|
Philip Wicksteed
Philip Henry Wicksteed (25 October 1844 – 18 March 1927) is known primarily as an economist. He was also a Georgist, Unitarian theologian, classicist, medievalist, and literary critic. Family background He was the son of Charles Wicksteed (1810–1885) and his wife Jane (1814–1902), and was named after his distant ancestor, Philip Henry (1631–1696), the Nonconformist clergyman and diarist. His father was a clergyman within the same tradition of English Dissent. His mother was born into the Lupton family, a socially progressive, politically active dynasty of businessmen and traders, long established in Leeds, a city both prosperous and squalid with the rapid growth of the Industrial Revolution. In 1835 Wicksteed had taken up the ministry of the Unitarian place of worship, Mill Hill Chapel, right on the city's central square, and two years later the couple married. In 1841 his sister Elizabeth married Jane's brother Arthur (1819–1867), also a Unitarian minister; Uncle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leeds
Leeds () is a city and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds district in West Yorkshire, England. It is built around the River Aire and is in the eastern foothills of the Pennines. It is also the third-largest settlement (by population) in England, after London and Birmingham. The city was a small manorial borough in the 13th century and a market town in the 16th century. It expanded by becoming a major production centre, including of carbonated water where it was invented in the 1760s, and trading centre (mainly with wool) for the 17th and 18th centuries. It was a major mill town during the Industrial Revolution. It was also known for its flax industry, iron foundries, engineering and printing, as well as shopping, with several surviving Victorian era arcades, such as Kirkgate Market. City status was awarded in 1893, a populous urban centre formed in the following century which absorbed surrounding villages and overtook the nearby York population. It is locate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonconformist (Protestantism)
In English church history, the Nonconformists, also known as a Free Church person, are Protestant Christians who did not "conform" to the governance and usages of the established church, the Church of England (Anglican Church). Use of the term in England was precipitated after the Restoration of the Stuart monarchy in 1660, when the Act of Uniformity 1662 renewed opposition to reforms within the established church. By the late 19th century the term specifically included other Reformed Christians ( Presbyterians and Congregationalists), plus the Baptists, Brethren, Methodists, and Quakers. The English Dissenters such as the Puritans who violated the Act of Uniformity 1559 – typically by practising radical, sometimes separatist, dissent – were retrospectively labelled as Nonconformists. By law and social custom, Nonconformists were restricted from many spheres of public life – not least, from access to public office, civil service careers, or degrees at university � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Wicksteed (engineer)
Charles Wicksteed (1847–1931) was a British engineer, businessman, and entrepreneur. He is best known as a manufacturer of playground equipment and as the founder of Wicksteed Park. Biography Wicksteed was born in Leeds in 1847. His father was Charles Wicksteed, a Unitarian minister and his mother was Jane Lupton. His parents met when Charles Senior arrived in Leeds in 1835 to lead Mill Hill Chapel, at the heart of that industrial city, and two years later they married. Wicksteed was one of nine children. Sisters included Janet, who wrote a memoir under the name of Mrs Arthur Lewis. Brothers included Philip (Henry), the economist and Unitarian theologian, and (Joseph) Hartley, president of the Institute of Mechanical Engineers, whose daughter Mary Cicely married the Australian surgeon Sir Alan Newton. They had the maverick MP and mining engineer Arnold Lupton as their first cousin. At the age of 16, Wicksteed accepted an apprenticeship at locomotive manufacturer Kitson & ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Mechanical Engineers
The Institution of Mechanical Engineers (IMechE) is an independent professional association and learned society headquartered in London, United Kingdom, that represents mechanical engineers and the engineering profession. With over 120,000 members in 140 countries, working across industries such as railways, automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, energy, biomedical and construction, the Institution is licensed by the Engineering Council to assess candidates for inclusion on its Register of Chartered Engineers, Incorporated Engineers and Engineering Technicians. The Institution was founded at the Queen's Hotel, Birmingham, by George Stephenson in 1847. It received a Royal Charter in 1930. The Institution's headquarters, purpose-built for the Institution in 1899, is situated at No. 1 Birdcage Walk in central London. Origins Informal meetings are said to have taken place in 1846, at locomotive designer Charles Beyer's house in Cecil Street, Manchester, or alternatively at Bromsgr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hartley Wicksteed
Hartley may refer to: Places Australia *Hartley, New South Wales * Hartley, South Australia **Electoral district of Hartley, a state electoral district Canada *Hartley Bay, British Columbia United Kingdom *Hartley, Cumbria *Hartley, Plymouth, Devon *Hartley Wespall, Hampshire *Hartley, Sevenoaks, Kent * Hartley, Tunbridge Wells, Kent *Hartley, Northumberland (Old Hartley), part of Seaton Sluice *New Hartley, Northumberland United States *Hartley, California *Hartley, Iowa *Hartley, Michigan * Hartley, South Dakota *Hartley, Texas *Hartley County, Texas *Brohard, West Virginia, also Hartley Zimbabwe *Chegutu, formerly Hartley People * Hartley (surname) * Hartley Burr Alexander, (1873–1939), American philosopher * Hartley Alleyne (born 1957), Barbadian cricketer * Hartley Booth (born 1946), British politician * Hartley Coleridge (1796–1849), English writer * Hartley Craig (1917–2007), Australian cricketer * Hartley Douglas Dent (1929–1993), Canadian politician ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold Lupton
Arnold Lupton (11 September 1846 – 23 May 1930) was a British Liberal Party Member of Parliament, academic, anti-vaccinationist, mining engineer and a managing director (collieries). He was jailed for pacifist activity during the First World War. Family background Arnold Lupton was the son of Arthur Lupton, (1819–1867) and Elizabeth Wicksteed. His father was a Unitarian minister. and member of the Lupton family of Leeds. His mother's brother was the Rev Charles Wicksteed, a minister at Mill Hill Chapel in Leeds. The Wicksteeds were "Unitarians of vigorous mind and keen intelligence". Career Lupton was articled to Woodhouse and Jeffcock, civil and mining engineers in Derby and became Professor of Coal Mining, at the Yorkshire College from 1878 to 1899 and an examiner in Mine Surveying for the City and Guilds of London Institute. The Royal Coal Commission employed him to prepare maps, sections and estimates of coal reserves in Yorkshire, Derbyshire and Nottinghamshire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Vincent
Henry Vincent (10 May 1813 – 29 December 1878) was active in the formation of early Working Men's Associations in Britain, a popular Chartist leader, brilliant and gifted public orator, prospective but ultimately unsuccessful Victorian member of parliament, and later an anti-slavery campaigner. Early life Vincent was born in High Holborn, the son of a goldsmith. He saw his father's business fail, a decline in circumstances that prompted the family to move to Kingston upon Hull. By 1828 Vincent was a young apprentice boy in the growing printing trade. Once his apprenticeship was completed he returned to London to pursue his printing career. At this time he was very interested in the views of Tom Paine and especially Paine's views on universal suffrage (including votes for women) and state welfare benefits. Political awakening By 1833 Vincent was in London working as a printer but also deepening his political awareness and knowledge. In 1836 he joined the recently forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chartism
Chartism was a working-class movement for political reform in the United Kingdom that erupted from 1838 to 1857 and was strongest in 1839, 1842 and 1848. It took its name from the People's Charter of 1838 and was a national protest movement, with particular strongholds of support in Northern England, the East Midlands, the Staffordshire Potteries, the Black Country, and the South Wales Valleys. The movement was fiercely opposed by government authorities who finally suppressed it. Support for the movement was at its highest when petitions signed by millions of working people were presented to the House of Commons. The strategy employed was to use the scale of support which these petitions and the accompanying mass meetings demonstrated to put pressure on politicians to concede manhood suffrage. Chartism thus relied on constitutional methods to secure its aims, though some became involved in insurrectionary activities, notably in South Wales and in Yorkshire. The People's Chart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Suffrage
Universal suffrage (also called universal franchise, general suffrage, and common suffrage of the common man) gives the right to vote to all adult citizens, regardless of wealth, income, gender, social status, race, ethnicity, or political stance, subject only to certain exceptions as in the case of children, felons, and for a time, women.Suffrage ''Encyclopedia Britannica''. In its original 19th-century usage by reformers in Britain, ''universal suffrage'' was understood to mean only ; the vote was extended to women later, during the |
Achilles
In Greek mythology, Achilles ( ) or Achilleus ( grc-gre, Ἀχιλλεύς) was a hero of the Trojan War, the greatest of all the Greek warriors, and the central character of Homer's ''Iliad''. He was the son of the Nereid Thetis and Peleus, king of Phthia. Achilles' most notable feat during the Trojan War was the slaying of the Trojan prince Hector outside the gates of Troy. Although the death of Achilles is not presented in the ''Iliad'', other sources concur that he was killed near the end of the Trojan War by Paris, who shot him with an arrow. Later legends (beginning with Statius' unfinished epic ''Achilleid'', written in the 1st century AD) state that Achilles was invulnerable in all of his body except for one heel, because when his mother Thetis dipped him in the river Styx as an infant, she held him by one of his heels. Alluding to these legends, the term " Achilles' heel" has come to mean a point of weakness, especially in someone or something with an otherwise strong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leeds City Square
City Square is a paved area north of Leeds railway station at the junction of Park Row to the east and Wellington Street to the south. It is a triangular area where six roads meet: Infirmary Street and Park Row to the north, Boar Lane and Bishopsgate Street to the south-east, and Quebec Street and Wellington Street to the south-west. The only building with a direct frontage is the former General Post Office, on the north-west side. History Proposals were made in 1893 to transform the area in front of the station. The demolition of Leeds' Coloured Cloth Hall and Quebec House gave an open space in which a new General Post Office was constructed in 1896 with a public space in front. One proposal was to name the development after John Smeaton, the famous local engineer, but the council unanimously opted to call it City Square, as Leeds was being made a city that year. The initial plan had tramway waiting rooms, and public lavatories welcoming new visitors to Leeds. However, Colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
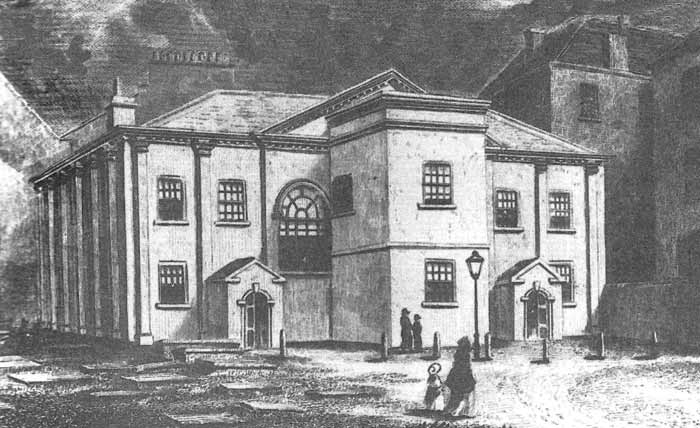
Mill Hill Chapel
Mill Hill Chapel is a Unitarian church in Leeds, West Yorkshire, England. It is a member of the General Assembly of Unitarian and Free Christian Churches, the umbrella organisation for British Unitarians. The building, which stands in the centre of the city on City Square, was granted Grade II* listed status in 1963. History As early as 1674, only a dozen years after the Great Ejection, the Dissenters in Leeds had built a chapel on the main town square. One of the founders was the father of the historian Ralph Thoresby who guided the chapel toward the Dissenter movement which, at Mill Hill Chapel, would become Unitarianism. 18th century During the late 18th century, Mill Hill's sister chapel was the Independent Congregationalist Call Lane Chapel, Leeds. Many of Leeds's leading families such as George William Oates at Low Hall, Potternewton and the Dixon family of Gledhow Hall were heavily involved with both churches at this time. Some local gentry, such as Hans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)





.jpg)