Colorimetry (chemical Method) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In physical and
In physical and
 In physical and
In physical and analytical chemistry
Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to separate, identify, and quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute the entire analysis or be combined with another method. Separati ...
, colorimetry or colourimetry is a technique used to determine the concentration of colored compounds in solution.
A colorimeter is a device used to test the concentration of a solution by measuring its absorbance of a specific wavelength of light (not to be confused with the tristimulus colorimeter used to measure colors in general).
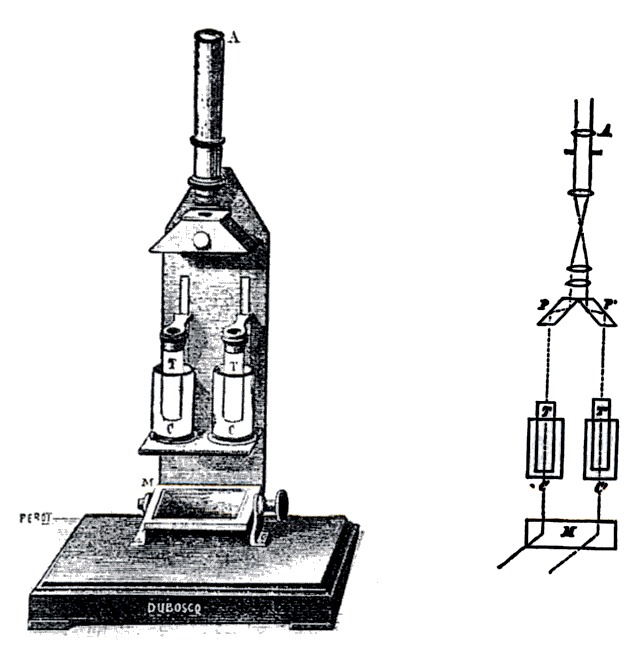
To use the colorimeter, different solutions must be made, including a control or reference of known concentration. With a visual colorimeter, for example the Duboscq Duboscq is a French surname. People with the name include:
* Genevieve Duboscq (1933–2018), author
* Hugues Duboscq (born 1981), Olympic breaststroke swimmer
* Jules Duboscq (18171886), instrument maker, inventor, and photographer
* Lucien Dubos ...
colorimeter illustrated, the length of the light path through the solutions can be varied while filtered light transmitted through them is compared for a visual match. The concentration times path length is taken to be equal when the colors match, so the concentration of the unknown can be determined by simple proportions. Nessler tube
Nessler cylinders (also named color comparison cylinders or color comparing cylinders) are Laboratory sample tube, laboratory tubes with a fixed volume, made of glass with optically plane bottom. On the walls, there are marks of the nominal stro ...
s work on the same principle.
There are also electronic automated colorimeters; before these machines are used, they must be calibrated with a cuvette containing the control solution. The concentration of a sample can be calculated from the intensity of light before and after it passes through the sample by using the Beer–Lambert law. Photoelectric analyzers came to dominate in the 1960s.
The color or wavelength of the filter chosen for the colorimeter is extremely important, as the wavelength of light that is transmitted by the colorimeter has to be the same as that absorbed by the substance being measured. For example, the filter on a colorimeter might be set to red if the liquid is blue.
Absorption colorimeter
A colorimeter is a device used to test the concentration of a solution by measuring its absorbance of a specific wavelength of light. To use this device, different solutions must be made, and a control (usually a mixture of distilled water and another solution) is first filled into a cuvette and placed inside a colorimeter to calibrate the machine. Only after the device has been calibrated you can use it to find the densities and/or concentrations of the other solutions. You do this by repeating the calibration, except with cuvettes filled with the other solutions. The filter on a colorimeter must be set to red if the liquid is blue. The size of the filter initially chosen for the colorimeter is extremely important, as the wavelength of light that is transmitted by the colorimeter has to be same as that absorbed by the substance.Colorimetric assays
{{main, Colorimetric analysis Colorimetric assays use reagents that undergo a measurable color change in the presence of the analyte. They are widely used in biochemistry to test for the presence of enzymes, specific compounds, antibodies, hormones and many more analytes. For example, *para-Nitrophenylphosphate
''para''-Nitrophenylphosphate (pNPP) is a non-proteinaceous chromogenic substrate for alkaline and acid phosphatases used in ELISA
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first des ...
is converted into a yellow product by alkaline phosphatase enzyme.
* Coomassie Blue once binding to proteins elicits a spectrum shift, allowing quantitative dosage. A similar colorimetric assay, the Bicinchoninic acid assay, uses a chemical reaction to determine protein concentration.
* Enzyme linked immunoassays use enzyme-complexed-antibodies to detect antigens. Binding of the antibody is often inferred from the color change of reagents such as TMB.
See also
*Jules Duboscq
Louis Jules Duboscq (March 5, 1817 – September 24, 1886) was a French instrument maker, inventor, and pioneering photographer. He was known in his time, and is remembered today, for the high quality of his optical instruments.
Life and wo ...
* Permanganometry
* Lovibond colorimeter
* Turbidimetry
References