|
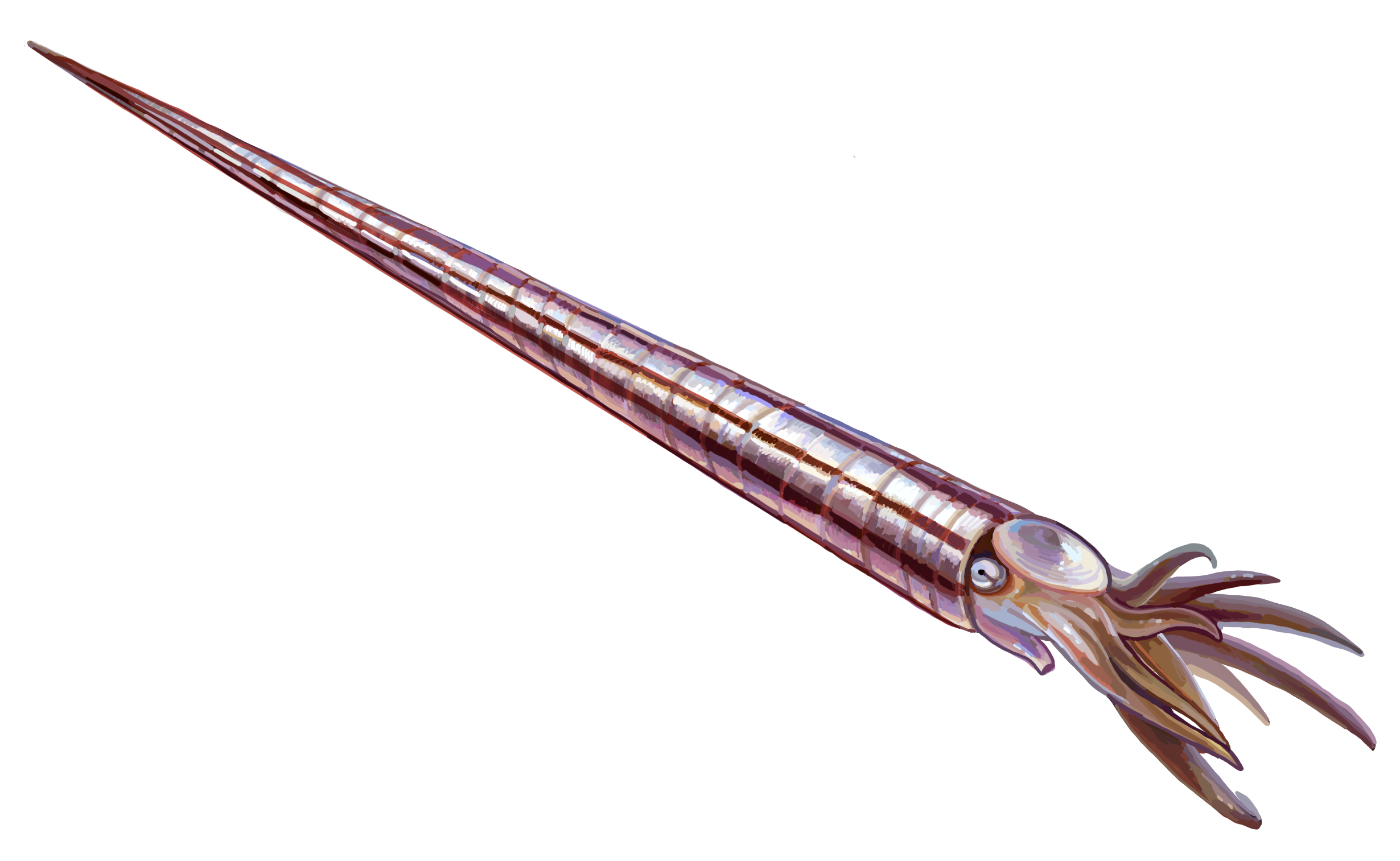
Proterocameroceras
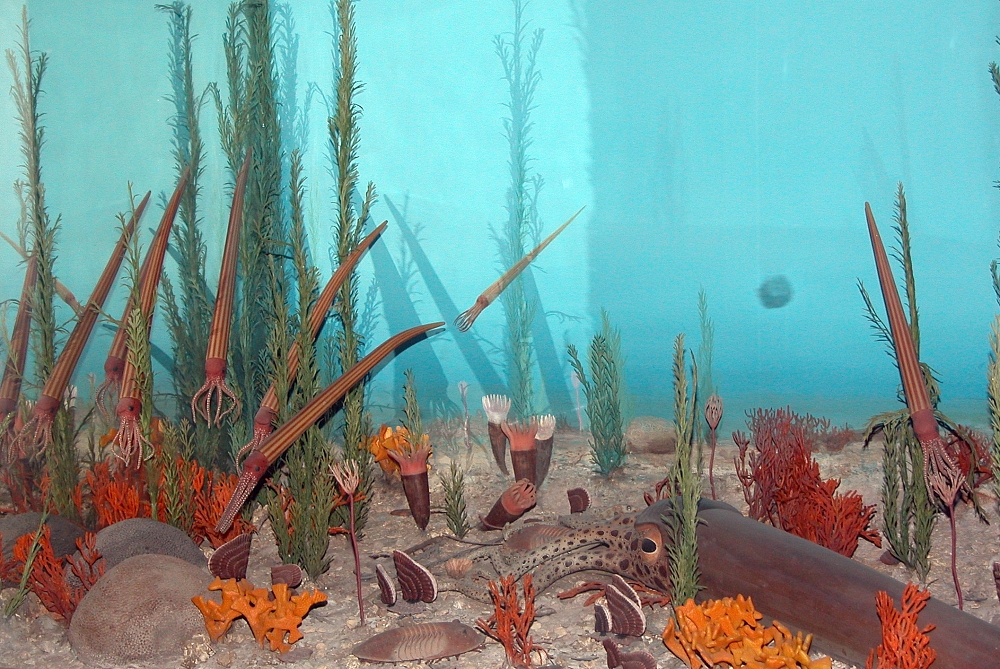
''Proterocameroceras'' is an early Endocerid from the upper Lower Ordovician belong to the Proterocameroceratidae The ''Proterocameroceratidae'' were the first of the Endocerida. They began early in the Ordovician with ''Proendoceras'' or similar genus which had developed endocones, replacing the diaphragms of the ellesmerocerid ancestor. Proterocamerocerat ..., characterized by a rather large, straight, longiconic shell, short chambers, generally straight sutures, and large ventral siphuncle with short septal necks, thick complex connecting rings, and endocones with three endosiphuncular blades toward the apex. ''Proterocameroceas'' has been found in N America, Greenland, Siberia, and Australia References * Curt Teichert, 1964. Endoceratoidea. Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology, Part K. Geol Soc. of America and Univ of Kansas press. Teichert and Moore (eds) {{Taxonbar, from=Q7251558 Fossils of Greenland Nautiloids Ordovician cephalopods Fossils of Russia Prehistor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proterocameroceratidae
The ''Proterocameroceratidae'' were the first of the Endocerida. They began early in the Ordovician with ''Proendoceras'' or similar genus which had developed endocones, replacing the diaphragms of the ellesmerocerid ancestor. Proterocameroceratids are long, straight or gently curved with a generally narrow siphuncle along the ventral margin. Septal necks are short, never quite reaching the previous septum and may vary in length ontogenically within a species. Connecting rings are thick and layered. Endocones are simple, especially in early forms but may be complex with secondary structures in later forms. The Proterocameroceratidae gave rise to the Piloceratidae early on, and later to the Manchuroceratidae and Chihlioceratidae, from which the Allotrioceratidae are derived, and later yet possibly to the Emmonsoceratidae and Najaceratidae. The Piloceratidae in turn may have given rise to the Endoceratidae although a proterocameroceratid ancestor remains possible. Proterocameroce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya. The Ordovician, named after the Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official period of the Paleozoic Era by the International Geological Congress. Life continued to flourish during the Ordovician as it did in the earlier C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocerida
Endocerida is an extinct nautiloid order, a group of cephalopods from the Lower Paleozoic with cone-like deposits in their siphuncle. Endocerida was a diverse group of cephalopods that lived from the Early Ordovician possibly to the Late Silurian. Their shells were variable in form. Some were straight ( orthoconic), others curved (cyrtoconic); some were long (longiconic), others short (breviconic). Some long-shelled forms like '' Endoceras'' attained shell lengths close to . The related '' Cameroceras'' is anecdotally reported to have reached lengths approaching , but these claims are problematic. The overwhelming majority of endocerids and nautiloids in general are much smaller, usually less than a meter long when fully grown. Morphology Endocerids had a relatively small body chamber as well as a proportionally large siphuncle, which in some genera reached nearly half the shell diameter. This suggests that much of the visceral mass may have been housed within the siphuncle i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya. The Ordovician, named after the Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official period of the Paleozoic Era by the International Geological Congress. Life continued to flourish during the Ordovician as it did in the earlier Cambrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of Greenland
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nautiloids
Nautiloids are a group of marine cephalopods ( Mollusca) which originated in the Late Cambrian and are represented today by the living ''Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. Fossil nautiloids are diverse and speciose, with over 2,500 recorded species. They flourished during the early Paleozoic era, when they constituted the main predatory animals. Early in their evolution, nautiloids developed an extraordinary diversity of shell shapes, including coiled morphologies and giant straight-shelled forms ( orthocones). Only a handful of rare coiled species, the nautiluses, survive to the present day. In a broad sense, "nautiloid" refers to a major cephalopod subclass or collection of subclasses (Nautiloidea ''sensu lato''). Nautiloids are typically considered one of three main groups of cephalopods, along with the extinct ammonoids (ammonites) and living coleoids (such as squid, octopus, and kin). While ammonoids and coleoids are monophyletic clades with exclusive ancestor-descendant rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordovician Cephalopods
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya. The Ordovician, named after the Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official period of the Paleozoic Era by the International Geological Congress. Life continued to flourish during the Ordovician as it did in the earlier Cambri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of Russia
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |