|
Phosphorus Deficiency
Phosphorus deficiency is a plant disorder associated with insufficient supply of phosphorus. Phosphorus refers here to salts of phosphates (PO43ŌłÆ), monohydrogen phosphate (HPO42ŌłÆ), and dihydrogen phosphate (H2PO4ŌłÆ). These anions readily interconvert, and the predominant species is determined by the pH of the solution or soil. Phosphates are required for the biosynthesis of genetic material as well as ATP, essential for life. Phosphorus deficiency can be controlled by applying sources of phosphorus such as bone meal, rock phosphate, manure, and phosphate-fertilizers.Heinrich W. Scherer "Fertilizers" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2000, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Symptoms In plants, phosphorus (P) is considered second to nitrogen as the most essential nutrient to ensure health and function. Phosphorus is used by plants in numerous processes such as photophosphorylation, genetic transfer, the transportation of nutrients, and phospholipid cell membranes. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid . The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosphoric acid by the removal of three protons . Removal of one or two protons gives the dihydrogen phosphate ion and the hydrogen phosphate ion ion, respectively. These names are also used for salts of those anions, such as ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and trisodium phosphate. File:3-phosphoric-acid-3D-balls.png, Phosphoricacid File:2-dihydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Dihydrogenphosphate File:1-hydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Hydrogenphosphate File:0-phosphate-3D-balls.png, Phosphate In organic chemistry, phosphate or orthophosphate is an organophosphate, an ester of orthophosphoric acid of the form where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups. An example is trimethyl phosphate, . The term also refers to the triv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons. Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed atomic or monatomic ions, while two or more atoms form molecular ions or polyatomic ions. In the case of physical ionization in a fluid (gas or liquid), "ion pairs" are created by spontaneous molecule collisions, where each generated pair consists of a free electron and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonymous with anabolism. The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. The human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day. It is also a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (adenine), the sugar ribose, and the Polyphosphate, triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of an adenine attached by the 9-nitrogen atom to the 1ŌĆ▓ carbon atom of a sugar (ribose), which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Meal
Bone meal is a mixture of finely and coarsely ground animal bones and slaughter-house waste products. It is used as a dietary supplement to supply calcium (Ca) and phosphorus (P) to monogastric livestock in the form of hydroxiapathite. As a slow-release organic fertilizer, it supplies phosphorus, calcium, and a small amount of nitrogen to plants. Uses Dietary supplement Bone meal, along with a variety of other meals, especially meat meal, is used as a dietary/mineral supplement for livestock. The improper application of bone and meat meal products in animal nutrition can contribute to the spread of Transmissible spongiform encephalopathy, commonly known in cattle as Mad Cow Disease. Proper heat control can reduce salmonella contaminants. Bone meal was historically used as a human dietary calcium supplement. Research has shown that calcium and lead in their ionic forms (Ca2+, Pb2+) have similar atomic structures and so create a potential for accumulation of lead in bones. Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Many sources of fertilizer exist, both natural and industrially produced. For most modern agricultural practices, fertilization focuses on three main macro nutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) with occasional addition of supplements like rock flour for micronutrients. Farmers apply these fertilizers in a variety of ways: through dry or pelletized or liquid application processes, using large agricultural equipment or hand-tool methods. Historically fertilization came from natural or organic sources: compost, animal manure, human manure, harvested minerals, crop rotations and byproducts of human-nature industries (i.e. fish processing waste, or bloodmeal from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. It has a concentration in the Earth's crust of about one gram per kilogram (compare copper at about 0.06 grams). In minerals, phosphorus generally occurs as phosphate. Elemental phosphorus was first isolated as white phosphorus in 1669. White phosphorus emits a faint glow when exposed to oxygen ŌĆō hence the name, taken from Greek mythology, meaning 'light-bearer' (Latin ), referring to the " Morning Star", the planet Venus. The term '' phosphorescence'', meaning glow after illumination, derives from this property of phosphorus, although the word has since been used for a different physical process that produces a glow. The glow of phosphorus is caused by oxidation of the white (but not red) phosphorus ŌĆö a process now called chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photophosphorylation
In the process of photosynthesis, the phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP using the energy of sunlight is called photophosphorylation. Cyclic photophosphorylation occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, driven by the main primary source of energy available to living organisms, which is sunlight. All organisms produce a phosphate compound, ATP, which is the universal energy currency of life. In photophosphorylation, light energy is used to pump protons across a biological membrane, mediated by flow of electrons through an electron transport chain. This stores energy in a proton gradient. As the protons flow back through an enzyme called ATP synthase, ATP is generated from ADP and inorganic phosphate. ATP is essential in the Calvin cycle to assist in the synthesis of carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and NADPH. ATP and reactions Both the structure of ATP synthase and its underlying gene are remarkably similar in all known forms of life. ATP synthase is powered by a transmembr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
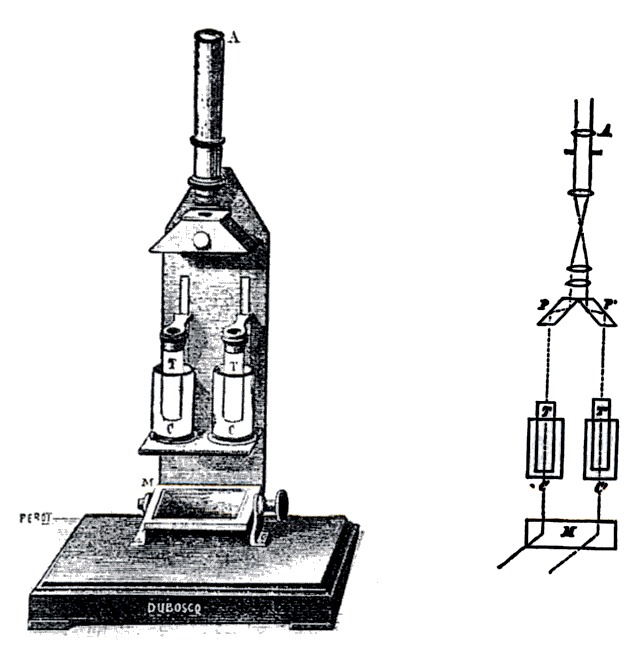
Colorimetry (chemical Method)
In physical and analytical chemistry, colorimetry or colourimetry is a technique used to determine the concentration of colored compounds in solution. A colorimeter is a device used to test the concentration of a solution by measuring its absorbance of a specific wavelength of light (not to be confused with the tristimulus colorimeter used to measure colors in general). To use the colorimeter, different solutions must be made, including a control or reference of known concentration. With a visual colorimeter, for example the Duboscq colorimeter illustrated, the length of the light path through the solutions can be varied while filtered light transmitted through them is compared for a visual match. The concentration times path length is taken to be equal when the colors match, so the concentration of the unknown can be determined by simple proportions. Nessler tubes work on the same principle. There are also electronic automated colorimeters; before these machines are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry
Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) is a type of mass spectrometry that uses an inductively coupled plasma to ionize the sample. It atomizes the sample and creates atomic and small polyatomic ions, which are then detected. It is known and used for its ability to detect metals and several non-metals in liquid samples at very low concentrations. It can detect different isotopes of the same element, which makes it a versatile tool in isotopic labeling. Compared to atomic absorption spectroscopy, ICP-MS has greater speed, precision, and sensitivity. However, compared with other types of mass spectrometry, such as thermal ionization mass spectrometry (TIMS) and glow discharge mass spectrometry (GD-MS), ICP-MS introduces many interfering species: argon from the plasma, component gases of air that leak through the cone orifices, and contamination from glassware and the cones. Components Inductively coupled plasma An inductively coupled plasma is a plasma that is ener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nondestructive Testing
Nondestructive testing (NDT) is any of a wide group of analysis techniques used in science and technology industry to evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage. The terms nondestructive examination (NDE), nondestructive inspection (NDI), and nondestructive evaluation (NDE) are also commonly used to describe this technology. Because NDT does not permanently alter the article being inspected, it is a highly valuable technique that can save both money and time in product evaluation, troubleshooting, and research. The six most frequently used NDT methods are eddy-current, magnetic-particle, liquid penetrant, radiographic, ultrasonic, and visual testing. NDT is commonly used in forensic engineering, mechanical engineering, petroleum engineering, electrical engineering, civil engineering, systems engineering, aeronautical engineering, medicine, and art. Innovations in the field of nondestructive testing have had a profound impact on medical im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |