|
Planetary Phase Of Civilization
The planetary phase of civilization is a term created by the Global Scenario Group (GSG) to describe the contemporary era in which increasing global interdependence and risks are binding the world into a unitary socio-ecological system. Characteristics of this phase include economic globalization, biospheric destabilization, mass migration, new global institutions, the Internet, new forms of transboundary conflict, and shifts in culture and consciousness. Background The notion of the planetary phase of civilization derives from the work of the Global Scenario Group, an international and interdisciplinary body convened in 1995 to examine alternative long-range futures. The GSG synthesized its findings for a non-technical audience in the essay ''Great Transition: The Promise and Lure of the Times Ahead''.Paul Raskin, Tariq Banuri, Gilberto Gallopín, Pablo Gutman, Al Hammond, Robert Kates, and Rob Swart, ''Great Transition: The Promise and Lure of the Times Ahead'' (Boston: Stockholm E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Scenario Group
The Global Scenario Group (GSG) was an international, interdisciplinary body convened in 1995 by the Tellus Institute and the Stockholm Environment Institute (SEI) to develop scenarios for world development in the twenty-first century. Further development of the Great Transition scenarios has been carried on by the Great Transition Initiative (GTI). The GSG's underlying scenario development work was rooted in the long-range integrated scenario analysis that Tellus Institute and Stockholm Environment Institute had undertaken through the PoleStar Project and its PoleStar System. Initially conceived in 1991 as a tool for integrated sustainability planning and long-range scenario analysis, the PoleStar System was inspired by the 1987 Brundtland Commission report ''Our Common Future'', which first put the concept of sustainable development on the international agenda. The work of the Global Scenario Group was widely adopted in high-level intergovernmental settings. The scenarios infor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
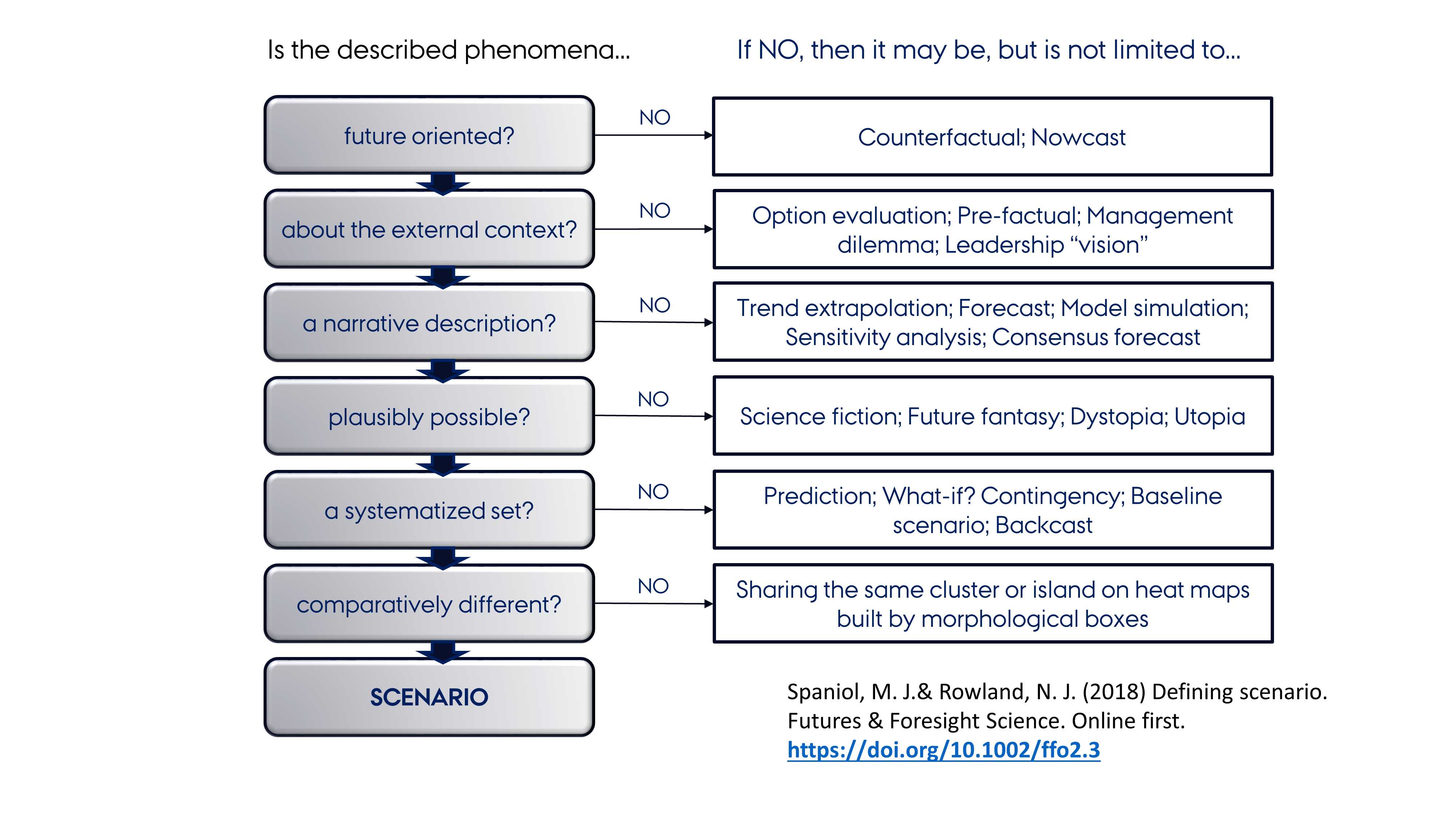
Scenario Analysis
Scenario planning, scenario thinking, scenario analysis, scenario prediction and the scenario method all describe a strategic planning method that some organizations use to make flexible long-term plans. It is in large part an adaptation and generalization of classic methods used by military intelligence. In the most common application of the method, analysts generate simulation games for policy makers. The method combines known facts, such as demographics, geography and mineral reserves, with military, political, and industrial information, and key driving forces identified by considering social, technical, economic, environmental, and political ("STEEP") trends. In business applications, the emphasis on understanding the behavior of opponents has been reduced while more attention is now paid to changes in the natural environment. At Royal Dutch Shell for example, scenario planning has been described as changing mindsets about the exogenous part of the world prior to formulating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Theories
Linearity is the property of a mathematical relationship (''function'') that can be graphically represented as a straight line. Linearity is closely related to '' proportionality''. Examples in physics include rectilinear motion, the linear relationship of voltage and current in an electrical conductor (Ohm's law), and the relationship of mass and weight. By contrast, more complicated relationships are ''nonlinear''. Generalized for functions in more than one dimension, linearity means the property of a function of being compatible with addition and scaling, also known as the superposition principle. The word linear comes from Latin ''linearis'', "pertaining to or resembling a line". In mathematics In mathematics, a linear map or linear function ''f''(''x'') is a function that satisfies the two properties: * Additivity: . * Homogeneity of degree 1: for all α. These properties are known as the superposition principle. In this definition, ''x'' is not necessarily a real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Geography
Economic geography is the subfield of human geography which studies economic activity and factors affecting them. It can also be considered a subfield or method in economics. There are four branches of economic geography. There is, primary sector, Secondary sector, Tertiary sector, & Quaternary sector. Economic geography takes a variety of approaches to many different topics, including the location of industries, economies of agglomeration (also known as "linkages"), transportation, international trade, development, real estate, gentrification, ethnic economies, gendered economies, core-periphery theory, the economics of urban form, the relationship between the environment and the economy (tying into a long history of geographers studying culture-environment interaction), and globalization. Theoretical background and influences There are varied methodological approaches. Neoclassical location theorists, following in the tradition of Alfred Weber, tend to focus on industria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Civilization
A planetary civilization or global civilization is a civilization of Type I on the Kardashev scale. This type of civilization is likely to be reliant on renewable energy sources such as stellar power, as well as powerful non-renewable sources such as nuclear fusion. A Type I civilization's energy consumption level is roughly equivalent to the solar insolation on Earth (between 1016 and 1017 watts) ─ around 3 orders of magnitude higher than that of contemporary humanity (around 2×1013 as of 2020). Planetary civilization – Type I civilization on Kardashev scale Soviet astronomer Nikolai Kardashev, in his 1964 paper titled "Transmission of Information by Extraterrestrial Civilizations", proposed a scale intended to measure the level of technological development of civilizations based on the amount of energy that they are able to utilize, eponymously named the Kardashev scale. A Type I civilization is planetary, consuming all energy that reaches its home planet from its pare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globalism
Globalism refers to various patterns of meaning beyond the merely international. It is used by political scientists, such as Joseph Nye, to describe "attempts to understand all the interconnections of the modern world—and to highlight patterns that underlie (and explain) them." While primarily associated with world-systems, it can be used to describe other global trends. The concept of globalism is also classically used to distinguish the ideologies of globalization (the subjective meanings) from the processes of globalization (the objective practices). In this sense, globalism is to globalization what nationalism is to nationality. The term is now frequently used as a pejorative by far-right movements and conspiracy theorists. False usage in this way has also been associated with antisemitism, as antisemites frequently appropriate ''globalist'' to refer to Jews. Definition Paul James defines ''globalism'' "at least in its more specific use ... as the dominant ideology and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ervin László
Ervin László (; born 12 June 1932) is a Hungarian philosopher of science, systems theorist, integral theorist, originally a classical pianist. He is an advocate of the theory of quantum consciousness. Early life and education László was born in Budapest, Hungary, the son of a shoe manufacturer and a mother who played the piano; László himself started playing the piano when he was five years old, and gave his first piano concert with the Budapest Symphony Orchestra at the age of nine. After World War II, he moved to the United States. Career László is a visiting faculty member at the Graduate Institute Bethany. He has published about 75 books and over 400 papers, and is editor of ''World Futures: The Journal of General Evolution''. László participated in the Stock Exchange of Visions project in 2006. In 2010, he was elected an external member of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. In Hungary, the minister of environment appointed Laszlo as one of the leaders of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Government
World government is the concept of a single political authority with jurisdiction over all humanity. It is conceived in a variety of forms, from tyrannical to democratic, which reflects its wide array of proponents and detractors. A world government with executive, legislative, and judicial functions and an administrative apparatus has never existed. The inception of the United Nations (UN) in the mid-20th century remains the closest approximation to a world government, as it is by far the largest and most powerful international institution. However, the UN is mostly limited to an advisory role, with the stated purpose of fostering cooperation between existing national governments, rather than exerting authority over them. Nevertheless, the organization is commonly viewed as either a model for, or preliminary step towards, a global government. The concept of universal governance has existed since antiquity and been the subject of discussion, debate, and even advocacy by some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tellus Institute
The Tellus Institute is an American non-profit organization established in 1976 with the aim of bringing scientific rigor and systemic vision to critical environmental and social issues. Tellus has conducted thousands of projects throughout the world, and now focuses on the global future and how to shape it. Background The Tellus Institute was founded as a non-profit research organization in 1976 by Paul Raskin and colleagues to conduct research on resource and environmental policy. Initially called Energy Systems Research Group (ESRG), the institute adopted its current name in 1990 to reflect its expanding focus on social-ecological systems from local to global levels (Tellus was the name of the Roman Earth Goddess). Tellus has partnered with hundreds of organizations, notably the Stockholm Environmental Institute, with which it coordinated programs from 1989 to 2006. The institute has conducted more than 3,500 studies worldwide. The methodology of Tellus projects has been the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socio-ecological System
A social-ecological system consists of 'a bio-geo-physical' unit and its associated social actors and institutions. Social-ecological systems are complex and adaptive and delimited by spatial or functional boundaries surrounding particular ecosystems and their context problems.Glaser, M., Krause, G., Ratter, B., and Welp, M. (2008) Human-Nature-Interaction in the Anthropocene. Potential of Social-Ecological Systems Analysis. ebsite Available from: ssessed: 28 Feb 2020/ref> Definitions A social-ecological system can be defined as:Redman, C., Grove, M. J. and Kuby, L. (2004). Integrating Social Science into the Long Term Ecological Research (LTER) Network: Social Dimensions of Ecological Change and Ecological Dimensions of Social Change. Ecosystems Vol.7(2), pp. 161-171.(p. 163) # A coherent system of biophysical and social factors that regularly interact in a resilient, sustained manner; # A system that is defined at several spatial, temporal, and organisational scales, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kardashev Scale
The Kardashev scale (Russian: Шкала Кардашева, ''Shkala Kardasheva'') is a method of measuring a civilization's level of technological advancement based on the amount of energy it is able to use. The measure was proposed by Soviet astronomer Nikolai Kardashev in 1964. The scale is hypothetical, and regards energy consumption on a cosmic scale. Various extensions of the scale have since been proposed, including a wider range of power levels (types 0, IV to VI) and the use of metrics other than pure power (e.g., computational growth). Kardashev first outlined his scale in a paper presented at the 1964 Byurakan conference, a scientific meeting that reviewed the Soviet radio astronomy space listening program. This paper, entitled "Передача информации внеземными цивилизациями" (and then translated into English "Transmission of Information by Extraterrestrial Civilizations"), proposes a classification of civilizations into thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices increase greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming. Due to climate change, deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Increased warming in the Arctic has contributed to melting permafrost, glacial retreat and sea ice loss. Higher temperatures are also causing m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |