|
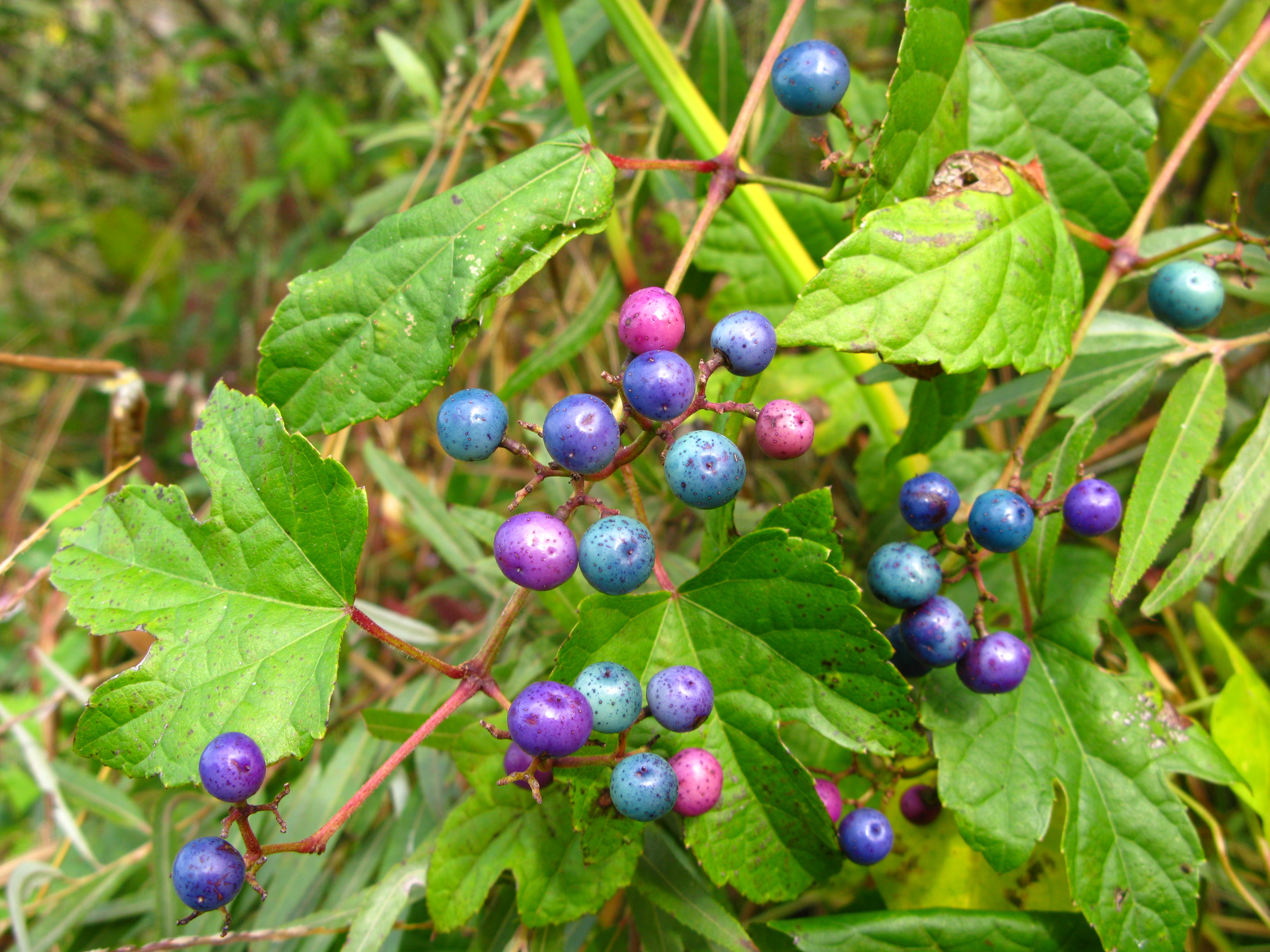
Parthenocissus Semicordata
''Parthenocissus semicordata'' (Wall) Planch. 1811 (synonym: ''P. himalayana'') is a creeper related to the grapevine family. It is a native plant of the Himalaya The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 ....''Flora of China'' 12: 173-7, 200(retrieved on 20-9-2010) Its name is derived from Latin 'corda' meaning heart. Growth ''Parthenocissus semicordata'' can grow in pots or on slopes. It is propagated from seeds or cuttings. Characteristics ''Parthenocissus semicordata'' is a vigorous climber. It has trifoliate leaves. Like most of the species of Parthenocissus it uses suction cups to hold itself to walls or trees. It has small fruit which look like grapes and are dark blue, almost black when ripe. References External links *Asianflora.com (Parthenocissus-himalayana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym (taxonomy)
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank - for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitaceae
The Vitaceae are a family of flowering plants, with 14 genera and around 910 known species, including common plants such as grapevines (''Vitis'' spp.) and Virginia creeper (''Parthenocissus quinquefolia''). The family name is derived from the genus ''Vitis''. Most ''Vitis'' species have 38 chromosomes (n=19), but 40 (n=20) in subgenus ''Muscadinia'', while ''Ampelocissus'', ''Parthenocissus'', and '' Ampelopsis'' also have 40 chromosomes (n=20) and ''Cissus'' has 24 chromosomes (n=12). The family is economically important as the berries of ''Vitis'' species, commonly known as grapes, are an important fruit crop and, when fermented, produce wine. Species of the genus ''Tetrastigma'' serve as hosts to parasitic plants in the family Rafflesiaceae. Taxonomy The name sometimes appears as Vitidaceae, but Vitaceae is a conserved name and therefore has priority over both Vitidaceae and another name sometimes found in the older literature, Ampelidaceae. In the APG III system (2009) onw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himalaya
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 peaks exceeding in elevation lie in the Himalayas. By contrast, the highest peak outside Asia (Aconcagua, in the Andes) is tall. The Himalayas abut or cross five countries: Bhutan, India, Nepal, China, and Pakistan. The sovereignty of the range in the Kashmir region is disputed among India, Pakistan, and China. The Himalayan range is bordered on the northwest by the Karakoram and Hindu Kush ranges, on the north by the Tibetan Plateau, and on the south by the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Some of the world's major rivers, the Indus, the Ganges, and the Tsangpo–Brahmaputra, rise in the vicinity of the Himalayas, and their combined drainage basin is home to some 600 million people; 53 million people live in the Himalayas. The Himalayas have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parthenocissus
''Parthenocissus'' , is a genus of tendril vine, climbing plants in the grape family (biology), family, Vitaceae. It contains about 12 species native plant, native to the Himalayas, eastern Asia and North America. Several are grown for ornamental use, notably ''P. henryana'', ''P. quinquefolia'' and ''P. tricuspidata''. Etymology The name derives from the Greek ''parthenos'', "virgin", and ''kissos'' (Latinized as "cissus"), "ivy". The reason is variously given as the ability of these creepers to form seeds without pollen, pollination or the English name of ''P. quinquefolia'', Virginia creeper, which has become attached to the whole genus. Fossil record Among the middle Miocene Sarmatian (age), Sarmatian palynology, palynoflora from the Lavanttal Basin Austria, Austrian researchers have recognized ''Parthenocissus'' fossil pollen. The sediment containing the ''Parthenocissus'' fossil pollen had accumulated in a lowland wetland environment with various vegetation units of mixed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parthenocissus Semicordata3
''Parthenocissus'' , is a genus of tendril climbing plants in the grape family, Vitaceae. It contains about 12 species native to the Himalayas, eastern Asia and North America. Several are grown for ornamental use, notably ''P. henryana'', ''P. quinquefolia'' and ''P. tricuspidata''. Etymology The name derives from the Greek ''parthenos'', "virgin", and ''kissos'' (Latinized as "cissus"), "ivy". The reason is variously given as the ability of these creepers to form seeds without pollination or the English name of ''P. quinquefolia'', Virginia creeper, which has become attached to the whole genus. Fossil record Among the middle Miocene Sarmatian palynoflora from the Lavanttal Basin Austrian researchers have recognized ''Parthenocissus'' fossil pollen. The sediment containing the ''Parthenocissus'' fossil pollen had accumulated in a lowland wetland environment with various vegetation units of mixed evergreen/deciduous broadleaved/conifer forests surrounding the wetland basin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |