensive care unit. Mechanical ventilation is termed invasive if it involves an instrument to create an airway that is placed inside the trachea. This is done through an endotracheal tube or nasotracheal tube. For non-invasive ventilation in people who are conscious, face or nasal masks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metered-dose Inhaler
A metered-dose inhaler (MDI) is a device that delivers a specific amount of medication to the lungs, in the form of a short burst of aerosolized medicine that is usually self-administered by the patient via inhalation. It is the most commonly used delivery system for treating asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and other respiratory diseases. The medication in a metered dose inhaler is most commonly a bronchodilator, corticosteroid or a combination of both for the treatment of asthma and COPD. Other medications less commonly used but also administered by MDI are mast cell stabilizers, such as cromoglicate or nedocromil. Description A metered-dose inhaler consists of three major components; the canister which is produced in aluminium or stainless steel by means of deep drawing, where the formulation resides; the metering valve, which allows a metered quantity of the formulation to be dispensed with each actuation; and an actuator (or mouthpiece) which allows t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by long-term respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms include shortness of breath and a cough, which may or may not produce mucus. COPD progressively worsens, with everyday activities such as walking or dressing becoming difficult. While COPD is incurable, it is preventable and treatable. The two most common conditions of COPD are emphysema and chronic bronchitis and they have been the two classic COPD phenotypes. Emphysema is defined as enlarged airspaces ( alveoli) whose walls have broken down resulting in permanent damage to the lung tissue. Chronic bronchitis is defined as a productive cough that is present for at least three months each year for two years. Both of these conditions can exist without airflow limitation when they are not classed as COPD. Emphysema is just one of the structural abnormalities that can limit airflow and can exist without ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Wright (bioengineer)
Basil Martin Wright (20 December 1912 – 4 March 2001) was a British bioengineer who invented several notable medical instruments, including the peak flow meter and syringe driver. The "alcolmeter" he developed won a Queen's Award for Industry and is the breathalyser most often used at the road-side in the United Kingdom. Early life Wright was born in Dulwich, the son of a clergyman of the Church of England, and was educated at Winchester College and Trinity College, Cambridge, where he graduated with a first in physiology. He then proceeded to St Bartholomew's Hospital and qualified as a doctor in 1938. Career After his time at Bart's as a medical registrar, in 1942 Wright joined the Royal Army Medical Corps to work as a pathologist. During the Second World War he was posted to Sierra Leone, and after the war to Singapore, where he organized the reinstatement of medical laboratory services. He rose to the rank of Colonel, and after demobilization continued to work as a patho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peak Flow Meter
The peak expiratory flow (PEF), also called peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR), is a person's maximum speed of expiration, as measured with a peak flow meter, a small, hand-held device used to monitor a person's ability to breathe out air. It measures the airflow through the bronchi and thus the degree of obstruction in the airways. Peak expiratory flow is typically measured in units of liters per minute (L/min). Function Peak flow readings are higher when patients are well, and lower when the airways are constricted. From changes in recorded values, patients and doctors may determine lung functionality, the severity of asthma symptoms, and treatment. Measurement of PEFR requires training to correctly use a meter and the normal expected value depends on the patient's sex, age, and height. It is classically reduced in obstructive lung disorders such as asthma. Due to the wide range of 'normal' values and the high degree of variability, peak flow is not the recommended test to ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |