|
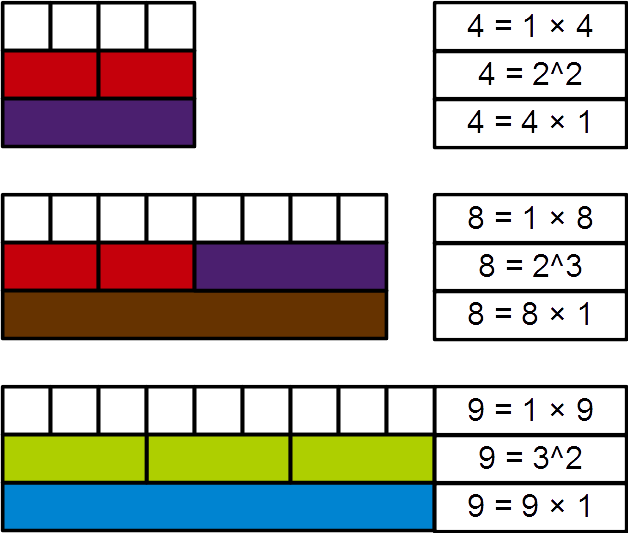
Prime Power
In mathematics, a prime power is a positive integer which is a positive integer power of a single prime number. For example: , and are prime powers, while , and are not. The sequence of prime powers begins: 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 11, 13, 16, 17, 19, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 32, 37, 41, 43, 47, 49, 53, 59, 61, 64, 67, 71, 73, 79, 81, 83, 89, 97, 101, 103, 107, 109, 113, 121, 125, 127, 128, 131, 137, 139, 149, 151, 157, 163, 167, 169, 173, 179, 181, 191, 193, 197, 199, 211, 223, 227, 229, 233, 239, 241, 243, 251, … . The prime powers are those positive integers that are divisible by exactly one prime number; in particular, the number 1 is not a prime power. Prime powers are also called primary numbers, as in the primary decomposition. Properties Algebraic properties Prime powers are powers of prime numbers. Every prime power (except powers of 2) has a primitive root; thus the multiplicative group of integers modulo ''p''''n'' (i.e. the group of units of the ring Z/''p''''n''Z) is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convergent Series
In mathematics, a series is the sum of the terms of an infinite sequence of numbers. More precisely, an infinite sequence (a_0, a_1, a_2, \ldots) defines a series that is denoted :S=a_0 +a_1+ a_2 + \cdots=\sum_^\infty a_k. The th partial sum is the sum of the first terms of the sequence; that is, :S_n = \sum_^n a_k. A series is convergent (or converges) if the sequence (S_1, S_2, S_3, \dots) of its partial sums tends to a limit; that means that, when adding one a_k after the other ''in the order given by the indices'', one gets partial sums that become closer and closer to a given number. More precisely, a series converges, if there exists a number \ell such that for every arbitrarily small positive number \varepsilon, there is a (sufficiently large) integer N such that for all n \ge N, :\left , S_n - \ell \right , 1 produce a convergent series: *: ++++++\cdots = . * Alternating the signs of reciprocals of powers of 2 also produces a convergent series: *: -+-+-+\cdots = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exponentials
Exponential may refer to any of several mathematical topics related to exponentiation, including: *Exponential function, also: **Matrix exponential, the matrix analogue to the above * Exponential decay, decrease at a rate proportional to value *Exponential discounting, a specific form of the discount function, used in the analysis of choice over time *Exponential growth, where the growth rate of a mathematical function is proportional to the function's current value *Exponential map (Riemannian geometry), in Riemannian geometry * Exponential map (Lie theory), in Lie theory * Exponential notation, also known as scientific notation, or standard form *Exponential object, in category theory *Exponential time, in complexity theory *in probability and statistics: ** Exponential distribution, a family of continuous probability distributions **Exponentially modified Gaussian distribution, describes the sum of independent normal and exponential random variables **Exponential family, a paramet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Numbers
A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways of writing it as a product, or , involve 5 itself. However, 4 is composite because it is a product (2 × 2) in which both numbers are smaller than 4. Primes are central in number theory because of the fundamental theorem of arithmetic: every natural number greater than 1 is either a prime itself or can be factorized as a product of primes that is unique up to their order. The property of being prime is called primality. A simple but slow method of checking the primality of a given number n, called trial division, tests whether n is a multiple of any integer between 2 and \sqrt. Faster algorithms include the Miller–Rabin primality test, which is fast but has a small chance of error, and the AKS primality test, which always pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MathWorld
''MathWorld'' is an online mathematics reference work, created and largely written by Eric W. Weisstein. It is sponsored by and licensed to Wolfram Research, Inc. and was partially funded by the National Science Foundation's National Science Digital Library grant to the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign. History Eric W. Weisstein, the creator of the site, was a physics and astronomy student who got into the habit of writing notes on his mathematical readings. In 1995 he put his notes online and called it "Eric's Treasure Trove of Mathematics." It contained hundreds of pages/articles, covering a wide range of mathematical topics. The site became popular as an extensive single resource on mathematics on the web. Weisstein continuously improved the notes and accepted corrections and comments from online readers. In 1998, he made a contract with CRC Press and the contents of the site were published in print and CD-ROM form, titled "CRC Concise Encyclopedia of Mathematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric W
The given name Eric, Erich, Erikk, Erik, Erick, or Eirik is derived from the Old Norse name ''Eiríkr'' (or ''Eríkr'' in Old East Norse due to monophthongization). The first element, ''ei-'' may be derived from the older Proto-Norse ''* aina(z)'', meaning "one, alone, unique", ''as in the form'' ''Æ∆inrikr'' explicitly, but it could also be from ''* aiwa(z)'' "everlasting, eternity", as in the Gothic form ''Euric''. The second element ''- ríkr'' stems either from Proto-Germanic ''* ríks'' "king, ruler" (cf. Gothic ''reiks'') or the therefrom derived ''* ríkijaz'' "kingly, powerful, rich, prince"; from the common Proto-Indo-European root * h₃rḗǵs. The name is thus usually taken to mean "sole ruler, autocrat" or "eternal ruler, ever powerful". ''Eric'' used in the sense of a proper noun meaning "one ruler" may be the origin of ''Eriksgata'', and if so it would have meant "one ruler's journey". The tour was the medieval Swedish king's journey, when newly elected, to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiprime
In mathematics, a semiprime is a natural number that is the product of exactly two prime numbers. The two primes in the product may equal each other, so the semiprimes include the squares of prime numbers. Because there are infinitely many prime numbers, there are also infinitely many semiprimes. Semiprimes are also called biprimes. Examples and variations The semiprimes less than 100 are: Semiprimes that are not square numbers are called discrete, distinct, or squarefree semiprimes: The semiprimes are the case k=2 of the k-almost primes, numbers with exactly k prime factors. However some sources use "semiprime" to refer to a larger set of numbers, the numbers with at most two prime factors (including unit (1), primes, and semiprimes). These are: Formula for number of semiprimes A semiprime counting formula was discovered by E. Noel and G. Panos in 2005. Let \pi_2(n) denote the number of semiprimes less than or equal to n. Then \pi_2(n) = \sum_^ pi(n/p_k) - k + 1 /math> where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfect Power
In mathematics, a perfect power is a natural number that is a product of equal natural factors, or, in other words, an integer that can be expressed as a square or a higher integer power of another integer greater than one. More formally, ''n'' is a perfect power if there exist natural numbers ''m'' > 1, and ''k'' > 1 such that ''mk'' = ''n''. In this case, ''n'' may be called a perfect ''k''th power. If ''k'' = 2 or ''k'' = 3, then ''n'' is called a perfect square or perfect cube, respectively. Sometimes 0 and 1 are also considered perfect powers (0''k'' = 0 for any ''k'' > 0, 1''k'' = 1 for any ''k''). Examples and sums A sequence of perfect powers can be generated by iterating through the possible values for ''m'' and ''k''. The first few ascending perfect powers in numerical order (showing duplicate powers) are : : 2^2 = 4,\ 2^3 = 8,\ 3^2 = 9,\ 2^4 = 16,\ 4^2 = 16,\ 5^2 = 25,\ 3^3 = 27, 2^5 = 32,\ 6^2 = 36,\ 7^2 = 49,\ 2^6 = 64,\ 4^3 = 64,\ 8^2 = 64, \dots The sum of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi–Dirac Prime
In number theory, a Fermi–Dirac prime is a prime power whose exponent is a power of two. These numbers are named from an analogy to Fermi–Dirac statistics in physics based on the fact that each integer has a unique representation as a product of Fermi–Dirac primes without repetition. Each element of the sequence of Fermi–Dirac primes is the smallest number that does not divide the product of all previous elements. Srinivasa Ramanujan used the Fermi–Dirac primes to find the smallest number whose number of divisors is a given power of two. Definition The Fermi–Dirac primes are a sequence of numbers obtained by raising a prime number to an exponent that is a power of two. That is, these are the numbers of the form p^ where p is a prime number and k is a non-negative integer. These numbers form the sequence: They can be obtained from the prime numbers by repeated squaring, and form the smallest set of numbers that includes all of the prime numbers and is closed under s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
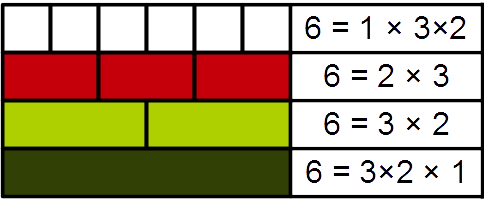
Almost Prime
In number theory, a natural number is called ''k''-almost prime if it has ''k'' prime factors. More formally, a number ''n'' is ''k''-almost prime if and only if Ω(''n'') = ''k'', where Ω(''n'') is the total number of primes in the prime factorization of ''n'' (can be also seen as the sum of all the primes' exponents): :\Omega(n) := \sum a_i \qquad\mbox\qquad n = \prod p_i^. A natural number is thus prime if and only if it is 1-almost prime, and semiprime if and only if it is 2-almost prime. The set of ''k''-almost primes is usually denoted by ''P''''k''. The smallest ''k''-almost prime is 2''k''. The first few ''k''-almost primes are: : The number π''k''(''n'') of positive integers less than or equal to ''n'' with exactly ''k'' prime divisors (not necessarily distinct) is asymptotic to: : \pi_k(n) \sim \left( \frac \right) \frac, a result of Landau. See also the Hardy–Ramanujan theorem In mathematics, the Hardy–Ramanujan theorem, proved by , states that the nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amicable Numbers
Amicable numbers are two different natural numbers related in such a way that the sum of the proper divisors of each is equal to the other number. That is, σ(''a'')=''b'' and σ(''b'')=''a'', where σ(''n'') is equal to the sum of positive divisors of ''n'' (see also divisor function). The smallest pair of amicable numbers is ( 220, 284). They are amicable because the proper divisors of 220 are 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 11, 20, 22, 44, 55 and 110, of which the sum is 284; and the proper divisors of 284 are 1, 2, 4, 71 and 142, of which the sum is 220. (A proper divisor of a number is a positive factor of that number other than the number itself. For example, the proper divisors of 6 are 1, 2, and 3.) The first ten amicable pairs are: (220, 284), (1184, 1210), (2620, 2924), (5020, 5564), (6232, 6368), (10744, 10856), (12285, 14595), (17296, 18416), (63020, 76084), and (66928, 66992). . (Also see and ) It is unknown if there are infinitely many pairs of amicable numbers. A pair of am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almost Prime
In number theory, a natural number is called ''k''-almost prime if it has ''k'' prime factors. More formally, a number ''n'' is ''k''-almost prime if and only if Ω(''n'') = ''k'', where Ω(''n'') is the total number of primes in the prime factorization of ''n'' (can be also seen as the sum of all the primes' exponents): :\Omega(n) := \sum a_i \qquad\mbox\qquad n = \prod p_i^. A natural number is thus prime if and only if it is 1-almost prime, and semiprime if and only if it is 2-almost prime. The set of ''k''-almost primes is usually denoted by ''P''''k''. The smallest ''k''-almost prime is 2''k''. The first few ''k''-almost primes are: : The number π''k''(''n'') of positive integers less than or equal to ''n'' with exactly ''k'' prime divisors (not necessarily distinct) is asymptotic to: : \pi_k(n) \sim \left( \frac \right) \frac, a result of Landau. See also the Hardy–Ramanujan theorem In mathematics, the Hardy–Ramanujan theorem, proved by , states that the nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |