|
Vitaceae
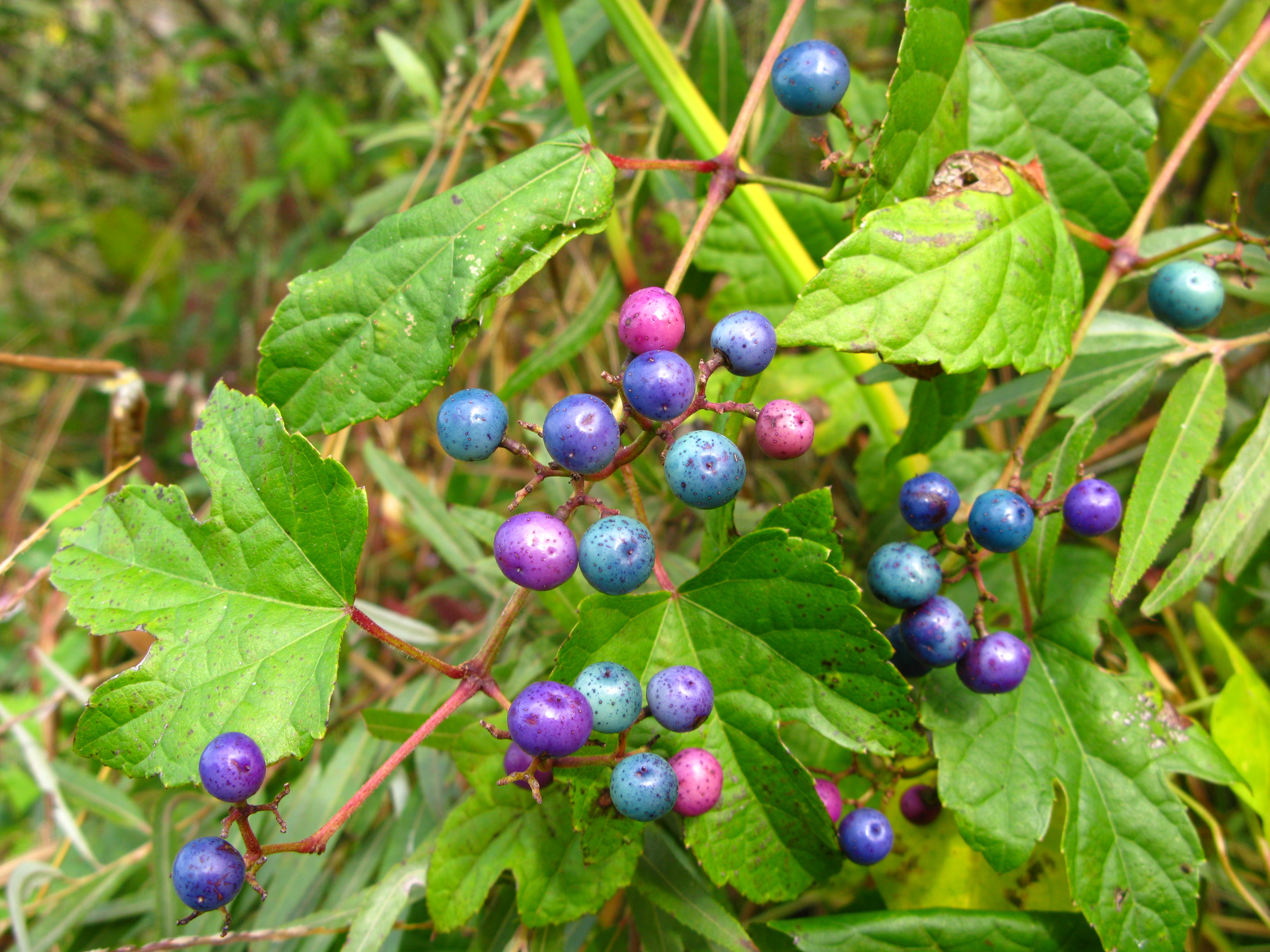
The Vitaceae are a family of flowering plants, with 14 genera and around 910 known species, including common plants such as grapevines (''Vitis'' spp.) and Virginia creeper (''Parthenocissus quinquefolia''). The family name is derived from the genus ''Vitis''. Most ''Vitis'' species have 38 chromosomes (n=19), but 40 (n=20) in subgenus '' Muscadinia'', while ''Ampelocissus'', '' Parthenocissus'', and ''Ampelopsis'' also have 40 chromosomes (n=20) and ''Cissus'' has 24 chromosomes (n=12). The family is economically important as the berries of ''Vitis'' species, commonly known as grapes, are an important fruit crop and, when fermented, produce wine. Species of the genus '' Tetrastigma'' serve as hosts to parasitic plants in the family Rafflesiaceae. Taxonomy The name sometimes appears as Vitidaceae, but Vitaceae is a conserved name and therefore has priority over both Vitidaceae and another name sometimes found in the older literature, Ampelidaceae. In the APG III system (2009) o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leea
''Leea'' (Tagalog: ''Talyantan'') is a genus of plants that are distributed throughout Northern and eastern Australia, New Guinea, South and Southeast Asia and parts of Africa. The APG IV system places ''Leea'' in the subfamily Leeoideae (Vitaceae). ''Leea'' is now placed in the family Vitaceae having previously been placed in its own family, Leeaceae, based on morphological differences between it and other Vitaceae genera. These differences include ovule number per locule (two in Vitaceae and one in Leeaceae), carpel number (two in Vitaceae and three in Leeaceae), and the absence or presence of a staminoidal tube (present in Leeaceae) and floral disc (present in Vitaceae). Pollen structure has also been examined for taxonomic demarcation, though studies have concluded that the pollen of Leeaceae and Vitaceae suggests the families should remain separate while other studies conclude that ''Leea'' should be included in Vitaceae. The genus was named by Linnaeus after James Lee, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscadinia
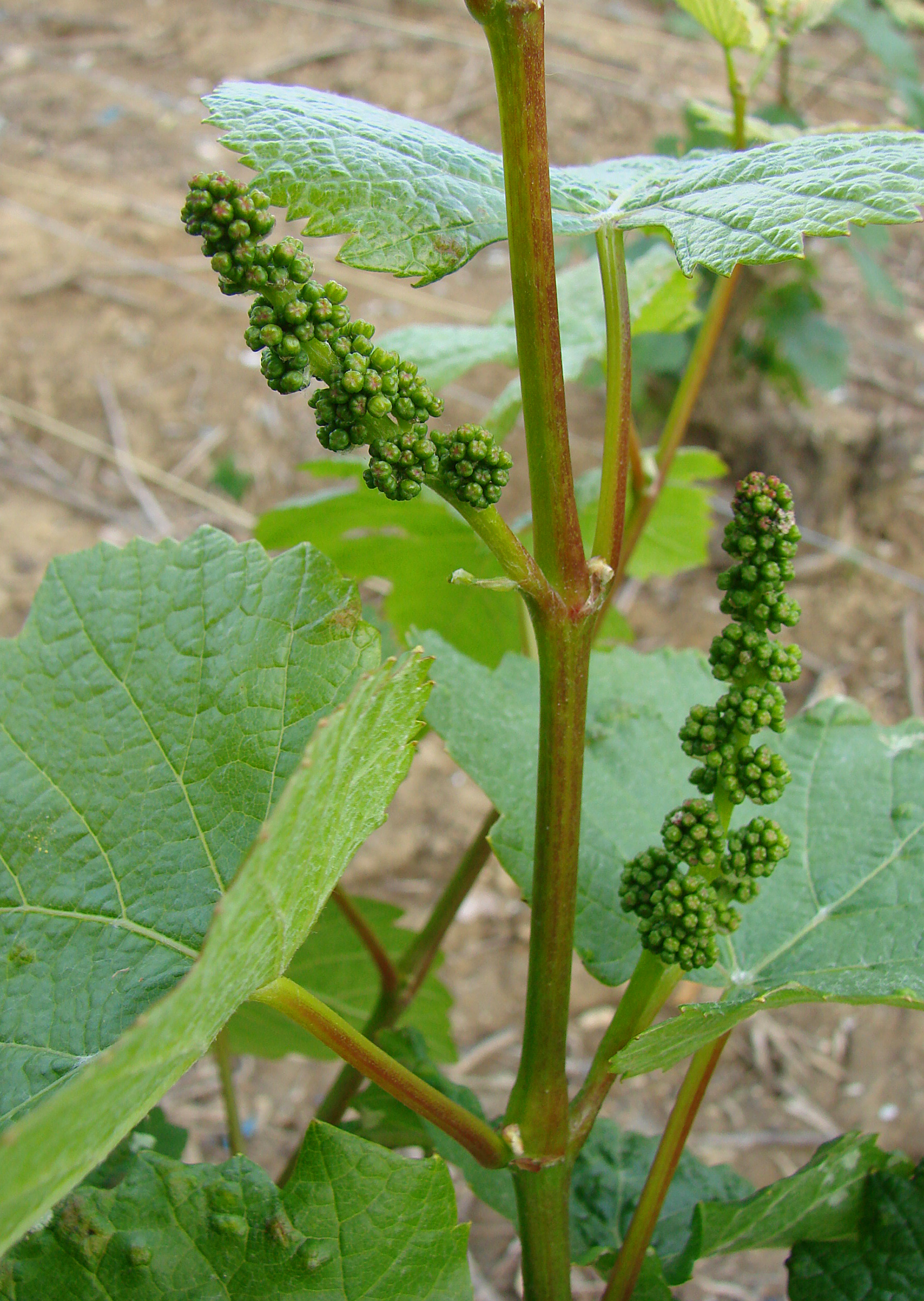
''Vitis'' (grapevine) is a genus of 79 accepted species of vining plants in the flowering plant family Vitaceae. The genus is made up of species predominantly from the Northern Hemisphere. It is economically important as the source of grapes, both for direct consumption of the fruit and for fermentation to produce wine. The study and cultivation of grapevines is called viticulture. Most cultivated ''Vitis'' varieties are wind-pollinated with hermaphroditic flowers containing both male and female reproductive structures, while wild species are dieceous. These flowers are grouped in bunches called inflorescences. In many species, such as ''Vitis vinifera'', each successfully pollinated flower becomes a grape berry with the inflorescence turning into a cluster of grapes. While the flowers of the grapevines are usually very small, the berries are often large and brightly colored with sweet flavors that attract birds and other animals to disperse the seeds contained within the berri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitis
''Vitis'' (grapevine) is a genus of 79 accepted species of vining plants in the flowering plant family Vitaceae. The genus is made up of species predominantly from the Northern Hemisphere. It is economically important as the source of grapes, both for direct consumption of the fruit and for fermentation to produce wine. The study and cultivation of grapevines is called viticulture. Most cultivated ''Vitis'' varieties are wind-pollinated with hermaphroditic flowers containing both male and female reproductive structures, while wild species are dieceous. These flowers are grouped in bunches called inflorescences. In many species, such as ''Vitis vinifera'', each successfully pollinated flower becomes a grape berry with the inflorescence turning into a cluster of grapes. While the flowers of the grapevines are usually very small, the berries are often large and brightly colored with sweet flavors that attract birds and other animals to disperse the seeds contained within the berr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrastigma
''Tetrastigma'' is a genus of plants in the grape family, Vitaceae. The plants are lianas that climb with tendrils and have palmately compound leaves. Plants are dioecious, with separate male and female plants; female flowers are characterized by their four-lobed stigmas. The species are found in subtropical and tropical regions of Asia, Malaysia, and Australia, where they grow in primary rainforest, gallery forest and monsoon forest and moister woodland. Species of this genus are notable as being the sole hosts of parasitic plants in the family Rafflesiaceae, one of which, ''Rafflesia arnoldii'', produces the largest single flower in the world. ''Tetrastigma'' is the donor species for horizontal gene transfer to '' Sapria'' and ''Rafflesia'' due to multiple gene theft events. Within the Vitaceae, ''Tetrastigma'' has long been considered closely related to ''Cayratia'' and ''Cyphostemma'' and is now placed in the tribe Cayratieae. Fossil record A fossil seed fragment from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clematicissus
''Clematicissus'' is a plant genus in the family Vitaceae The Vitaceae are a family of flowering plants, with 14 genera and around 910 known species, including common plants such as grapevines (''Vitis'' spp.) and Virginia creeper (''Parthenocissus quinquefolia''). The family name is derived from the ge .... References External links * * * Vitaceae genera Vitaceae {{Vitaceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ampelocissus
''Ampelocissus'' is a genus of Vitaceae having 90 or more species found variously in tropical Africa, Asia, Central America, and Oceania. The type species, ''A. latifolia'', was originally treated under its basionym, ''Vitis latifolia'', and was collected from the Indian subcontinent. Species of ''Ampelocissus'' are herbaceous or woody, hermaphroditic or polygamo-dioecious flowering plants with tendrils for climbing. Fruits are grape-like berries having 1-4 seeds. Their diploid chromosomal number is 40 (2n=40). Species '' Plants of the World Online'' currently includes: # '' Ampelocissus abyssinica'' (Hochst. ex A.Rich.) Planch. # '' Ampelocissus acapulcensis'' (Kunth) Planch. # '' Ampelocissus acetosa'' (F.Muell.) Planch. # '' Ampelocissus aculeata'' (Span.) Planch. # '' Ampelocissus africana'' (Lour.) Merr. # '' Ampelocissus amentacea'' Ridl. # '' Ampelocissus angolensis'' (Baker) Planch. # '' Ampelocissus arachnoidea'' (Hassk.) Planch. # '' Ampelocissus araneosa'' (Dalz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parthenocissus
''Parthenocissus'' , is a genus of tendril climbing plants in the grape family, Vitaceae. It contains about 12 species native to the Himalayas, eastern Asia and North America. Several are grown for ornamental use, notably ''P. henryana'', ''P. quinquefolia'' and ''P. tricuspidata''. Etymology The name derives from the Greek ''parthenos'', "virgin", and ''kissos'' (Latinized as "cissus"), "ivy". The reason is variously given as the ability of these creepers to form seeds without pollination or the English name of ''P. quinquefolia'', Virginia creeper, which has become attached to the whole genus. Fossil record Among the middle Miocene Sarmatian palynoflora from the Lavanttal Basin Austrian researchers have recognized ''Parthenocissus'' fossil pollen. The sediment containing the ''Parthenocissus'' fossil pollen had accumulated in a lowland wetland environment with various vegetation units of mixed evergreen/deciduous broadleaved/conifer forests surrounding the wetland basin. Ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhoicissus
''Rhoicissus'' is an Afrotropical plant genus in the grape family Vitaceae and subfamily Vitoideae. There are between nine and twenty-two accepted species. The leaves of species '' R. tomentosa'' and ''R. tridentata'' are eaten by caterpillars of the silver striped hawkmoth (''Hippotion celerio''). Selected species The genus includes the following species: De Wild. References Vitaceae Vitaceae genera Creepers of South Africa {{vitaceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nekemias
''Nekemias'' is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Vitaceae. Its native range is Assam to Temperate Eastern Asia and Western and Central Malesia, Central and Eastern USA. Species '' Plants of the World Online'' currently includes: #''Nekemias arborea'' #''Nekemias cantoniensis'' (synonym ''N. hypoglauca'') #''Nekemias celebica'' #''Nekemias chaffanjonii'' #''Nekemias gongshanensis'' #''Nekemias grossedentata'' #''Nekemias megalophylla'' #''Nekemias rubifolia ''Nekemias'' is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Vitaceae. Its native range is Assam to Temperate Eastern Asia and Western and Central Malesia, Central and Eastern USA. Species ''Plants of the World Online'' currently inclu ...'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q42791296 Vitaceae Vitaceae genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ampelopsis Glandulosa Var
''Ampelopsis'', commonly known as peppervine or porcelainberry, is a genus of climbing shrubs, in the grape family Vitaceae. The name is derived from the grc, ἅμπελος (''ampelos''), which means "vine". The genus was named in 1803. It is disjunctly distributed in eastern Asia and eastern North America extending to Mexico. ''Ampelopsis'' is primarily found in mountainous regions in temperate zones with some species in montane forests at mid-altitudes in subtropical to tropical regions. ''Ampelopsis glandulosa'' is a popular garden plant and an invasive weed. Species ''Plants of the World Online'' currently includes: # ''Ampelopsis aconitifolia'' Bunge # ''Ampelopsis acutidentata'' W.T.Wang # ''Ampelopsis bodinieri'' (H.Lév. & Vaniot) Rehder # ''Ampelopsis chondisensis'' (Vassilcz. & V.N.Vassil.) Tulyag. # ''Ampelopsis cordata'' Michx. – False grape, raccoon-grape, heart-leaf peppervine or heart-leaf ampelopsis # ''Ampelopsis delavayana'' Planch. ex Franch. # ''Ampelopsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ampelopsis
''Ampelopsis'', commonly known as peppervine or porcelainberry, is a genus of climbing shrubs, in the grape family Vitaceae. The name is derived from the grc, ἅμπελος (''ampelos''), which means "vine". The genus was named in 1803. It is disjunctly distributed in eastern Asia and eastern North America extending to Mexico. ''Ampelopsis'' is primarily found in mountainous regions in temperate zones with some species in montane forests at mid-altitudes in subtropical to tropical regions. ''Ampelopsis glandulosa'' is a popular garden plant and an invasive weed. Species ''Plants of the World Online'' currently includes: # ''Ampelopsis aconitifolia'' Bunge # ''Ampelopsis acutidentata'' W.T.Wang # ''Ampelopsis bodinieri'' (H.Lév. & Vaniot) Rehder # '' Ampelopsis chondisensis'' (Vassilcz. & V.N.Vassil.) Tulyag. # '' Ampelopsis cordata'' Michx. – False grape, raccoon-grape, heart-leaf peppervine or heart-leaf ampelopsis # ''Ampelopsis delavayana'' Planch. ex Franch. # ''Ampel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhamnales
The Rhamnales Lindl. are an order of dicotyledon plants in the subclass Rosidae. In the Cronquist system, the following families were placed here: * Family Elaeagnaceae – (Oleaster family) * Family Leeaceae * Family Rhamnaceae (buckthorn family) * Family Vitaceae (grape family) '' Leea'' may be included within the Vitaceae. The Rhamnaceae are no longer considered close relatives of these other forms, and newer systems move them to the Rosales. The order then becomes the Vitales. Under the APG III system of classification, Rhamnales is not recognized. Instead, the families previously included here under the Cronquist system are included under the following orders: * Elaeagnaceae and Rhamnaceae are placed within Rosales * ''Leea'', formerly recognized in its own family Leeaceae, is included within Vitaceae, which is recognized in its own order, Vitales The Vitaceae are a family of flowering plants, with 14 genera and around 910 known species, including common plants such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |