|
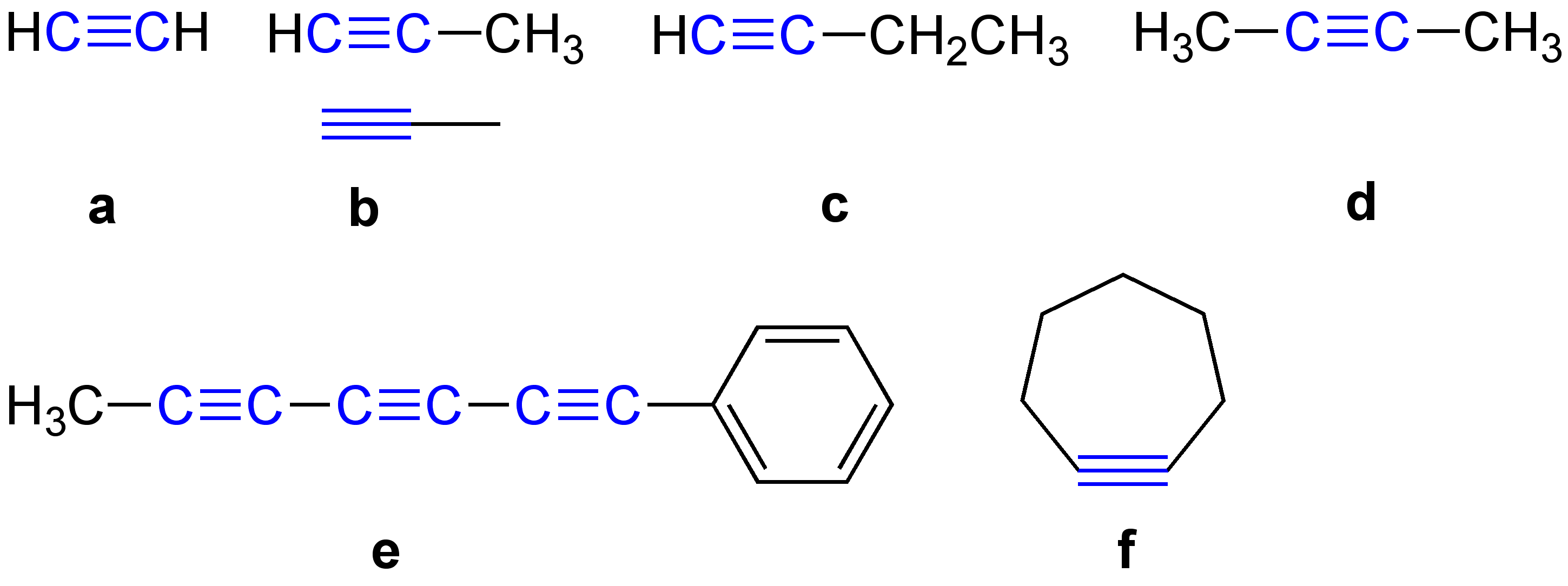
Polyyne
In organic chemistry, a polyyne () is any organic compound with alternating single and triple bonds; that is, a series of consecutive alkynes, with ''n'' greater than 1. These compounds are also called polyacetylenes, especially in the natural products and chemical ecology literature, even though this nomenclature more properly refers to acetylene polymers composed of alternating single and double bonds with ''n'' greater than 1. They are also sometimes referred to as oligoynes, or carbinoids after "carbyne" , the hypothetical allotrope of carbon that would be the ultimate member of the series. In ''Avancés récentes en chimie des acétylènes – Recent advances in acetylene chemistry'' The synthesis of this substance has been claimed several times since the 1960s, but those reports have been disputed. Indeed, the substances identified as short chains of "carbyne" in many early organic synthesis attempts would be called polyynes today. The simplest polyyne is diacetylene o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyne
\ce \ce Acetylene \ce \ce \ce Propyne \ce \ce \ce \ce 1-Butyne In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula . Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name ''acetylene'' also refers specifically to , known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic. Structure and bonding In acetylene, the H–C≡C bond angles are 180°. By virtue of this bond angle, alkynes are rod-like. Correspondingly, cyclic alkynes are rare. Benzyne cannot be isolated. The C≡C bond distance of 121 picometers is much shorter than the C=C distance in alkenes (134 pm) or the C–C bond in alkanes (153 pm). : The triple bond is very strong with a bond strength of 839 kJ/mol. The sigma bond contribute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyne
\ce \ce Acetylene \ce \ce \ce Propyne \ce \ce \ce \ce 1-Butyne In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula . Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name ''acetylene'' also refers specifically to , known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic. Structure and bonding In acetylene, the H–C≡C bond angles are 180°. By virtue of this bond angle, alkynes are rod-like. Correspondingly, cyclic alkynes are rare. Benzyne cannot be isolated. The C≡C bond distance of 121 picometers is much shorter than the C=C distance in alkenes (134 pm) or the C–C bond in alkanes (153 pm). : The triple bond is very strong with a bond strength of 839 kJ/mol. The sigma bond contribute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Acetylenic Carbon
Linear acetylenic carbon (LAC), also known as carbyne or Linear Carbon Chain (LCC), is an allotrope of carbon that has the chemical structure as a repeat unit, with alternating single and triple bonds. It would thus be the ultimate member of the polyyne family. This polymeric carbyne is of considerable interest to nanotechnology as its Young's modulus is – forty times that of diamond; this extraordinary number is, however, based on a novel definition of cross-sectional area that does not correspond to the space occupied by the structure. Carbyne has also been identified in interstellar space; however, its existence in condensed phases has been contested recently, as such chains would crosslink exothermically (and perhaps explosively) if they approached each other. History and controversy The first claims of detection of this allotrope were made in 1960Sladkov A.M, Kudryavtsev Y.P Diamond, graphite, carbyne 3/4 the allotropic forms of carbon, Priroda (Nature), 1969, 58:37 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyothereol Skeletal
Ichthyothereol is a toxic polyyne compound found in the leaves and flowers of several plants in South and Central America. These plant sources and their extracts are known for their toxic effects on fish, and have long been used by various native tribes in the lower Amazon basin for fishing. The name of the genus ''Ichthyothere'', the members of which contain noticeable amounts of the natural product in their leaves, literally translates as ''fish poison.'' It is so toxic, fish will jump out of the water if ''Ichthyothere terminalis'' leaves are used as bait. This chemical is also found in the leaves and flowers of '' Dahlia coccinea''. The actual chemical was isolated by several different groups and its full chemical structure determined in 1965. The first total synthesis was published in 2001. It is also toxic to mice and dogs, producing convulsant effects that are similar to those of picrotoxin Picrotoxin, also known as cocculin, is a poisonous crystalline plant compound. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fritsch–Buttenberg–Wiechell Rearrangement
The Fritsch–Buttenberg–Wiechell rearrangement, named for Paul Ernst Moritz Fritsch (1859–1913), Wilhelm Paul Buttenberg, and Heinrich G. Wiechell, is a chemical reaction whereby a 1,1-diaryl-2-bromo-alkene rearranges to a 1,2-diaryl- alkyne by reaction with a strong base such as an alkoxide. This rearrangement is also possible with alkyl substituents. Reaction mechanism The strong base deprotonates the vinylic hydrogen, which after alpha-elimination forms a vinyl carbene. A 1,2-aryl migration forms the 1,2-diaryl-alkyne product. The mechanism of the FBW rearrangement was a subject of on-surface studies where the vinyl radical was visualised with sub-atomic resolution. Scope One study explored this reaction for the synthesis of novel polyynes:The metal acetylide intermediate is captured by electrophile methyl iodide. The reaction product is a biomolecule found in for instance Bidens pilosa See also *Corey–Fuchs reaction The Corey–Fuchs reaction, also known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadiot–Chodkiewicz Coupling
The Cadiot–Chodkiewicz coupling in organic chemistry is a coupling reaction between a terminal alkyne and a haloalkyne catalyzed by a copper(I) salt such as copper(I) bromide and an amine base.Cadiot, P.; Chodkiewicz, W. In Chemistry of Acetylenes; Viehe, H. G., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, 1969; pp. 597–647. The reaction product is a 1,3-diyne or di-alkyne. The reaction mechanism involves deprotonation by base of the terminal alkyne proton followed by formation of a copper(I) acetylide. A cycle of oxidative addition and reductive elimination on the copper centre then creates a new carbon-carbon bond. Scope Unlike the related Glaser coupling the Cadiot–Chodkiewicz coupling proceeds selectively and will only couple the alkyne to the haloalkyne, giving a single product. By comparison the Glaser coupling would simply produce a distribution of all possible couplings. In one study the Cadiot–Chodkiewicz coupling has been applied in the synthesis of acetylene macrocycles st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tris(3,5-di-t-butylphenyl)methyl
Tris, or tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, or known during medical use as tromethamine or THAM, is an organic compound with the formula (HOCH2)3CNH2, one of the twenty Good's buffers. It is extensively used in biochemistry and molecular biology as a component of buffer solutions such as in TAE and TBE buffers, especially for solutions of nucleic acids. It contains a primary amine and thus undergoes the reactions associated with typical amines, e.g. condensations with aldehydes. Tris also complexes with metal ions in solution. In medicine, tromethamine is occasionally used as a drug, given in intensive care for its properties as a buffer for the treatment of severe metabolic acidosis in specific circumstances. Some medications are formulated as the "tromethamine salt" including Hemabate (carboprost as trometamol salt), and " ketorolac trometamol". Buffering features The conjugate acid of tris has a p''K''a of 8.07 at 25 °C, which implies that the buffer has an effective pH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenyl
In organic chemistry, the phenyl group, or phenyl ring, is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula C6 H5, and is often represented by the symbol Ph. Phenyl group is closely related to benzene and can be viewed as a benzene ring, minus a hydrogen, which may be replaced by some other element or compound to serve as a functional group. Phenyl group has six carbon atoms bonded together in a hexagonal planar ring, five of which are bonded to individual hydrogen atoms, with the remaining carbon bonded to a substituent. Phenyl groups are commonplace in organic chemistry. Although often depicted with alternating double and single bonds, phenyl group is chemically aromatic and has equal bond lengths between carbon atoms in the ring. Nomenclature Usually, a "phenyl group" is synonymous with C6H5− and is represented by the symbol Ph or, archaically, Φ. Benzene is sometimes denoted as PhH. Phenyl groups are generally attached to other atoms or groups. For example, triphenylmethane (Ph3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendrimer
Dendrimers are highly ordered, branched polymeric molecules. Synonymous terms for dendrimer include arborols and cascade molecules. Typically, dendrimers are symmetric about the core, and often adopt a spherical three-dimensional morphology. The word dendron is also encountered frequently. A dendron usually contains a single chemically addressable group called the focal point or core. The difference between dendrons and dendrimers is illustrated in the top figure, but the terms are typically encountered interchangeably. The first dendrimers were made by divergent synthesis approaches by Fritz Vögtle in 1978, R.G. Denkewalter at Allied Corporation in 1981, Donald Tomalia at Dow Chemical in 1983 and in 1985, and by George R. Newkome in 1985. In 1990 a convergent synthetic approach was introduced by Craig Hawker and Jean Fréchet. Dendrimer popularity then greatly increased, resulting in more than 5,000 scientific papers and patents by the year 2005. Properties Dendritic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the alkyl or aryl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether" (). Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin. Structure and bonding Ethers feature bent C–O–C linkages. In dimethyl ether, the bond angle is 111° and C–O distances are 141 pm. The barrier to rotation about the C–O bonds is low. The bonding of oxygen in ethers, alcohols, and water is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatic
In chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property of cyclic ( ring-shaped), ''typically'' planar (flat) molecular structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that gives increased stability compared to saturated compounds having single bonds, and other geometric or connective non-cyclic arrangements with the same set of atoms. Aromatic rings are very stable and do not break apart easily. Organic compounds that are not aromatic are classified as aliphatic compounds—they might be cyclic, but only aromatic rings have enhanced stability. The term ''aromaticity'' with this meaning is historically related to the concept of having an aroma, but is a distinct property from that meaning. Since the most common aromatic compounds are derivatives of benzene (an aromatic hydrocarbon common in petroleum and its distillates), the word ''aromatic'' occasionally refers informally to benzene derivatives, and so it was first defined. Nevertheless, many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Compound
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the Periodic Table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom are common. These compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)
