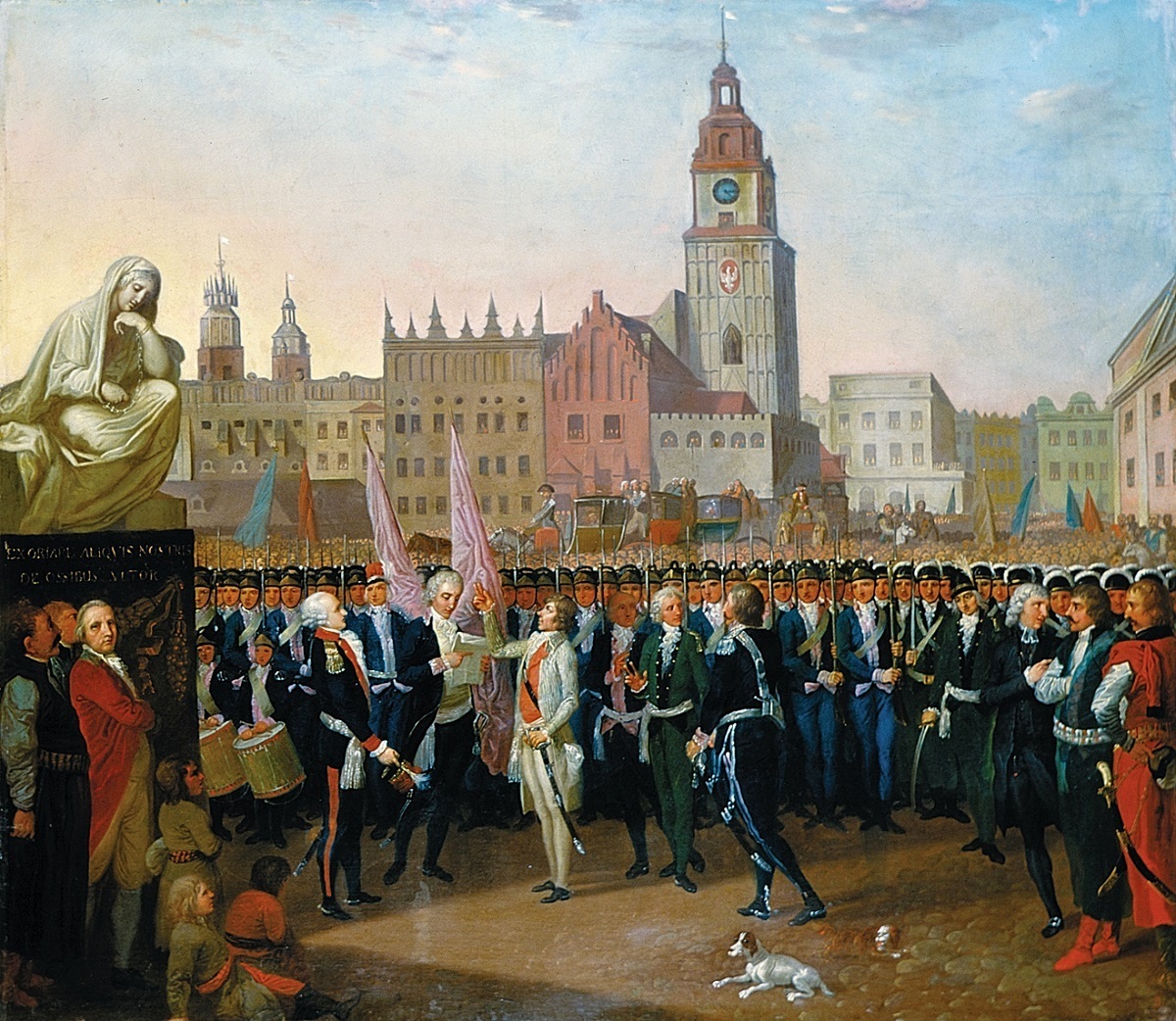|
Piotr Aigner
Chrystian Piotr Aigner (1756 in Puławy, Poland – 9 February 1841 in Florence, Italy) was a Polish architect and theoretician of architecture. Life Chrystian Piotr Aigner acquired extensive knowledge of architecture in the course of several journeys to Italy that he made in the company of his patron and subsequent collaborator and friend Stanisław Kostka Potocki. He studied in Italy. Later, during a long association with the city of Warsaw, he created many Classicist buildings in the Polish capital. A member of Rome's Academy of St. Luke, and of the Warsaw Society of Friends of Learning, and from 1817 a professor of architecture at Warsaw University, he was active in Warsaw until 1825 and in Kraków before leaving for Italy for good in 1827. Aigner at first applied the decorative forms of early Neoclassicism (Marynka's Palace in Puławy) or made reference to the works of Andrea Palladio (the façade of St. Anne's Church in Warsaw). In a later period, he reworked patterns draw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrystian Piotr Aigner
Chrystian Piotr Aigner (1756 in Puławy, Poland – 9 February 1841 in Florence, Italy) was a Polish architect and theoretician of architecture. Life Chrystian Piotr Aigner acquired extensive knowledge of architecture in the course of several journeys to Italy that he made in the company of his patron and subsequent collaborator and friend Stanisław Kostka Potocki. He studied in Italy. Later, during a long association with the city of Warsaw, he created many Classicist buildings in the Polish capital. A member of Rome's Academy of St. Luke, and of the Warsaw Society of Friends of Learning, and from 1817 a professor of architecture at Warsaw University, he was active in Warsaw until 1825 and in Kraków before leaving for Italy for good in 1827. Aigner at first applied the decorative forms of early Neoclassicism (Marynka's Palace in Puławy) or made reference to the works of Andrea Palladio (the façade of St. Anne's Church in Warsaw). In a later period, he reworked patterns dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596 and has traditionally been one of the leading centres of Polish academic, economic, cultural and artistic life. Cited as one of Europe's most beautiful cities, its Old Town with Wawel Royal Castle was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1978, one of the first 12 sites granted the status. The city has grown from a Stone Age settlement to Poland's second-most-important city. It began as a hamlet on Wawel Hill and was reported by Ibrahim Ibn Yakoub, a merchant from Cordoba, as a busy trading centre of Central Europe in 985. With the establishment of new universities and cultural venues at the emergence of the Second Polish Republic in 1918 and throughout the 20th century, Kraków reaffirmed its role as a major national academic and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igołomia
Igołomia is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Igołomia-Wawrzeńczyce, within Kraków County, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, in southern Poland. It lies approximately south-west of Wawrzeńczyce and east of the regional capital Kraków. The village has a population of 1,100. Notable people * Albert Chmielowski, painter, Catholic Saint * Wincenty Wodzinowski Wincenty Wodzinowski (1866 in Igołomia – 1940 in Kraków) was a Polish painter and art teacher; associated with the Young Poland movement. Biography He took his first drawing lessons from 1880 to 1881 with Wojciech Gerson in Warsaw. From 188 ..., painter References Villages in Kraków County Kielce Governorate Kielce Voivodeship (1919–1939) {{Kraków-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olesin, Puławy County
Olesin is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Kurów, within Puławy County, Lublin Voivodeship The Lublin Voivodeship, also known as the Lublin Province (Polish: ''województwo lubelskie'' ), is a voivodeship (province) of Poland, located in southeastern part of the country. It was created on January 1, 1999, out of the former Lublin, Che� ..., in eastern Poland. The village has a population of 343. References Villages in Puławy County {{Puławy-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pikeman
A pike is a very long thrusting spear formerly used in European warfare from the Late Middle Ages and most of the Early Modern Period, and were wielded by foot soldiers deployed in pike square formation, until it was largely replaced by bayonet-equipped muskets. The pike was particularly well-known as the primary weapon of Swiss mercenary and German Landsknecht units. A similar weapon, the sarissa, had been used in antiquity by Alexander the Great's Macedonian phalanx infantry. Design The pike was a long weapon, varying considerably in size, from long. Generally, a spear becomes a pike when it is too long to be wielded with one hand in combat. It was approximately in weight, with the 16th century military writer Sir John Smythe recommending lighter rather than heavier pikes. It had a wooden shaft with an iron or steel spearhead affixed. The shaft near the head was often reinforced with metal strips called "cheeks" or langets. When the troops of opposing armies both car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Scythe
A war scythe or military scythe is a form of pole weapon with a curving single-edged blade with the cutting edge on the concave side of the blade. Its blade bears a superficial resemblance to that of an agricultural scythe from which it is likely to have evolved, but the war scythe is otherwise unrelated to agricultural tools and is a purpose-built infantry melee weapon. The blade of a war scythe has regularly proportioned flats, a thickness comparable to that of a spear or sword blade, and slightly curves along its edge as it tapers to its point. This is very different from farming scythes, which have very thin and irregularly curved blades, specialised for mowing grass and wheat only, unsuitable as blades for improvised spears or polearms. Compared to a fauchard (which is believed to have evolved from the war scythe), the blade of the war scythe has the cutting edge on the concave side like the agricultural tool whereas the fauchard has the edge along the convex side. As an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kościuszko Uprising
The Kościuszko Uprising, also known as the Polish Uprising of 1794 and the Second Polish War, was an uprising against the Russian Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia led by Tadeusz Kościuszko in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Prussian partition in 1794. It was a failed attempt to liberate the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from external influence after the Second Partition of Poland (1793) and the creation of the Targowica Confederation. Background Decline of the Commonwealth By the early 18th century, the magnates of Poland and Lithuania controlled the state – or rather, they managed to ensure that no reforms would be carried out that might weaken their privileged status (the "Golden Freedoms"). Through the abuse of the '' liberum veto'' rule which enabled any deputy to paralyze the Sejm (Commonwealth's parliament) proceedings, deputies bribed by magnates or foreign powers or those simply content to believe they were living in an unprecedented "Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotunda (architecture)
A rotunda () is any building with a circular ground plan, and sometimes covered by a dome. It may also refer to a round room within a building (a famous example being the one below the dome of the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C.). The Pantheon in Rome is a famous rotunda. A ''band rotunda'' is a circular bandstand, usually with a dome. Rotunda in Central Europe A great number of parochial churches were built in this form in the 9th to 11th centuries CE in Central Europe. These round churches can be found in great number in Hungary, Poland, Slovakia, Croatia (particularly Dalmatia) Austria, Bavaria, Germany, and the Czech Republic. It was thought of as a structure descending from the Roman Pantheon. However, it can be found mainly not on former Roman territories, but in Central Europe. Generally its size was 6–9 meters inner diameter and the apse was directed toward the east. Sometimes three or four apses were attached to the central circle and this type has relatives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate period from 1800 to 1850. Romanticism was characterized by its emphasis on emotion and individualism, clandestine literature, paganism, idealization of nature, suspicion of science and industrialization, and glorification of the past with a strong preference for the medieval rather than the classical. It was partly a reaction to the Industrial Revolution, the social and political norms of the Age of Enlightenment, and the scientific rationalization of nature. It was embodied most strongly in the visual arts, music, and literature, but had a major impact on historiography, education, chess, social sciences, and the natural sciences. It had a significant and complex effect on politics, with romantic thinkers influencing conservatism, libe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire Style
The Empire style (, ''style Empire'') is an early-nineteenth-century design movement in architecture, furniture, other decorative arts, and the visual arts, representing the second phase of Neoclassicism. It flourished between 1800 and 1815 during the Consulate and the First French Empire periods, although its life span lasted until the late-1820s. From France it spread into much of Europe and the United States. The Empire style originated in and takes its name from the rule of the Emperor Napoleon I in the First French Empire, when it was intended to idealize Napoleon's leadership and the French state. The previous fashionable style in France had been the Directoire style, a more austere and minimalist form of Neoclassicism that replaced the Louis XVI style, and the new Empire style brought a full return to ostentatious richness. The style corresponds somewhat to the Biedermeier style in the German-speaking lands, Federal style in the United States, and the Regency style in Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neogothic
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly serious and learned admirers of the neo-Gothic styles sought to revive medieval Gothic architecture, intending to complement or even supersede the neoclassical styles prevalent at the time. Gothic Revival draws upon features of medieval examples, including decorative patterns, finials, lancet windows, and hood moulds. By the middle of the 19th century, Gothic had become the preeminent architectural style in the Western world, only to fall out of fashion in the 1880s and early 1890s. The Gothic Revival movement's roots are intertwined with philosophical movements associated with Catholicism and a re-awakening of high church or Anglo-Catholic belief concerned by the growth of religious nonconformism. Ultimately, the "Anglo-Catholicism" tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parish Church
A parish church (or parochial church) in Christianity is the church which acts as the religious centre of a parish. In many parts of the world, especially in rural areas, the parish church may play a significant role in community activities, often allowing its premises to be used for non-religious community events. The church building reflects this status, and there is considerable variety in the size and style of parish churches. Many villages in Europe have churches that date back to the Middle Ages, but all periods of architecture are represented. Roman Catholic Church Each diocese (administrative unit, headed by a Bishop) is divided into parishes. Normally, a parish comprises all Catholics living within its geographically defined area. Within a diocese, there can also be overlapping parishes for Catholics belonging to a particular rite, language, nationality, or community. Each parish has its own central church called the parish church, where religious services take pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |