|
Philippines Education During Spanish Rule
During the Spanish colonial period in the Philippines (1521–1898), the different cultures of the archipelago experienced a gradual unification from a variety of native Asian and Islamic customs and traditions, including animist religious practices, to what is known today as Filipino culture, a unique hybrid of Southeast Asian and Western culture, namely Spanish, including the Spanish language and the Catholic faith. Spanish education played a major role in that transformation. The oldest universities, colleges, and vocational schools, dating as far back as the late 16th century were created during the colonial period, as well as the first modern public education system in Asia, established in 1863. By the time Spain was replaced by the United States as the colonial power, Filipinos were among the most educated peoples in all of Asia, boasting one of the highest literacy rates in that continent. Simultaneously, the knowledge of Filipinos about neighboring cultures receded. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santo Tomas Libreria
Santo (' saint' in various languages) may refer to: People * Santo (given name) * Santo (surname) * El Santo, Rodolfo Guzmán Huerta (1917–1984), Mexican wrestler and actor * Bob Santo or Santo, stage name of Ghanaian comedian John Evans Kwadwo Bosompem (1940-2002) * Ferdinand III of Castile (1200–1252) called "''el Santo''" ("the Saint") Places * Santo, Ouest, Haiti, a village * Santō, Shiga, Japan, a town *Santo, Texas, United States, an unincorporated community * Basilica of Saint Anthony of Padua, Italy, known locally as ''il Santo'' *Espiritu Santo, the largest island of Vanuatu, nicknamed Santo **Luganville, known locally as Santo Arts and entertainment *Santo (art), a wooden or ivory statue depicting a holy figure * ''Santo'' (EP), by Alonso Brito, 2008 * "Santo" (song), by Christina Aguilera, 2022 *"Santo", a song by Ely Buendia * ''Il Santo'' (novel), Antonio Fogazzaro, 1905 See also * * *Los Santos (other) *Santos (other) *Santa (disambiguat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustinians
Augustinians are members of Christian religious orders that follow the Rule of Saint Augustine, written in about 400 AD by Augustine of Hippo. There are two distinct types of Augustinians in Catholic religious orders dating back to the 12th–13th centuries: * Various congregations of Canons Regular also follow the Rule of Saint Augustine, embrace the evangelical counsels and lead a semi-monastic life, while remaining committed to pastoral care appropriate to their primary vocation as priests. They generally form one large community which might serve parishes in the vicinity, and are organized into autonomous congregations. * Several orders of friars who live a mixed religious life of contemplation and apostolic ministry. The largest and most familiar is the Order of Saint Augustine (OSA), founded in 1244 and originally known as the Hermits of Saint Augustine (OESA). They are commonly known as the Austin Friars in England. Two other orders, the Order of Augustinian Recollec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arevalo, Iloilo City
Villa de Arevalo (; ), commonly known as simply Villa or Arevalo, is one of the seven districts of Iloilo City in the province of Iloilo, on the island of Panay in Western Visayas, in the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 55,476 people. Arevalo is the westernmost district of Iloilo City and it borders Oton to the west. Its church, Santo Niño de Arevalo Parish, possesses the third oldest '' Santo Niño'' (Infant Jesus) image in the Philippines. Arevalo is sometimes given the title "Flower Capital of Iloilo", where potted plants, flowers, bouquets, wreaths can be bought. Arevalo is also famous for its firecrackers and fireworks. Its prominent attraction is the Villa Beach ''(Playa de Villa de Arevalo)'' along the coast which boasts several resorts and an outdoor nightlife such as open air restaurants and bars. Camiña Balay nga Bato (formally known as the Avanceña Ancestral House) is a heritage house and a restaurant in Arevalo that was construc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaniards
Spaniards, or Spanish people, are a Romance ethnic group native to Spain. Within Spain, there are a number of national and regional ethnic identities that reflect the country's complex history, including a number of different languages, both indigenous and local linguistic descendants of the Roman-imposed Latin language, of which Spanish is the largest and the only one that is official throughout the whole country. Commonly spoken regional languages include, most notably, the sole surviving indigenous language of Iberia, Basque, as well as other Latin-descended Romance languages like Spanish itself, Catalan and Galician. Many populations outside Spain have ancestors who emigrated from Spain and share elements of a Hispanic culture. The most notable of these comprise Hispanic America in the Western Hemisphere. The Roman Republic conquered Iberia during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC. Hispania, the name given to Iberia by the Romans as a province of their Empire, became highly accu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visayan People
Visayans (Visayan: ''mga Bisaya''; ) or Visayan people are a Philippine ethnolinguistic group or metaethnicity native to the Visayas, the southernmost islands of Luzon and a significant portion of Mindanao. When taken as a single ethnic group, they are both the most numerous in the entire country at around 33.5 million, as well as the most geographically widespread. The Visayans broadly share a maritime culture with strong Roman Catholic traditions integrated into a precolonial indigenous core through centuries of interaction and migration mainly across the Visayan, Sibuyan, Camotes, Bohol and Sulu seas. In more inland or otherwise secluded areas, ancient animistic-polytheistic beliefs and traditions either were reinterpreted within a Roman Catholic framework or syncretized with the new religion. Visayans are generally speakers of one or more of the Bisayan languages, the most widely spoken being Cebuano, followed by Hiligaynon (Ilonggo) and Waray-Waray. Terminology ''Kabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedro Chirino
Pedro Chirino (1557 – 16 September 1635) was a Spanish priest and historian who served as a Jesuit missionary in the Philippines. He is most remembered for his work, ''Relación de las Islas Filipinas'' (1604), one of the earliest works about the Philippines and its people that was written. He was born in 1557 in the town of Osuna in Andalusia, Spain. A graduate in both civil and canon laws at Sevilla, he entered the Society of Jesus at age 23. He was soon appointed to the mission in the Philippines, arriving in the country in 1590 along with Gomez Perez Dasmariñas, the newly-appointed governor-general of the Philippines. He was first assigned to Balayan before he was appointed to be the parish priest of the town of Taytay in 1591. During his tenure as parish priest, he transferred the location of Taytay parish from its original site near Laguna de Bay to a hilltop area where it has remained to this day. He also began to immerse himself in the study of the Tagalog language and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
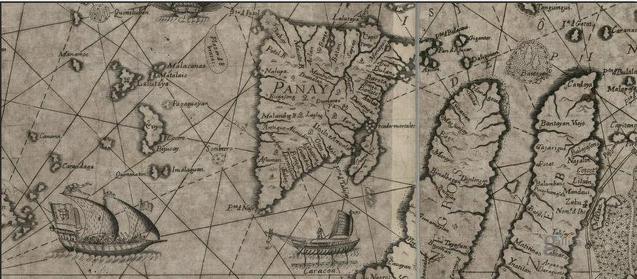
Panay
Panay is the sixth-largest and fourth-most populous island in the Philippines, with a total land area of and has a total population of 4,542,926 as of 2020 census. Panay comprises 4.4 percent of the entire population of the country. The City of Iloilo is its largest settlement with a total population of 457,626 inhabitants as of 2020 census. Panay is a triangular island, located in the western part of the Visayas. It is about across. It is divided into four provinces: Aklan, Antique, Capiz and Iloilo, all in the Western Visayas Region. Just closely off the mid-southeastern coast lies the island-province of Guimaras. It is located southeast of the island of Mindoro and northwest of Negros across the Guimaras Strait. To the north and northeast is the Sibuyan Sea, Jintotolo Channel and the island-provinces of Romblon and Masbate; to the west and southwest is the Sulu Sea and the Palawan archipelago and to the south is Panay Gulf. Panay is the only main island in the V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iloilo
Iloilo (), officially the Province of Iloilo ( hil, Kapuoran sang Iloilo; krj, Kapuoran kang Iloilo; tl, Lalawigan ng Iloilo), is a province in the Philippines located in the Western Visayas region. Its capital is the City of Iloilo, the regional center of Western Visayas. Iloilo occupies a major southeast portion of the Visayan island of Panay and is bordered by the province of Antique to the west, Capiz to the north, the Jintotolo Channel to the northeast, the Guimaras Strait to the east, and the Iloilo Strait and Panay Gulf to the southwest. Just off Iloilo's southeast coast is the island province of Guimaras, once part of Iloilo but now an independent province. Across the Panay Gulf and Guimaras Strait is Negros Occidental, occupying the northwestern half of the larger island of Negros. Iloilo City, its capital, is the center of the Iloilo–Guimaras Metropolitan Area or Metro Iloilo–Guimaras, and is geographically located in the province and is grouped unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigbauan, Iloilo
Tigbauan, officially the Municipality of Tigbauan ( krj, Banwa kang Tigbauan; hil, Banwa sang Tigbauan; tl, Bayan ng Tigbauan), is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Iloilo, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 65,245 people. Etymology The Maragtas Legend tells that in the 13th century, ten Bornean datus or chieftains left their homeland in the island of Borneo. In order to escape the cruel tyranny of their king, Sultan Makatunaw, they sailed towards the north in their long boats called balang-hais or balangays. They landed on the island of Panay, in order to live a life of unrestricted freedom. The ten Bornean datus or chieftains were led by Datu Puti. They bought the island of Panay from Datu Marikudo, the native chieftain of the Aetas or Negritos. For Panay Island, they paid Datu Marikudo with one golden salakot (headgear), and one gold necklace for his wife Maniwantiwan. (The Aetas or Negritos then went on to live in the mountains.) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bataan
Bataan (), officially the Province of Bataan ( fil, Lalawigan ng Bataan ), is a province in the Central Luzon region of the Philippines. Its capital is the city of Balanga while Mariveles is the largest town in the province. Occupying the entire Bataan Peninsula on Luzon, Bataan is bordered by the provinces of Zambales and Pampanga to the north. The peninsula faces the South China Sea to the west and Subic Bay to the north-west, and encloses Manila Bay to the east. The Battle of Bataan is known in history as one of the last stands of American and Filipino soldiers before they were overwhelmed by the Japanese forces in World War II. The Bataan Death March was named after the province, where the infamous march started. History Classical Period The first inhabitants of the Bataan peninsula are the Ayta Magbeken people, who are one of the first Negrito ancestors of present-day Filipinos. Later on, Tagalog communities from southern Luzon migrated to parts of Bataan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominican Order
The Order of Preachers ( la, Ordo Praedicatorum) abbreviated OP, also known as the Dominicans, is a Catholic mendicant order of Pontifical Right for men founded in Toulouse, France, by the Spanish priest, saint and mystic Dominic of Caleruega. It was approved by Pope Honorius III via the papal bull '' Religiosam vitam'' on 22 December 1216. Members of the order, who are referred to as ''Dominicans'', generally carry the letters ''OP'' after their names, standing for ''Ordinis Praedicatorum'', meaning ''of the Order of Preachers''. Membership in the order includes friars, nuns, active sisters, and lay or secular Dominicans (formerly known as tertiaries). More recently there has been a growing number of associates of the religious sisters who are unrelated to the tertiaries. Founded to preach the Gospel and to oppose heresy, the teaching activity of the order and its scholastic organisation placed the Preachers in the forefront of the intellectual life of the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_OldCathedral_1901.jpg)

