Peak Expiratory Flow Rate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The peak expiratory flow (PEF), also called peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR), is a person's maximum speed of expiration, as measured with a peak flow meter, a small, hand-held device used to monitor a person's ability to breathe out air. It measures the airflow through the
 Peak flow readings are higher when patients are well, and lower when the airways are constricted. From changes in recorded values, patients and doctors may determine lung functionality, the severity of asthma symptoms, and treatment.
Measurement of PEFR requires training to correctly use a meter and the normal expected value depends on the patient's sex, age, and height. It is classically reduced in obstructive lung disorders such as
Peak flow readings are higher when patients are well, and lower when the airways are constricted. From changes in recorded values, patients and doctors may determine lung functionality, the severity of asthma symptoms, and treatment.
Measurement of PEFR requires training to correctly use a meter and the normal expected value depends on the patient's sex, age, and height. It is classically reduced in obstructive lung disorders such as
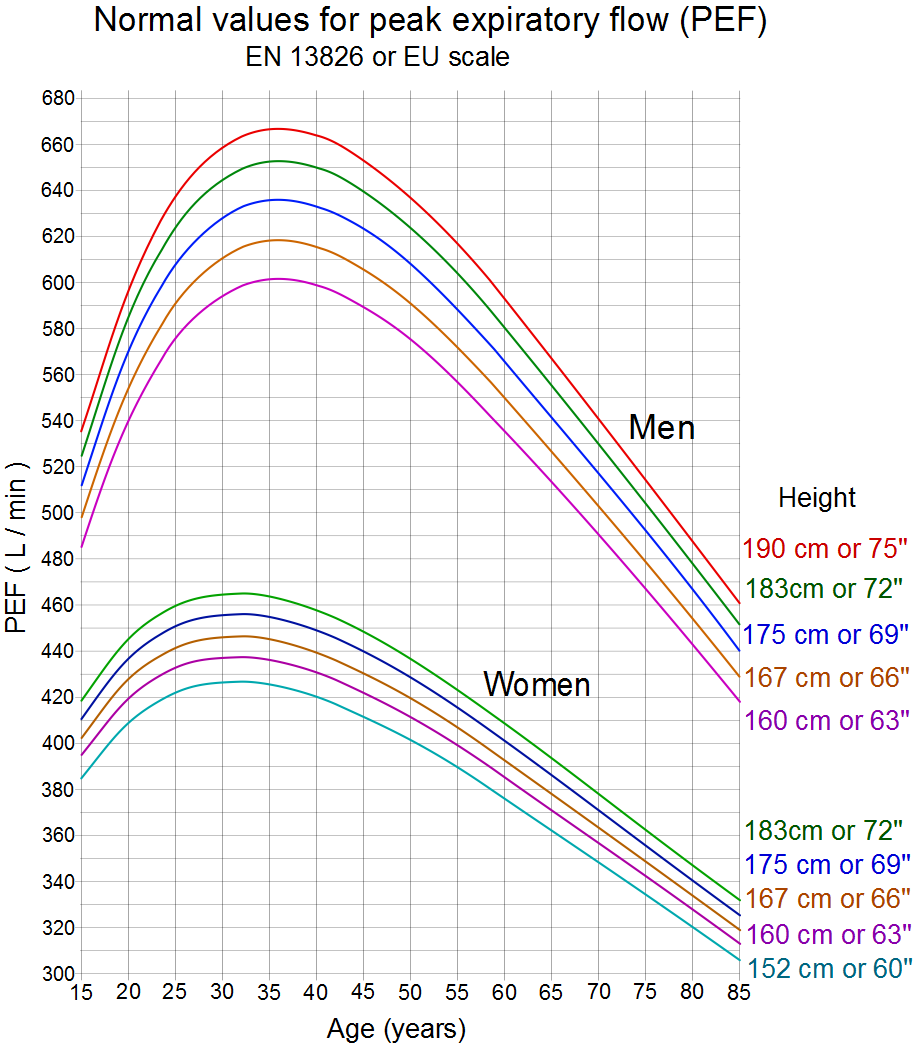 To interpret the significance of peak expiratory flow measurements, a comparison is made to reference (normal, predicted) values based on measurements taken from the general population. Various reference values have been published in the literature and vary by population, ethnic group, age, sex, height and weight of the patient. For this reason, tables or charts are used to determine the normal value for a particular individual. More recently,
To interpret the significance of peak expiratory flow measurements, a comparison is made to reference (normal, predicted) values based on measurements taken from the general population. Various reference values have been published in the literature and vary by population, ethnic group, age, sex, height and weight of the patient. For this reason, tables or charts are used to determine the normal value for a particular individual. More recently,
National Asthma Council of AustraliaEstimated Peak Expiratory Flow Calculator
{{Respiratory physiology American inventions Flow meters Medical equipment Respiratory therapy Asthma
bronchi
A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi pronounced (BRAN-KAI) to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. ...
and thus the degree of obstruction in the airways. Peak expiratory flow is typically measured in units of liters per minute (L/min).
Function
 Peak flow readings are higher when patients are well, and lower when the airways are constricted. From changes in recorded values, patients and doctors may determine lung functionality, the severity of asthma symptoms, and treatment.
Measurement of PEFR requires training to correctly use a meter and the normal expected value depends on the patient's sex, age, and height. It is classically reduced in obstructive lung disorders such as
Peak flow readings are higher when patients are well, and lower when the airways are constricted. From changes in recorded values, patients and doctors may determine lung functionality, the severity of asthma symptoms, and treatment.
Measurement of PEFR requires training to correctly use a meter and the normal expected value depends on the patient's sex, age, and height. It is classically reduced in obstructive lung disorders such as asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, cou ...
.
Due to the wide range of 'normal' values and the high degree of variability, peak flow is not the recommended test to identify asthma. However, it can be useful in some circumstances.
A small portion of people with asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, cou ...
may benefit from regular peak flow monitoring. When monitoring is recommended, it is usually done in addition to reviewing asthma symptoms and frequency of reliever medication use.
When peak flow is being monitored regularly, the results may be recorded on a peak flow chart.
It is important to use the same peak flow meter every time.
Scales or reference values
 To interpret the significance of peak expiratory flow measurements, a comparison is made to reference (normal, predicted) values based on measurements taken from the general population. Various reference values have been published in the literature and vary by population, ethnic group, age, sex, height and weight of the patient. For this reason, tables or charts are used to determine the normal value for a particular individual. More recently,
To interpret the significance of peak expiratory flow measurements, a comparison is made to reference (normal, predicted) values based on measurements taken from the general population. Various reference values have been published in the literature and vary by population, ethnic group, age, sex, height and weight of the patient. For this reason, tables or charts are used to determine the normal value for a particular individual. More recently, medical calculators
A medical calculator is a type of medical computer software, whose purpose is to allow easy calculation of various scores and indices, presenting the user with a friendly interface that hides the complexity of the formulas. Most offer further helpf ...
have been developed to calculate predicted values for peak expiratory flow. There are a number of non-equivalent scales used in the interpretation of peak expiratory flow.
Some examples of Reference Values are given below. There is a wide natural variation in results from healthy test subjects.
* ''Wright'' scale - Predicted peak expiratory flow in normal adults using Wright-scale - Predicted peak expiratory flow in normal children using Wright-scale
* ''EN 13826'' or EU scale - Downloadable PDF charts for adults and children using EU scale
* NHANESIII reference values provided by the US Centers for Disease Control (CDC)
In 2004 the UK switched from the original Wright scale to the newer, more accurate European scale. Wright values may be converted to the EU scale using the following formula:
:
The reverse calculation is:
:
Where is the value in the Wright scale.
These formulas have also been trended over time in both rural and metropolitan areas both as air quality studies and as studies on asthma due to the Peak Flow measurement's accuracy as a predictor of mortality and poor prognosis.
Measurement
Measurements may be based on 1 second or less but are usually reported as a volume per minute. Electronic devices will sample the flow and multiply the sample volume(Litres) by 60, divided by the sample time(seconds) for a result measured in L/minute : The highest of three readings is used as the recorded value of the Peak Expiratory Flow Rate. It may be plotted out ongraph paper
Graph paper, coordinate paper, grid paper, or squared paper is writing paper that is printed with fine lines making up a regular grid. The lines are often used as guides for plotting graphs of functions or experimental data and drawing curves. I ...
charts together with a record of symptoms or using peak flow charting software. This allows patients to self-monitor and pass information back to their doctor or nurse. - for recording chart of PEFR readings
Peak flow readings are often classified into 3 zones of measurement according to the American Lung Association
The American Lung Association is a voluntary health organization whose mission is to save lives by improving lung health and preventing lung disease through education, advocacy and research.
History
The organization was founded in 1904 to figh ...
; green, yellow, and red. Doctors and health practitioners can develop an asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, cou ...
management plan based on the green-yellow-red zones.
History
The measurement of peak expiratory flow was pioneered by Martin Wright, who produced the first meter specifically designed to measure this index of lung function. Since the original design of instrument was introduced in the late 1950s, and the subsequent development of a more portable, lower cost version (the "Mini-Wright" peak flow meter), other designs and copies have become available across the world.See also
*Asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, cou ...
* Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by long-term respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms include shortness of breath and a cough, which may or may not produce ...
(COPD)
* Metered-dose inhaler
A metered-dose inhaler (MDI) is a device that delivers a specific amount of medication to the lungs, in the form of a short burst of aerosolized medicine that is usually self-administered by the patient via inhalation. It is the most commonly used ...
* Respiratory monitoring
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air i ...
* Salbutamol
Salbutamol, also known as albuterol and sold under the brand name Ventolin among others, is a medication that opens up the medium and large airways in the lungs. It is a short-acting β2 adrenergic receptor agonist which works by causing rel ...
* Spirometry
Spirometry (meaning ''the measuring of breath'') is the most common of the pulmonary function tests (PFTs). It measures lung function, specifically the amount (volume) and/or speed (flow) of air that can be inhaled and exhaled. Spirometry is he ...
References
External links
National Asthma Council of Australia
{{Respiratory physiology American inventions Flow meters Medical equipment Respiratory therapy Asthma