|
Polyethylene 2,5-furandicarboxylate
Polyethylene 2,5-furandicarboxylate, also named poly(ethylene 2,5-furandicarboxylate), polyethylene furanoate and poly(ethylene furanoate) and generally abbreviated as PEF, is a polymer that can be produced by polycondensation or ring-opening polymerization of 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA) and ethylene glycol.E. de Jong et al., Furandicarboxylic Acid (FDCA), A Versatile Building Block for a Very Interesting Class of Polyesters, in Biobased Monomers, Polymers, and Materials; Eds. Smith, P., et al., 2012J.-G. Rosenboom et al., Bottle-grade polyethylene furanoate from ring-opening polymerisation of cyclic oligomers, Nature Communications, 2018 As an aromatic polyester from ethylene glycol it is a chemical analogue of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polyethylene naphthalate (PEN). PEF has been described in (patent) literature since 1951,US 2551731 A, Polyesters from heterocyclic components, 1951 but has gained renewed attention since the US department of energy proclaimed its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycondensation
In polymer chemistry, condensation polymers are any kind of polymers whose process of polymerization involves a condensation reaction (i.e. a small molecule, such as water or methanol, is produced as a byproduct). Condensation polymers are formed by polycondensation, when the polymer is formed by condensation reactions between species of all degrees of polymerization, or by condensative chain polymerization, when the polymer is formed by sequential addition of monomers to an active site in a chain reaction. The main alternative forms of polymerization are chain polymerization and polyaddition, both of which give addition polymers. Condensation polymerization is a form of step-growth polymerization. Linear polymers are produced from bifunctional monomers, i.e. compounds with two reactive end-groups. Common condensation polymers include polyamides, polyacetals, and proteins. Polyamides One important class of condensation polymers are polyamides. They arise from the rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
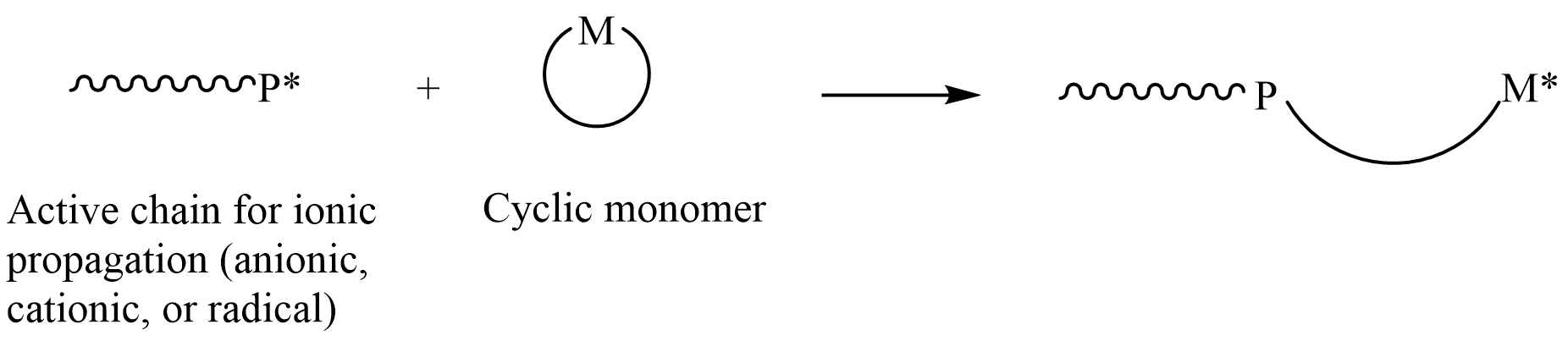
Ring-opening Polymerization
In polymer chemistry, ring-opening polymerization (ROP) is a form of chain-growth polymerization, in which the terminus of a polymer chain attacks cyclic monomers to form a longer polymer (see figure). The reactive center can be radical, anionic or cationic. Some cyclic monomers such as norbornene or cyclooctadiene can be polymerized to high molecular weight polymers by using metal catalysts. ROP is a versatile method for the synthesis of biopolymers. Ring-opening of cyclic monomers is often driven by the relief of bond-angle strain. Thus, as is the case for other types of polymerization, the enthalpy change in ring-opening is negative. Monomers Cyclic monomers that are amenable to ROP include epoxides, cyclic trisiloxanes, some lactones, lactides, cyclic carbonates, and amino acid N-carboxyanhydrides. Many strained cycloalkenes, e.g norbornene, are suitable monomers via ring-opening metathesis polymerization. History Ring-opening polymerization has been used since the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2,5-furandicarboxylic Acid
2,5-Furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA) is an organic chemical compound consisting of two carboxylic acid groups attached to a central furan ring. It was first reported as ''dehydromucic acid'' by Rudolph Fittig and Heinzelmann in 1876, who produced it via the action of concentrated hydrobromic acid upon mucic acid. It can be produced from certain carbohydrates and as such is a renewable resource, it was identified by the US Department of Energy as one of 12 priority chemicals for establishing the “green” chemistry industry of the future. Furan-2,5-dicarboxylic acid (FDCA) has been suggested as an important renewable building block because it can substitute for terephthalic acid (PTA) in the production of polyesters and other current polymers containing an aromatic moiety.T. Werpy, G. Petersen: ''Top Value Added Chemicals from Biomass. Volume I – Results of Screening for Potential Candidates from Sugars and Synthesis Gas.'' Produced by the Staff at Pacific Northwest National Lab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylene Glycol
Ethylene glycol ( IUPAC name: ethane-1,2-diol) is an organic compound (a vicinal diol) with the formula . It is mainly used for two purposes, as a raw material in the manufacture of polyester fibers and for antifreeze formulations. It is an odorless, colorless, flammable, viscous liquid. Ethylene glycol has a sweet taste, but it is toxic in high concentrations. Production Industrial routes Ethylene glycol is produced from ethylene (ethene), via the intermediate ethylene oxide. Ethylene oxide reacts with water to produce ethylene glycol according to the chemical equation: This reaction can be catalyzed by either acids or bases, or can occur at neutral pH under elevated temperatures. The highest yields of ethylene glycol occur at acidic or neutral pH with a large excess of water. Under these conditions, ethylene glycol yields of 90% can be achieved. The major byproducts are the oligomers diethylene glycol, triethylene glycol, and tetraethylene glycol. The separation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyethylene Terephthalate
Polyethylene terephthalate (or poly(ethylene terephthalate), PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P), is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in fibres for clothing, containers for liquids and foods, and thermoforming for manufacturing, and in combination with glass fibre for engineering resins. In 2016, annual production of PET was 56 million tons. The biggest application is in fibres (in excess of 60%), with bottle production accounting for about 30% of global demand. In the context of textile applications, PET is referred to by its common name, polyester, whereas the acronym ''PET'' is generally used in relation to packaging. Polyester makes up about 18% of world polymer production and is the fourth-most-produced polymer after polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). PET consists of repeating (C10H8O4) units. PET is commonly recycled, and has the digit 1 (♳) as its resin identification code (R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyethylene Naphthalate
Polyethylene naphthalate (poly(ethylene 2,6-naphthalate) or PEN) is a polyester derived from naphthalene-2,6-dicarboxylic acid and ethylene glycol. As such it is related to poly(ethylene terephthalate), but with superior barrier properties. Production Two major manufacturing routes exist for polyethylene naphthalate (PEN), i.e. an ester or an acid process, named according to whether the starting monomer is a diester or a diacid derivative, respectively. In both cases for PEN, the glycol monomer is ethylene glycol. Solid-state polymerization (SSP) of the melt-produced resin pellets is the preferred process to increase the average molecular weight of PEN. Applications Because it provides a very good oxygen barrier, it is well-suited for bottling beverages that are susceptible to oxidation, such as beer. It is also used in making high performance sailcloth. Significant commercial markets have been developed for its application in textile and industrial fibers, films, and foamed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terephthalic Acid
Terephthalic acid is an organic compound with formula C6H4(CO2H)2. This white solid is a commodity chemical, used principally as a precursor to the polyester PET, used to make clothing and plastic bottles. Several million tonnes are produced annually. The common name is derived from the turpentine-producing tree '' Pistacia terebinthus'' and phthalic acid. History Terephthalic acid was first isolated (from turpentine) by the French chemist Amédée Cailliot (1805–1884) in 1846. Terephthalic acid became industrially important after World War II. Terephthalic acid was produced by oxidation of ''p''-xylene with dilute nitric acid. Air oxidation of ''p''-xylene gives ''p''-toluic acid, which resists further air-oxidation. Conversion of ''p''-toluic acid to methyl p-toluate (CH3C6H4CO2CH3) opens the way for further oxidation to monomethyl terephthalate, which is further esterified to dimethyl terephthalate. In 1955, Mid-Century Corporation and ICI announced the bromide-promoted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life-cycle Assessment
Life cycle assessment or LCA (also known as life cycle analysis) is a methodology for assessing environmental impacts associated with all the stages of the life cycle of a commercial product, process, or service. For instance, in the case of a manufactured product, environmental impacts are assessed from raw material extraction and processing (cradle), through the product's manufacture, distribution and use, to the recycling or final disposal of the materials composing it (grave). An LCA study involves a thorough inventory of the energy and materials that are required across the industry value chain of the product, process or service, and calculates the corresponding emissions to the environment. LCA thus assesses cumulative potential environmental impacts. The aim is to document and improve the overall environmental profile of the product. Widely recognized procedures for conducting LCAs are included in the 14000 series of environmental management standards of the Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and large oil and gas companies, many state-owned by OPEC and Russia. Human-caused emissions have increased atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but it was consistent among all greenhouse gases (GHG). Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than ever before. Electricity generation and transport are major emitters; the largest single source, according to the United States Environmental Protection Agency, is transportation, accounting for 27% of all USA greenhouse gas emissions. Deforestation and other changes in land use also emit carbon dioxide and methane. The largest source of anthropogenic methane emissions is agriculture, closely follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-renewable Energy
A non-renewable resource (also called a finite resource) is a natural resource that cannot be readily replaced by natural means at a pace quick enough to keep up with consumption. An example is carbon-based fossil fuels. The original organic matter, with the aid of heat and pressure, becomes a fuel such as oil or gas. Earth minerals and metal ores, fossil fuels (coal, petroleum, natural gas) and groundwater in certain aquifers are all considered non-renewable resources, though individual elements are always conserved (except in nuclear reactions, nuclear decay or atmospheric escape). Conversely, resources such as timber (when harvested sustainably) and wind (used to power energy conversion systems) are considered renewable resources, largely because their localized replenishment can occur within time frames meaningful to humans as well. Earth minerals and metal ores Earth minerals and metal ores are examples of non-renewable resources. The metals themselves are prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Polymers
A polymer (; Greek ''poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part") is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. The term "polymer" derives from the Greek word πολύς (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and μέρος (''meros'', meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |