|
Pistosauria
Pistosauroidea is a group of marine reptiles within the superorder Sauropterygia that first appeared in the latter part of the Early Triassic and were the ancestors of plesiosaurs. Pistosauroids are rare in Triassic marine assemblages, and are represented by only a few fossils from central Europe, the United States, and China. Recent phylogenetic analyses consider the Triassic pistosauroids to be a paraphyletic grouping, meaning that they do not form a true clade. Plesiosauria is now placed within Pistosauroidea, while the traditional pistosauroids are successively more basal, or primitive, sauropterygians. Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ... of pistosauroid relationships from Cheng ''et al.'' (2006): Below is a cladogram of pistosauroid re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plesiosauria
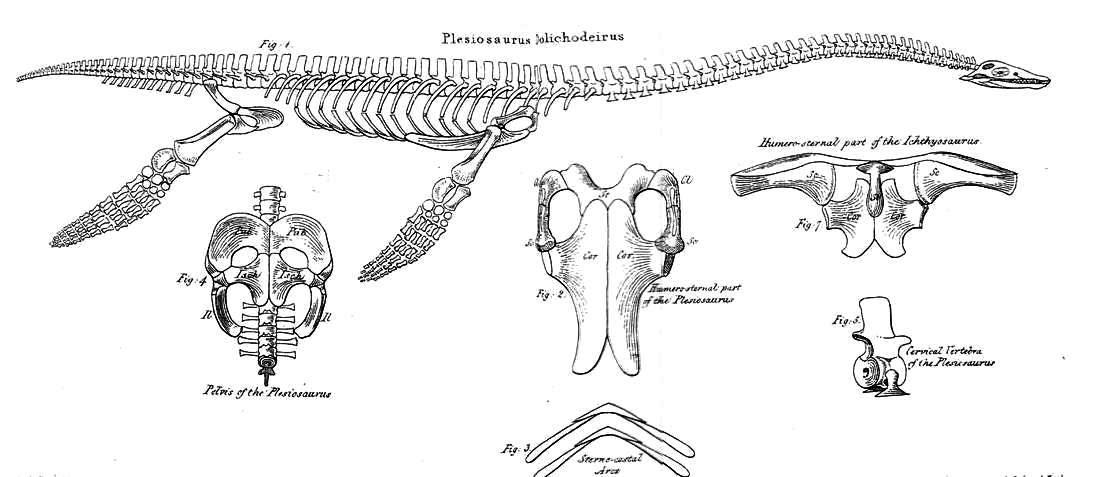
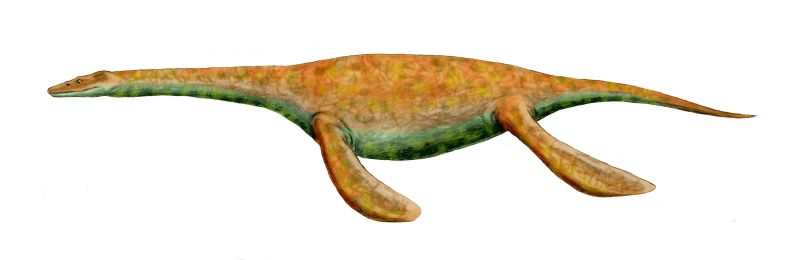
The Plesiosauria (; Greek: πλησίος, ''plesios'', meaning "near to" and ''sauros'', meaning "lizard") or plesiosaurs are an order or clade of extinct Mesozoic marine reptiles, belonging to the Sauropterygia. Plesiosaurs first appeared in the latest Triassic Period, possibly in the Rhaetian stage, about 203 million years ago. They became especially common during the Jurassic Period, thriving until their disappearance due to the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous Period, about 66 million years ago. They had a worldwide oceanic distribution, and some species at least partly inhabited freshwater environments. Plesiosaurs were among the first fossil reptiles discovered. In the beginning of the nineteenth century, scientists realised how distinctive their build was and they were named as a separate order in 1835. The first plesiosaurian genus, the eponymous '' Plesiosaurus'', was named in 1821. Since then, more than a hundred valid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plesiosaur
The Plesiosauria (; Greek: πλησίος, ''plesios'', meaning "near to" and ''sauros'', meaning "lizard") or plesiosaurs are an order or clade of extinct Mesozoic marine reptiles, belonging to the Sauropterygia. Plesiosaurs first appeared in the latest Triassic Period, possibly in the Rhaetian stage, about 203 million years ago. They became especially common during the Jurassic Period, thriving until their disappearance due to the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous Period, about 66 million years ago. They had a worldwide oceanic distribution, and some species at least partly inhabited freshwater environments. Plesiosaurs were among the first fossil reptiles discovered. In the beginning of the nineteenth century, scientists realised how distinctive their build was and they were named as a separate order in 1835. The first plesiosaurian genus, the eponymous '' Plesiosaurus'', was named in 1821. Since then, more than a hundred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pistosaurus BW
''Pistosaurus'' (''pistos'' in Greek meaning 'credible' and ''sauros'' 'lizard') is an extinct genus of aquatic sauropterygian reptile closely related to plesiosaurs. Fossils have been found in France and Germany, and date to the Middle Triassic. It contains a single species, ''Pistosaurus longaevus. Pistosaurus'' is known as the oldest "subaquatic flying" reptile on earth. The skull of ''Pistosaurus'' generally resembles that of other Triassic sauropterygians. However, there are several synapomorphies that make ''Pistosaurus'' distinguished: the long, slender, snout; the possession of splint-like nasals that are excluded from the external naris; and the posterior extension of the premaxilla to the frontals. Based on synapomorphies such as the small nasals size and the presence of interpterygoid vacuity, ''Pistosaurus'' is more closely related to Plesiosauria than to ''Nothosaurus''. ''Pistosaurus'' is often mistaken with ''Nothosaurus'' and Plesiosauria. ''Nothosaurus'' belon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustasaurus
''Augustasaurus'' is a genus of aquatic sauropterygian reptile belonging to the Pistosauria, a clade containing plesiosaurs and their close relatives. ''Pistosaurus'' and ''Augustasaurus'' were thought to be the only known members of the family Pistosauridae.Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. Article: pp. 577–592. THE SKULL OF THE PISTOSAUR AUGUSTASAURUS FROM THE MIDDLE TRIASSIC OF NORTHWESTERN NEVADA. OLIVIER RIEPPEL, P. MARTIN SANDER, and GLENN W. STORRS. 1997 However, some recent cladistic analyses found ''Augustasaurus'' to be a more advanced pistosaur, as a sister group of the order Plesiosauria. The only known species of ''Augustasaurus'' is ''Augustasaurus hagdorni'', which was first described in 1997. Etymology The first part of ''Augustasaurus name comes from the Augusta Mountains of northwestern Nevada, USA, where its fossil bones were first discovered. The second part of the name is the Greek word ' (), which means "lizard" or " reptile." The type species, ''Au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauropterygia
Sauropterygia ("lizard flippers") is an extinct taxon of diverse, aquatic reptiles that developed from terrestrial ancestors soon after the end-Permian extinction and flourished during the Triassic before all except for the Plesiosauria became extinct at the end of that period. The plesiosaurs would continue to diversify until the end of the Mesozoic. Sauropterygians are united by a radical adaptation of their pectoral girdle, adapted to support powerful flipper strokes. Some later sauropterygians, such as the pliosaurs, developed a similar mechanism in their pelvis. Uniquely among reptiles, sauropterygians moved their tail vertically like modern cetaceans and sirenians. Origins and evolution The earliest sauropterygians appeared about 247 million years ago (Ma), at the start of the Middle Triassic: the first definite sauropterygian with exact stratigraphic datum lies within the Spathian division of the Olenekian era in South China. Early examples were small (around 60 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pistosaurus
''Pistosaurus'' (''pistos'' in Greek meaning 'credible' and ''sauros'' 'lizard') is an extinct genus of aquatic sauropterygian reptile closely related to plesiosaurs. Fossils have been found in France and Germany, and date to the Middle Triassic. It contains a single species, ''Pistosaurus longaevus. Pistosaurus'' is known as the oldest "subaquatic flying" reptile on earth. The skull of ''Pistosaurus'' generally resembles that of other Triassic sauropterygians. However, there are several synapomorphies that make ''Pistosaurus'' distinguished: the long, slender, snout; the possession of splint-like nasals that are excluded from the external naris; and the posterior extension of the premaxilla to the frontals. Based on synapomorphies such as the small nasals size and the presence of interpterygoid vacuity, ''Pistosaurus'' is more closely related to Plesiosauria than to ''Nothosaurus''. ''Pistosaurus'' is often mistaken with ''Nothosaurus'' and Plesiosauria. ''Nothosaurus'' belon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal (phylogenetics)
In phylogenetics, basal is the direction of the ''base'' (or root) of a rooted phylogenetic tree or cladogram. The term may be more strictly applied only to nodes adjacent to the root, or more loosely applied to nodes regarded as being close to the root. Note that extant taxa that lie on branches connecting directly to the root are not more closely related to the root than any other extant taxa. While there must always be two or more equally "basal" clades sprouting from the root of every cladogram, those clades may differ widely in taxonomic rank, species diversity, or both. If ''C'' is a basal clade within ''D'' that has the lowest rank of all basal clades within ''D'', ''C'' may be described as ''the'' basal taxon of that rank within ''D''. The concept of a 'key innovation' implies some degree of correlation between evolutionary innovation and diversification. However, such a correlation does not make a given case predicable, so ancestral characters should not be imputed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to descendants, nor does it show how much they have changed, so many differing evolutionary trees can be consistent with the same cladogram. A cladogram uses lines that branch off in different directions ending at a clade, a group of organisms with a last common ancestor. There are many shapes of cladograms but they all have lines that branch off from other lines. The lines can be traced back to where they branch off. These branching off points represent a hypothetical ancestor (not an actual entity) which can be inferred to exhibit the traits shared among the terminal taxa above it. This hypothetical ancestor might then provide clues about the order of evolution of various features, adaptation, and other evolutionary narratives about an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placodontia
Placodonts (" Tablet teeth") are an extinct order of marine reptiles that lived during the Triassic period, becoming extinct at the end of the period. They were part of Sauropterygia, the group that includes plesiosaurs. Placodonts were generally between in length, with some of the largest measuring long. The first specimen was discovered in 1830. They have been found throughout central Europe, North Africa, the Middle East and China. Palaeobiology The earliest forms, like '' Placodus'', which lived in the early to middle Triassic, resembled barrel-bodied lizards superficially similar to the marine iguana of today, but larger. In contrast to the marine iguana, which feeds on algae, the placodonts ate molluscs and so their teeth were flat and tough to crush shells. In the earliest periods, their size was probably enough to keep away the top sea predators of the time: the sharks. However, as time passed, other kinds of carnivorous reptiles began to colonize the seas, such as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachypleurosauria
left, 220px, '' Pachypleurosaurus'' Pachypleurosauria is an extinct clade of primitive sauropterygian reptiles that vaguely resembled aquatic lizards, and were limited to the Triassic period. They were elongate animals, ranging in size from , with small heads, long necks, paddle-like limbs, and long, deep tails. The limb girdles are greatly reduced, so it is unlikely these animals could move about on land. The widely spaced peg-like teeth project at the front of the jaws, indicating that these animals fed on fish. In the species '' Prosantosaurus'', it was observed that they fed on small fishes and crustaceans which they devoured entirely and that its teeth regrew after they broke off. This was the first observation of tooth replacement in a European pachypleurosaur, the only other discovery of such an event was made in China. Classification Pachypleurosaurs were originally and are often still included within the Nothosauroidea (Carroll 1988, Benton 2004). In some more rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placodus BW
''Placodus'' (meaning 'flat tooth') was a genus of marine reptiles belonging to the order Placodontia, which swam in the shallow seas of the middle Triassic period (c. 240 million years ago). Fossils of ''Placodus'' have been found in Central Europe (Germany, France, Poland) and China. Palaeobiology ''Placodus'' had a stocky body with a long tail, and reached a total length of and body mass of . It had a short neck, and a heavy skull. They were specialized for a durophagous diet of shellfish, such as bivalves. Chisel-like incisors protruded from the anterior margin of the snout, and were probably used to pluck hard-shelled benthic prey from the substrate. The back teeth were broad and flattened, and would have helped to crush the prey. Before the animals' anatomy was known, they were regarded as fishes' teeth. Similar smaller teeth were present on the palatine bones. ''Placodus'' and its relatives were not as well-adapted to aquatic life as some later reptile groups, lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphyletic
In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In contrast, a monophyletic group (a clade) includes a common ancestor and ''all'' of its descendants. The terms are commonly used in phylogenetics (a subfield of biology) and in the tree model of historical linguistics. Paraphyletic groups are identified by a combination of Synapomorphy and apomorphy, synapomorphies and symplesiomorphy, symplesiomorphies. If many subgroups are missing from the named group, it is said to be polyparaphyletic. The term was coined by Willi Hennig to apply to well-known taxa like Reptilia (reptiles) which, as commonly named and traditionally defined, is paraphyletic with respect to mammals and birds. Reptilia contains the last common ancestor of reptiles a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |