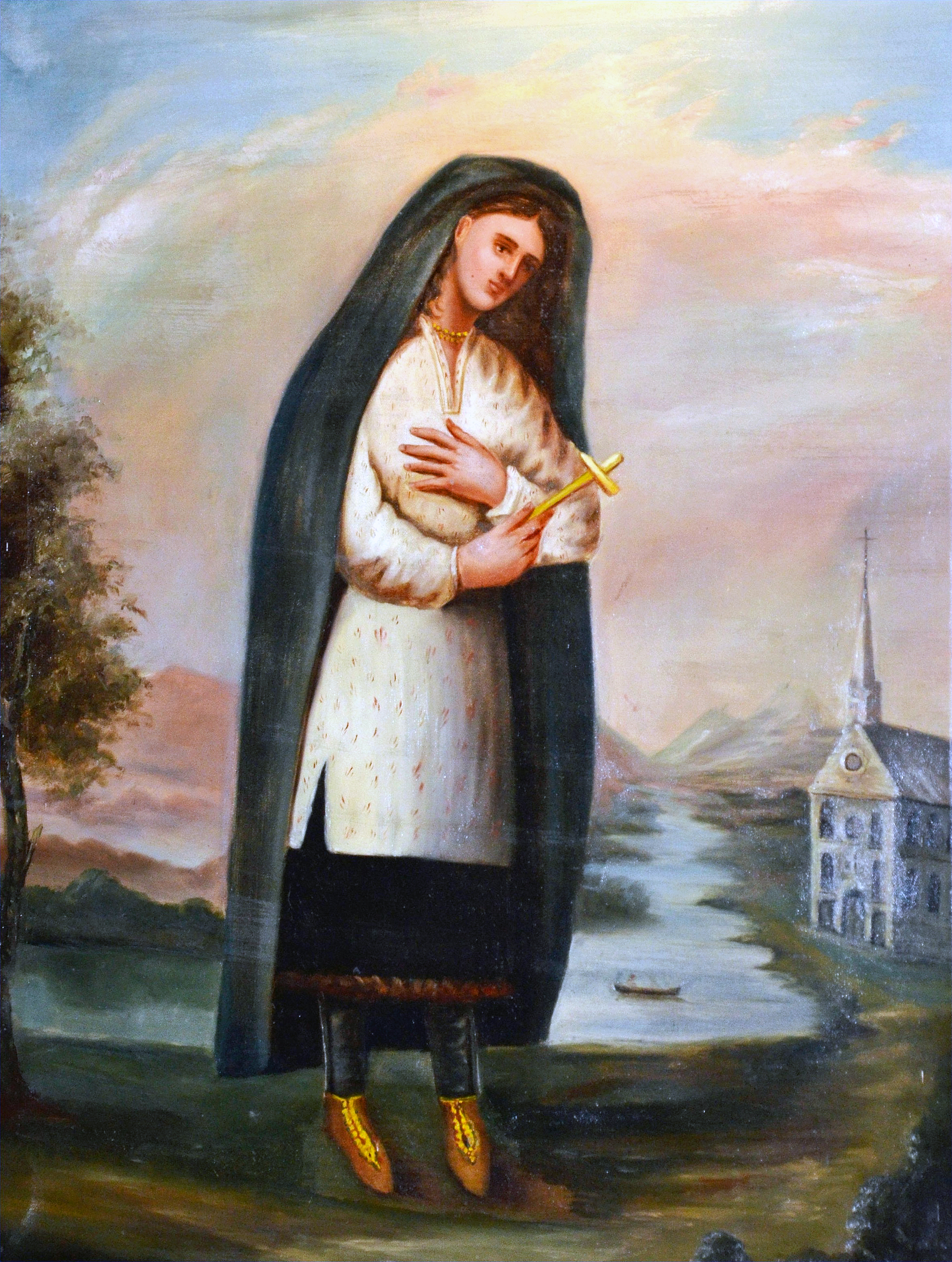 |
Pierre Cholenec
Pierre Cholenec (June 29, 1641 – October 30, 1723) was a French Jesuit missionary and biographer in New France. He ministered to First Nations in present-day Canada, particularly at the village of Kahnawake south of Montreal. He served as superior of the Jesuit residence in Montréal. He is known for writing multiple biographies about Kateri Tekakwitha which contributed to her canonization in 2012 by Pope Benedict XVI. Early life and education Cholenec was born in the Diocese of Saint-Pol-de-Léon, Finistère, in the west of Brittany. He attended Catholic schools. After completing his education in seminary, Cholenec entered the Society of Jesus in Paris, 8 October 1659 at the age of eighteen. He taught in the colleges of Moulins, Allier and Eu, Seine-Maritime from 1661 to 1670. Also during that period, he studied philosophy for three years at Collège Henri IV in La Flèche. After four years more of theology study in Paris at Collège de Clermont, Cholenec departed for Canada i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Jesuit
The Society of Jesus ( la, Societas Iesu; abbreviation: SJ), also known as the Jesuits (; la, Iesuitæ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rome. It was founded in 1540 by Ignatius of Loyola and six companions, with the approval of Pope Paul III. The society is engaged in evangelization and apostolic ministry in 112 nations. Jesuits work in education, research, and cultural pursuits. Jesuits also give retreats, minister in hospitals and parishes, sponsor direct social and humanitarian ministries, and promote Ecumenism, ecumenical dialogue. The Society of Jesus is consecrated under the patron saint, patronage of Madonna della Strada, a title of the Blessed Virgin Mary, and it is led by a Superior General of the Society of Jesus, Superior General. The headquarters of the society, its Curia, General Curia, is in Rome. The historic curia of Ignatius is now part of the attached to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Theology
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the supernatural, but also deals with religious epistemology, asks and seeks to answer the question of revelation. Revelation pertains to the acceptance of God, gods, or deities, as not only transcendent or above the natural world, but also willing and able to interact with the natural world and, in particular, to reveal themselves to humankind. While theology has turned into a secular field , religious adherents still consider theology to be a discipline that helps them live and understand concepts such as life and love and that helps them lead lives of obedience to the deities they follow or worship. Theologians use various forms of analysis and argument ( experiential, philosophical, ethnographic, historical, and others) to help u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg) |
1641 Births
Events January–March * January 4 – The stratovolcano Mount Parker (Philippines), Mount Parker in the Philippines) has a major eruption. * January 18 – Pau Claris proclaims the Catalan Republic (1641), Catalan Republic. * February 16 – King Charles I of England gives his assent to the Triennial Act, reluctantly committing himself to parliamentary sessions of at least fifty days, every three years. * March 7 – King Charles I of England decrees that all Roman Catholic priests must leave England by April 7 or face being arrested and treated as traitors. * March 22 – The trial for high treason begins for Thomas Wentworth, 1st Earl of Strafford, director of England's Council of the North. * March 27 – **The Battle of Preßnitz, Battle of Pressnitz begins between the Holy Roman Empire and Sweden. **The Siege of São Filipe begins in the Azores as the Portuguese Navy fights to drive the Spanish out. After almost 11 months, the Portuguese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple-peaked hill around which the early city of Ville-Marie is built. The city is centred on the Island of Montreal, which obtained its name from the same origin as the city, and a few much smaller peripheral islands, the largest of which is Île Bizard. The city is east of the national capital Ottawa, and southwest of the provincial capital, Quebec City. As of 2021, the city had a population of 1,762,949, and a metropolitan population of 4,291,732, making it the second-largest city, and second-largest metropolitan area in Canada. French is the city's official language. In 2021, it was spoken at home by 59.1% of the population and 69.2% in the Montreal Census Metropolitan Area. Overall, 85.7% of the population of the city of Montreal co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Hagiography
A hagiography (; ) is a biography of a saint or an ecclesiastical leader, as well as, by extension, an adulatory and idealized biography of a founder, saint, monk, nun or icon in any of the world's religions. Early Christian hagiographies might consist of a biography or ', a description of the saint's deeds or miracles (from Latin ''vita'', life, which begins the title of most medieval biographies), an account of the saint's martyrdom (called a ), or be a combination of these. Christian hagiographies focus on the lives, and notably the miracles, ascribed to men and women canonized by the Roman Catholic church, the Eastern Orthodox Church, the Oriental Orthodox churches, and the Church of the East. Other religious traditions such as Buddhism, Hinduism, Taoism, Islam, Sikhism and Jainism also create and maintain hagiographical texts (such as the Sikh Janamsakhis) concerning saints, gurus and other individuals believed to be imbued with sacred power. Hagiographic works, especi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Kateri Tekakwitha - Claude Chauchetiere
Kateri Tekakwitha ( in Mohawk), given the name Tekakwitha, baptized as Catherine and informally known as Lily of the Mohawks (1656 – April 17, 1680), is a Catholic saint and virgin who was an Algonquin– Mohawk. Born in the Mohawk village of Ossernenon, on the south side of the Mohawk River in present-day New York State, she contracted smallpox in an epidemic; her family died and her face was scarred. She converted to Catholicism at age nineteen, when she was baptized and given the Christian name Kateri in honor of Catherine of Siena. Refusing to marry, she left her village and moved for the remaining five years of her life to the Jesuit mission village of Kahnawake, south of Montreal on the St. Lawrence River in New France, now Canada. Kateri Tekakwitha took a vow of perpetual virginity. Upon her death at the age of 24, witnesses said that her scars vanished minutes later, and her face appeared radiant and beautiful. Known for her virtue of chastity and mortification of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Akwesasne
The Mohawk Nation at Akwesasne ( ; french: Nation Mohawk à Akwesasne; moh, Ahkwesáhsne) is a Mohawk Nation (''Kanienʼkehá:ka'') territory that straddles the intersection of international (United States and Canada) borders and provincial (Ontario and Quebec) boundaries on both banks of the St. Lawrence River. Although divided by an international border, the residents consider themselves to be one community. They maintain separate police forces due to jurisdictional issues and national laws. The community was founded in the mid-18th century by Mohawk families from Kahnawake (also known as Caughnawaga), a Catholic Mohawk village that developed south of Montreal along the St. Lawrence River. Today Akwesasne has a total of 12,000 residents, with the largest population and land area of any ''Kanienʼkehá:ka'' community. From its development in the mid-eighteenth century, Akwesasne was considered one of the Seven Nations of Canada. It is one of several ''Kanienʼkehá꞉ka'' (Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Indian Reserve
In Canada, an Indian reserve (french: réserve indienne) is specified by the ''Indian Act'' as a "tract of land, the legal title to which is vested in Her Majesty, that has been set apart by Her Majesty for the use and benefit of a band." Indian reserves are the areas set aside for First Nations, an indigenous Canadian group, after a contract with the Canadian state ("the Crown"), and are not to be confused with land claims areas, which involve all of that First Nations' traditional lands: a much larger territory than any reserve. Demographics A single "band" (First Nations government) may control one reserve or several, while other reserves are shared between multiple bands. In 2003, the Department of Indian and Northern Affairs stated there were 2,300 reserves in Canada, comprising . According to Statistics Canada in 2011, there are more than 600 First Nations/Indian bands in Canada and 3,100 Indian reserves across Canada. Examples include the Driftpile First Nation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
.jpg) |
Mortification Of The Flesh
Mortification of the flesh is an act by which an individual or group seeks to mortify or deaden their sinful nature, as a part of the process of sanctification. In Christianity, mortification of the flesh is undertaken in order to repent for sins and share in the Passion of Jesus. Common forms of Christian mortification that are practiced to this day include fasting, abstinence, as well as pious kneeling. Also common among Christian religious orders in the past were the wearing of sackcloth, as well as self-flagellation in imitation of Jesus Christ's suffering and death. Christian theology holds that the Holy Spirit helps believers in the "mortification of the sins of the flesh." Verses in the Old Testament (Hebrew Bible) considered to be precursors to Christian ideas of self-mortification include Zechariah 13:6 and 1 Kings 18:28–29. Although the term 'mortification of the flesh', which is derived from the King James version of Romans 8:13 and Colossians 3:5, is primaril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to the French as the Iroquois League, and later as the Iroquois Confederacy. The English called them the Five Nations, comprising the Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, and Seneca (listed geographically from east to west). After 1722, the Iroquoian-speaking Tuscarora people from the southeast were accepted into the confederacy, which became known as the Six Nations. The Confederacy came about as a result of the Great Law of Peace, said to have been composed by Deganawidah the Great Peacemaker, Hiawatha, and Jigonsaseh the Mother of Nations. For nearly 200 years, the Six Nations/Haudenosaunee Confederacy were a powerful factor in North American colonial policy, with some scholars arguing for the concept of the Middle Ground, in that Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
L'Ancienne-Lorette, Quebec
L'Ancienne-Lorette is a city in central Quebec, Canada. It is a suburb of and an enclave within Quebec City. It was merged with Quebec City on January 1, 2002 as part of a 2000–2006 municipal reorganization in Quebec, but, after a 2004 referendum, it was reconstituted as a separate city on January 1, 2006. Its history dates to 1674, when a group of Huron (Wyandot) fleeing war with the Iroquois settled there under the protection of the French. It was founded as a mission village by the Jesuits. The Wyandot left after a few decades, and French settlers took over the land. History The Jesuit missionary Pierre Chaumonot in 1674 founded a settlement here when he built a chapel for the Huron (Wyandot). Following his third and final trip to the shrine of Loreto in Italy, Chaumonot was cured of a terrible headache. In gratitude, he placed the colony under the patronage of Our Lady of the Annunciation, but it is still commonly called Lorette. In 1697, the Huron left the village ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Stone Church Of Saint Francis Xavier, Kahnawake
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks form the Earth's outer solid layer, the crust, and most of its interior, except for the liquid outer core and pockets of magma in the asthenosphere. The study of rocks involves multiple subdisciplines of geology, including petrology and mineralogy. It may be limited to rocks found on Earth, or it may include planetary geology that studies the rocks of other celestial objects. Rocks are usually grouped into three main groups: igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks are formed when magma cools in the Earth's crust, or lava cools on the ground surface or the seabed. Sedimentary rocks are formed by diagenesis and lithification of sediments, which in turn are formed by the weathering, transport, and deposition of existing rocks. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |