|
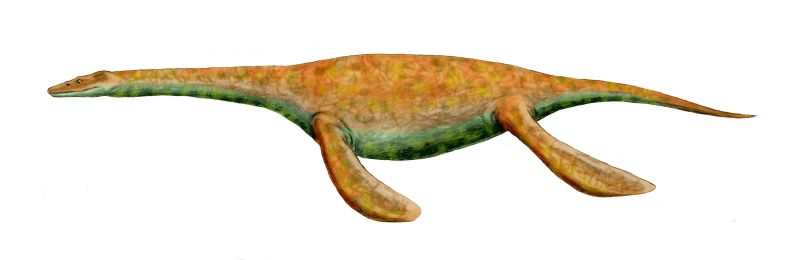
Pistosaurus BW
''Pistosaurus'' (''pistos'' in Greek meaning 'credible' and ''sauros'' 'lizard') is an extinct genus of aquatic sauropterygian reptile closely related to plesiosaurs. Fossils have been found in France and Germany, and date to the Middle Triassic. It contains a single species, ''Pistosaurus longaevus. Pistosaurus'' is known as the oldest "subaquatic flying" reptile on earth. The skull of ''Pistosaurus'' generally resembles that of other Triassic sauropterygians. However, there are several synapomorphies that make ''Pistosaurus'' distinguished: the long, slender, snout; the possession of splint-like nasals that are excluded from the external naris; and the posterior extension of the premaxilla to the frontals. Based on synapomorphies such as the small nasals size and the presence of interpterygoid vacuity, ''Pistosaurus'' is more closely related to Plesiosauria than to ''Nothosaurus''. ''Pistosaurus'' is often mistaken with ''Nothosaurus'' and Plesiosauria. ''Nothosaurus'' belongs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pistosaurus Skull
''Pistosaurus'' (''pistos'' in Greek meaning 'credible' and ''sauros'' 'lizard') is an extinct genus of aquatic sauropterygian reptile closely related to plesiosaurs. Fossils have been found in France and Germany, and date to the Middle Triassic. It contains a single species, ''Pistosaurus longaevus. Pistosaurus'' is known as the oldest "subaquatic flying" reptile on earth. The skull of ''Pistosaurus'' generally resembles that of other Triassic sauropterygians. However, there are several synapomorphies that make ''Pistosaurus'' distinguished: the long, slender, snout; the possession of splint-like nasals that are excluded from the external naris; and the posterior extension of the premaxilla to the frontals. Based on synapomorphies such as the small nasals size and the presence of interpterygoid vacuity, ''Pistosaurus'' is more closely related to Plesiosauria than to ''Nothosaurus''. ''Pistosaurus'' is often mistaken with ''Nothosaurus'' and Plesiosauria. ''Nothosaurus'' belongs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pistosaurus Longaevus From Caldonazzo
''Pistosaurus'' (''pistos'' in Greek meaning 'credible' and ''sauros'' 'lizard') is an extinct genus of aquatic sauropterygian reptile closely related to plesiosaurs. Fossils have been found in France and Germany, and date to the Middle Triassic. It contains a single species, ''Pistosaurus longaevus. Pistosaurus'' is known as the oldest "subaquatic flying" reptile on earth. The skull of ''Pistosaurus'' generally resembles that of other Triassic sauropterygians. However, there are several synapomorphies that make ''Pistosaurus'' distinguished: the long, slender, snout; the possession of splint-like nasals that are excluded from the external naris; and the posterior extension of the premaxilla to the frontals. Based on synapomorphies such as the small nasals size and the presence of interpterygoid vacuity, ''Pistosaurus'' is more closely related to Plesiosauria than to ''Nothosaurus''. ''Pistosaurus'' is often mistaken with ''Nothosaurus'' and Plesiosauria. ''Nothosaurus'' belongs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pistosaurus BW
''Pistosaurus'' (''pistos'' in Greek meaning 'credible' and ''sauros'' 'lizard') is an extinct genus of aquatic sauropterygian reptile closely related to plesiosaurs. Fossils have been found in France and Germany, and date to the Middle Triassic. It contains a single species, ''Pistosaurus longaevus. Pistosaurus'' is known as the oldest "subaquatic flying" reptile on earth. The skull of ''Pistosaurus'' generally resembles that of other Triassic sauropterygians. However, there are several synapomorphies that make ''Pistosaurus'' distinguished: the long, slender, snout; the possession of splint-like nasals that are excluded from the external naris; and the posterior extension of the premaxilla to the frontals. Based on synapomorphies such as the small nasals size and the presence of interpterygoid vacuity, ''Pistosaurus'' is more closely related to Plesiosauria than to ''Nothosaurus''. ''Pistosaurus'' is often mistaken with ''Nothosaurus'' and Plesiosauria. ''Nothosaurus'' belongs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Triassic
In the geologic timescale, the Middle Triassic is the second of three epochs of the Triassic period or the middle of three series in which the Triassic system is divided in chronostratigraphy. The Middle Triassic spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Early Triassic Epoch and followed by the Late Triassic Epoch. The Middle Triassic is divided into the Anisian and Ladinian ages or stages. Formerly the middle series in the Triassic was also known as Muschelkalk. This name is now only used for a specific unit of rock strata with approximately Middle Triassic age, found in western Europe. Middle Triassic fauna Following the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the most devastating of all mass-extinctions, life recovered slowly. In the Middle Triassic, many groups of organisms reached higher diversity again, such as the marine reptiles (e.g. ichthyosaurs, sauropterygians, thallatosaurs), ray-finned fish and many invertebrate groups like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entepicondylar Foramen
The entepicondylar foramen is an opening in the distal (far) end of the humerus (upper arm bone) present in some mammals. It is often present in primitive placentals, such as the enigmatic Madagascan ''Plesiorycteropus''. In most Neotominae and all Tylomyinae among cricetid rodents, it is located above the medial epicondyle of the humerus, but it is absent in all Sigmodontinae and Arvicolinae and this trait has been suggested as a synapomorphy In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to hav ... for the former subfamily. See also * Supratrochlear foramen References Literature cited * * {{Refend Mammal anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliosauroidea
Pliosauroidea is an extinct clade of plesiosaurs, known from the earliest Jurassic to early Late Cretaceous. They are best known for the subclade Thalassophonea, which contained crocodile-like short-necked forms with large heads and massive toothed jaws, commonly known as pliosaurs. More primitive non-thalassophonean pliosauroids resembled pleisiosaurs in possessing relatively long necks and smaller heads. They originally included only members of the family Pliosauridae, of the order Plesiosauria, but several other genera and families are now also included, the number and details of which vary according to the classification used. The distinguishing characteristics are a short neck and an elongated head, with larger hind flippers compared to the fore flippers, the opposite of the plesiosaurs. They were carnivorous and their long and powerful jaws carried many sharp, conical teeth. Pliosaurs range from 4 to 15 metres and more in length. Their prey may have included fish, sharks, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yunguisaurus Liae
''Yunguisaurus'' is an extinct genus of pistosaur known from the Guizhou Province of China. Description ''Yunguisaurus'' is known from the holotype NMNS 004529/F003862, an articulated and almost complete skeleton missing only the distal tail. The preserved skeleton has a length of about with estimated total length about , while paratype specimen became much larger with length around . It was collected near Huangnihe River, Chajiang of Guizhou, from the Falang Formation. It is thought to belong to the ''Paragondolella naantangensis-P. polygnathiformis'' Assemblage Zone, dating to the Carnian stage of the early Late Triassic. It differs from other pistosauroids by a combination of characters. Nevertheless, its original description is a preliminary report while the postcranial skeleton still waits for further preparation and full description. Etymology ''Yunguisaurus'' was first named by Yen-Nien Cheng, Tamaki Sato, Xiao-Chun Wu and Chun Li in 2006 and the type species is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bobosaurus Forojuliensis
''Bobosaurus'' is an extinct genus of sauropterygian reptile related to plesiosaurs. It is based on the holotype MFSN 27285, a partial skeleton found in Early Carnian-age rocks (early Late Triassic) of the Rio del Lago Formation, northeastern Italy. ''Bobosaurus'' was named in 2006 by Fabio M. Dalla Vecchia and the type species is ''B. forojuliensis''. It may be a pistosaurid, or closer to Plesiosauria. A recent cladistic analysis found it to be a pistosaur. It was relatively large animal, with more than in length. See also * Timeline of plesiosaur research * List of plesiosaur genera This list of plesiosaurs is a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the order Plesiosauria, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered inv ... References Fossil taxa described in 2006 Plesiosaurs of Europe Sauropterygians Triassic sauropterygians Sauropterygian genera< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustasaurus Hagdorni
''Augustasaurus'' is a genus of aquatic sauropterygian reptile belonging to the Pistosauria, a clade containing plesiosaurs and their close relatives. ''Pistosaurus'' and ''Augustasaurus'' were thought to be the only known members of the family Pistosauridae.Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. Article: pp. 577–592. THE SKULL OF THE PISTOSAUR AUGUSTASAURUS FROM THE MIDDLE TRIASSIC OF NORTHWESTERN NEVADA. OLIVIER RIEPPEL, P. MARTIN SANDER, and GLENN W. STORRS. 1997 However, some recent cladistic analyses found ''Augustasaurus'' to be a more advanced pistosaur, as a sister group of the order Plesiosauria. The only known species of ''Augustasaurus'' is ''Augustasaurus hagdorni'', which was first described in 1997. Etymology The first part of ''Augustasaurus name comes from the Augusta Mountains of northwestern Nevada, USA, where its fossil bones were first discovered. The second part of the name is the Greek word ' (), which means "lizard" or "reptile." The type species, ''Augustas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pistosauria
Pistosauroidea is a group of marine reptiles within the superorder Sauropterygia that first appeared in the latter part of the Early Triassic and were the ancestors of plesiosaurs. Pistosauroids are rare in Triassic marine assemblages, and are represented by only a few fossils from central Europe, the United States, and China. Recent phylogenetic analyses consider the Triassic pistosauroids to be a paraphyletic grouping, meaning that they do not form a true clade. Plesiosauria is now placed within Pistosauroidea, while the traditional pistosauroids are successively more basal, or primitive, sauropterygians. Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ... of pistosauroid relationships from Cheng ''et al.'' (2006): Below is a cladogram of pistosauroi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustasaurus
''Augustasaurus'' is a genus of aquatic sauropterygian reptile belonging to the Pistosauria, a clade containing plesiosaurs and their close relatives. ''Pistosaurus'' and ''Augustasaurus'' were thought to be the only known members of the family Pistosauridae.Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. Article: pp. 577–592. THE SKULL OF THE PISTOSAUR AUGUSTASAURUS FROM THE MIDDLE TRIASSIC OF NORTHWESTERN NEVADA. OLIVIER RIEPPEL, P. MARTIN SANDER, and GLENN W. STORRS. 1997 However, some recent cladistic analyses found ''Augustasaurus'' to be a more advanced pistosaur, as a sister group of the order Plesiosauria. The only known species of ''Augustasaurus'' is ''Augustasaurus hagdorni'', which was first described in 1997. Etymology The first part of ''Augustasaurus name comes from the Augusta Mountains of northwestern Nevada, USA, where its fossil bones were first discovered. The second part of the name is the Greek word ' (), which means "lizard" or "reptile." The type species, ''Augustas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauropterygia
Sauropterygia ("lizard flippers") is an extinct taxon of diverse, aquatic reptiles that developed from terrestrial ancestors soon after the end-Permian extinction and flourished during the Triassic before all except for the Plesiosauria became extinct at the end of that period. The plesiosaurs would continue to diversify until the end of the Mesozoic. Sauropterygians are united by a radical adaptation of their pectoral girdle, adapted to support powerful flipper strokes. Some later sauropterygians, such as the pliosaurs, developed a similar mechanism in their pelvis. Uniquely among reptiles, sauropterygians moved their tail vertically like modern cetaceans and sirenians. Origins and evolution The earliest sauropterygians appeared about 247 million years ago (Ma), at the start of the Middle Triassic: the first definite sauropterygian with exact stratigraphic datum lies within the Spathian division of the Olenekian era in South China. Early examples were small (around 60 c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |