|
Pistoia Baptistery 01
Pistoia (, is a city and ''comune'' in the Italian region of Tuscany, the capital of a province of the same name, located about west and north of Florence and is crossed by the Ombrone Pistoiese, a tributary of the River Arno. It is a typical Italian medieval city, and it attracts many tourists, especially in the summer. The city is famous throughout Europe for its plant nurseries. History ''Pistoria'' (in Latin other possible forms are ''Pistorium'' or ''Pistoriae'') was a centre of Gallic, Ligurian and Etruscan settlements before becoming a Roman colony in the 6th century BC, along the important road Via Cassia: in 62 BC the demagogue Catiline and his fellow conspirators were slain nearby. From the 5th century the city was a bishopric, and during the Lombardic kingdom it was a royal city and had several privileges. Pistoia's most splendid age began in 1177 when it proclaimed itself a free commune: in the following years it became an important political centre, erectin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuscany
Tuscany ( ; it, Toscana ) is a Regions of Italy, region in central Italy with an area of about and a population of about 3.8 million inhabitants. The regional capital is Florence (''Firenze''). Tuscany is known for its landscapes, history, artistic legacy, and its influence on high culture. It is regarded as the birthplace of the Italian Renaissance and of the foundations of the Italian language. The prestige established by the Tuscan dialect's use in literature by Dante Alighieri, Petrarch, Giovanni Boccaccio, Niccolò Machiavelli and Francesco Guicciardini led to its subsequent elaboration as the language of culture throughout Italy. It has been home to many figures influential in the history of art and science, and contains well-known museums such as the Uffizi and the Palazzo Pitti. Tuscany is also known for its wines, including Chianti, Vino Nobile di Montepulciano, Morellino di Scansano, Brunello di Montalcino and white Vernaccia di San Gimignano. Having a strong linguisti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauls
The Gauls ( la, Galli; grc, Γαλάται, ''Galátai'') were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They spoke Gaulish, a continental Celtic language. The Gauls emerged around the 5th century BC as bearers of La Tène culture north and west of the Alps. By the 4th century BC, they were spread over much of what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland, Southern Germany, Austria, and the Czech Republic, by virtue of controlling the trade routes along the river systems of the Rhône, Seine, Rhine, and Danube. They reached the peak of their power in the 3rd century BC. During the 4th and 3rd centuries BC, the Gauls expanded into Northern Italy ( Cisalpine Gaul), leading to the Roman–Gallic wars, and into the Balkans, leading to war with the Greeks. These latter Gauls eventually settled in Anatolia, becoming known as Galatians. After the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanni Fucci
Vanni Fucci di Pistoia is a minor character in ''Inferno'', the first part of Dante Alighieri's epic poem the ''Divine Comedy'', appearing in Cantos XXIV & XXV. He was a thief who lived in Pistoia, as his name ("di Pistoia" meaning "of Pistoia") indicates; when he died, he was sent to the seventh bolgia (round; in Italian, "ditch" or "pouch") of the eighth circle of Hell, where thieves are punished. In that bolgia, his punishment was to be stung by a serpent, reduced to ashes, and then restored to his former shape for more torturing. Dante and Virgil meet him and ask him why he was there. He replied that he stole a treasure from the Church of St. James in his hometown; he had wrongly accused an innocent man, Vanni della Nona, with the crime, for which della Nona was executed. Fucci says he was not caught but he still went to Hell. He then predicts the overthrow of the Florentine Whites to spite Dante and then insults God by making obscene gestures at him, and is attacked by numero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dante Alighieri
Dante Alighieri (; – 14 September 1321), probably baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri and often referred to as Dante (, ), was an Italian poet, writer and philosopher. His ''Divine Comedy'', originally called (modern Italian: ''Commedia'') and later christened by Giovanni Boccaccio, is widely considered one of the most important poems of the Middle Ages and the greatest literary work in the Italian language. Dante is known for establishing the use of the vernacular in literature at a time when most poetry was written in Latin, which was accessible only to the most educated readers. His ''De vulgari eloquentia'' (''On Eloquence in the Vernacular'') was one of the first scholarly defenses of the vernacular. His use of the Florentine dialect for works such as '' The New Life'' (1295) and ''Divine Comedy'' helped establish the modern-day standardized Italian language. His work set a precedent that important Italian writers such as Petrarch and Boccaccio would later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divina Commedia
The ''Divine Comedy'' ( it, Divina Commedia ) is an Italian narrative poem by Dante Alighieri, begun 1308 and completed in around 1321, shortly before the author's death. It is widely considered the pre-eminent work in Italian literature and one of the greatest works of world literature. The poem's imaginative vision of the afterlife is representative of the medieval worldview as it existed in the Western Church by the 14th century. It helped establish the Tuscan language, in which it is written, as the standardized Italian language. It is divided into three parts: ''Inferno'', ''Purgatorio'', and '' Paradiso''. The narrative takes as its literal subject the state of the soul after death and presents an image of divine justice meted out as due punishment or reward, and describes Dante's travels through Hell, Purgatory, and Heaven. Allegorically, the poem represents the soul's journey towards God, beginning with the recognition and rejection of sin (''Inferno''), followed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guelphs And Ghibellines
The Guelphs and Ghibellines (, , ; it, guelfi e ghibellini ) were factions supporting the Pope and the Holy Roman Emperor, respectively, in the Italian city-states of Central Italy and Northern Italy. During the 12th and 13th centuries, rivalry between these two parties formed a particularly important aspect of the internal politics of medieval Italy. The struggle for power between the Papacy and the Holy Roman Empire arose with the Investiture Controversy, which began in 1075, and ended with the Concordat of Worms in 1122. History Origins The Guelph vs Ghibelline conflict initially arose from the division caused by the Investiture Controversy, about whether secular rulers or the pope had the authority to appoint bishops and abbots. Upon the death of Emperor Henry V, of the Salian dynasty, the dukes elected an opponent of his dynasty, Lothair III, as the new emperor. This displeased the Hohenstaufen, who were allied with and related to the old dynasty. Out of fear of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghibelline
The Guelphs and Ghibellines (, , ; it, guelfi e ghibellini ) were factions supporting the Pope and the Holy Roman Emperor, respectively, in the Italian city-states of Central Italy and Northern Italy. During the 12th and 13th centuries, rivalry between these two parties formed a particularly important aspect of the internal politics of medieval Italy. The struggle for power between the Papacy and the Holy Roman Empire arose with the Investiture Controversy, which began in 1075, and ended with the Concordat of Worms in 1122. History Origins The Guelph vs Ghibelline conflict initially arose from the division caused by the Investiture Controversy, about whether secular rulers or the pope had the authority to appoint bishops and abbots. Upon the death of Emperor Henry V, of the Salian dynasty, the dukes elected an opponent of his dynasty, Lothair III, as the new emperor. This displeased the Hohenstaufen, who were allied with and related to the old dynasty. Out of fear of the H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comune
The (; plural: ) is a local administrative division of Italy, roughly equivalent to a township or municipality. It is the third-level administrative division of Italy, after regions ('' regioni'') and provinces (''province''). The can also have the title of ('city'). Formed ''praeter legem'' according to the principles consolidated in medieval municipalities, the is provided for by art. 114 of the Constitution of Italy. It can be divided into ''frazioni'', which in turn may have limited power due to special elective assemblies. In the autonomous region of the Aosta Valley, a ''comune'' is officially called a ''commune'' in French. Overview The provides essential public services: registry of births and deaths, registry of deeds, and maintenance of local roads and public works. Many have a '' Polizia Comunale'' (communal police), which is responsible for public order duties. The also deal with the definition and compliance with the (general regulator plan), a document ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774. The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 and 796) that the Lombards descended from a small tribe called the Winnili,: "From Proto-Germanic '' winna-'', meaning "to fight, win" who dwelt in southern Scandinavia (''Scadanan'') before migrating to seek new lands. By the time of the Roman-era - historians wrote of the Lombards in the 1st century AD, as being one of the Suebian peoples, in what is now northern Germany, near the Elbe river. They continued to migrate south. By the end of the fifth century, the Lombards had moved into the area roughly coinciding with modern Austria and Slovakia north of the Danube, where they subdued the Heruls and later fought frequent wars with the Gepids. The Lombard king Audoin defeated the Gepid leader Thurisind in 551 or 552, and his successor Alboin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catiline
Lucius Sergius Catilina ( 108 BC – January 62 BC), known in English as Catiline (), was a Roman politician and soldier. He is best known for instigating the Catilinarian conspiracy, a failed attempt to violently seize control of the Roman state in 63 BC. Born to an ancient patrician family, he joined Sulla during Sulla's civil war and profited from Sulla's purges of his political enemies, becoming a wealthy man. In the early 60s BC, he served as praetor and then as governor of Africa. Upon his return to the city, he attempted to stand for the consulship but was rebuffed; he then was beset with legal challenges over alleged corruption in Africa and his actions during the proscriptions. Acquitted on all charges with the support of influential friends from across Roman politics, he stood for the consulship twice in 64 and 63 BC. Twice defeated in the consular ''comitia'', he concocted a violent plot to take the consulship by force, bringing together poor r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
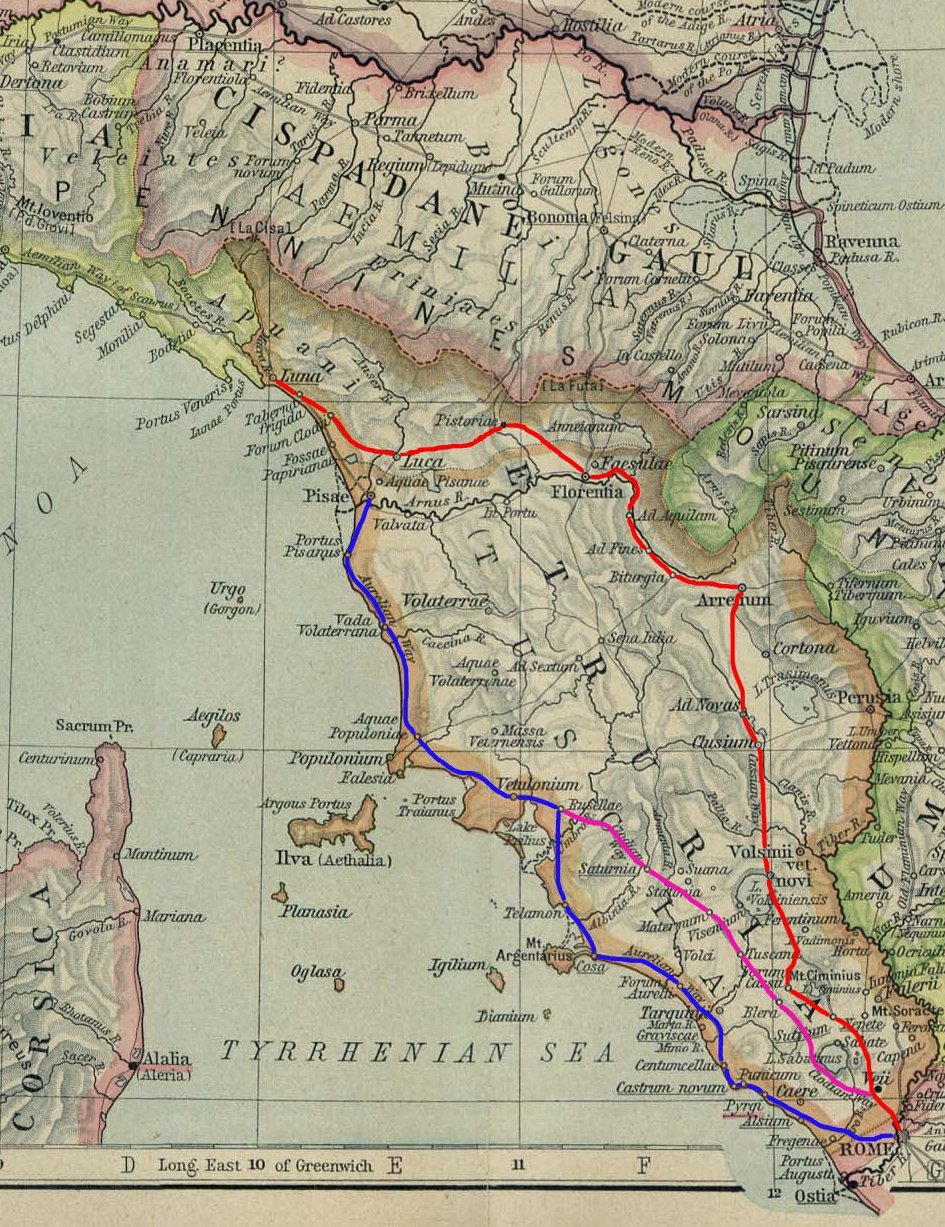
Via Cassia
The ''Via Cassia'' ("way of Cassius") was an important Roman road striking out of the ''Via Flaminia'' near the Milvian Bridge in the immediate vicinity of Rome and, passing not far from Veii, traversed Etruria. The ''Via Cassia'' passed through Baccanae, Sutrium, Volsinii, Clusium, Arretium, Florentia, Pistoria, and Luca, joining the ''Via Aurelia'' at Luna. The ''Via Cassia'' intersected other important roads. At mile 11 the ''Via Clodia'' diverged north-north-west. At Sette Vene, another road, probably the ''Via Annia'', branched off to Falerii. In Sutrium, the ''Via Ciminia'' split off and later rejoined. The date of its construction is uncertain: it cannot have been earlier than 187 BC, when the consul Gaius Flaminius constructed a road from Bononia to Arretium, which must have coincided with a portion of the later Via Cassia. It is not mentioned by any ancient authorities before the time of Cicero, who in 45 BC speaks of the existence of three roads from Rome to Muti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonia (Roman)
A Roman (plural ) was originally a Roman outpost established in conquered territory to secure it. Eventually, however, the term came to denote the highest status of a Roman city. It is also the origin of the modern term ''colony''. Characteristics Under the Roman Republic, which had no standing army, bodies of their own citizens were planted in conquered towns as a kind of garrison. There were two types: * Roman colonies, ''coloniae civium Romanorum'' or ''coloniae maritimae'', as they were often built near the sea, e.g. Ostia (350 BC) and Rimini (268 BC). The colonists consisted of about three hundred Roman families and were given a small plot of land so were probably small business owners. * Latin colonies (''coloniae Latinae'') were considerably larger than Roman colonies. They were military strongholds near or in enemy territory. The colonists were given large estates up to 35 hectares. They lost their citizenship which they could regain if they returned to Rome. Af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

.jpg)