|
Philadelphus Purpurascens
''Philadelphus purpurascens'' is a deciduous shrub native to Yunnan and Sichuan in southwestern China, growing in mixed forests, thickets and on mountain slopes. It is a shrub growing tall. The leaves are ovate to elliptic, glabrous or sparsely villous along the veins. The flowers are produced in racemes of 5-7 (-9) together; the individual flowers are white, with a purple or dark brown calyx. Flowering is in spring or early summer. Three varieties are recognized by the ''Flora of China'': *''Philadelphus purpurascens'' var. ''szechuanensis'' *''Philadelphus purpurascens'' var. ''purpurascens'' *''Philadelphus purpurascens'' var. ''venustus'' Cultivation It is easy to grow in ordinary garden soil. It tolerates dry conditions and prefers full sun. Plants are tolerant of pruning and could be cut back every year after flowering to promote next years flowers. It is hardy to USDA The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the federal executive department responsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernhard Adalbert Emil Koehne
Bernhard Adalbert Emil Koehne (12 February 1848 – 12 October 1918) was a German botanist and dendrologist born near Striegau, a town known today as Strzegom, Poland. Koehne was a professor of botany in Berlin and was a leading authority of the plant family Lythraceae. In Adolf Engler's treatise ''Das Pflanzenreich'' ("The Plant Kingdom"), he was author of the chapter on Lythraceae. He also made important contributions involving Lythraceae to Engler and Karl Prantl's ''Die Natürlichen Pflanzenfamilien'' ("The Natural Plant Families"), as well as to Karl Friedrich Philipp von Martius' ''Flora Brasiliensis''. Another noted written effort by Koehne was the 1893 ''Deutsche Dendrologie'' ("German Dendrology"). Two plant genera have been named in his honor; '' Koehneola'' from Cuba, in the (family Asteraceae) was named in 1901, and ''Koehneria ''Koehneria'' is a monotypic genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Lythraceae. The only species is ''Koehneria madagas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raceme
A raceme ( or ) or racemoid is an unbranched, indeterminate type of inflorescence bearing flowers having short floral stalks along the shoots that bear the flowers. The oldest flowers grow close to the base and new flowers are produced as the shoot grows in height, with no predetermined growth limit. Examples of racemes occur on mustard (genus ''Brassica'') and radish (genus ''Raphanus'') plants. Definition A ''raceme'' or ''racemoid'' is an unbranched, indeterminate type of inflorescence bearing pedicellate flowers (flowers having short floral stalks called ''pedicels'') along its axis. In botany, an ''axis'' means a shoot, in this case one bearing the flowers. In indeterminate inflorescence-like racemes, the oldest flowers grow close to the base and new flowers are produced as the shoot grows in height, with no predetermined growth limit. A plant that flowers on a showy raceme may have this reflected in its scientific name, e.g. the species ''Cimicifuga racemosa''. A compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Alfred Rehder
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philadelphus
''Philadelphus'' () (mock-orange) is a genus of about 60 species of shrubs from 3–20 ft (1–6 m) tall, native to North America, Central America, Asia and (locally) in southeast Europe. They are named "mock-orange" in reference to their flowers, which in wild species look somewhat similar to those of oranges and lemons (''Citrus'') at first glance, and smell of orange flowers and jasmine (''Jasminum''). But ''Philadelphus'' is a basal asterid, not closely related to ''Jasminum'' (advanced asterids), and among the eudicots quite distant from ''Citrus'' (advanced rosids). An entirely misleading name for ''Philadelphus'' that is sometimes encountered is ''syringa''; this properly refers to the lilacs, which are fairly close relatives of jasmine. The connection of the two shrubs lies in their introduction from Ottoman gardens to European ones, effected at the same time by the Holy Roman emperor's ambassador to the Sublime Porte, Ogier Ghiselin de Busbecq, who returned to Vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the United States federal executive departments, federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, rural economic development, and food. It aims to meet the needs of commercial farming and livestock food production, promotes agricultural trade and production, works to assure food safety, protects natural resources, fosters rural communities and works to end hunger in the United States and internationally. It is headed by the United States Secretary of Agriculture, Secretary of Agriculture, who reports directly to the President of the United States and is a member of the president's Cabinet of the United States, Cabinet. The current secretary is Tom Vilsack, who has served since February 24, 2021. Approximately 80% of the USDA's $141 billion budget goes to the Food and Nutrition Service (FNS) program. The largest component of the FNS budget is the Supplementa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
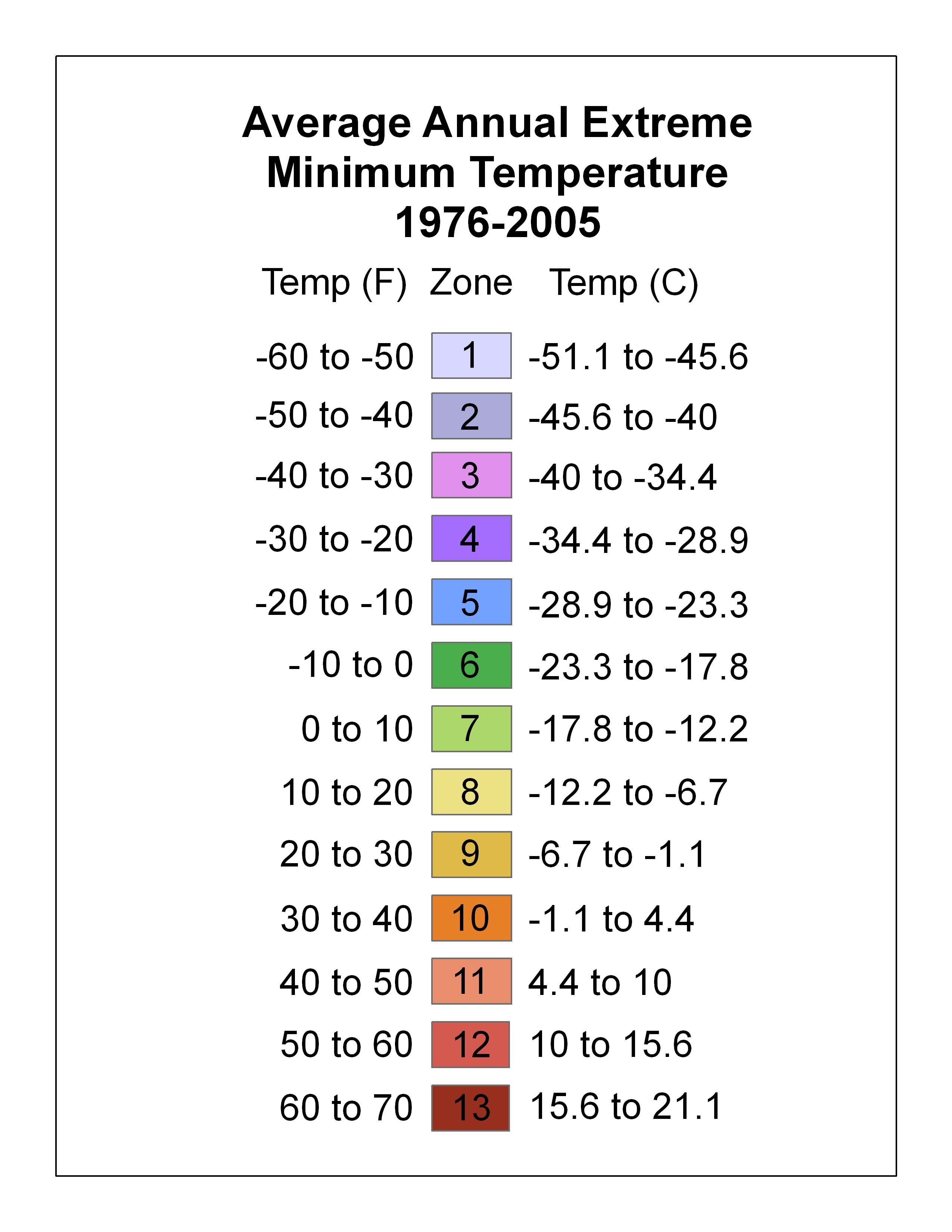
Hardiness Zone
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most widely used system, developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) as a rough guide for landscaping and gardening, defines 13 zones by long-term average annual extreme minimum temperatures. It has been adapted by and to other countries (such as Canada) in various forms. Unless otherwise specified, in American contexts "hardiness zone" or simply "zone" usually refers to the USDA scale. For example, a plant may be described as "hardy to zone 10": this means that the plant can withstand a minimum temperature of 30 °F (−1.1 °C) to 40 °F (4.4 °C). Other hardiness rating schemes have been developed as well, such as the UK Royal Horticultural Society and US Sunset Western Garden Book systems. A heat zone (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variety (biology)
In botanical nomenclature, variety (abbreviated var.; in la, varietas) is a taxonomic rank below that of species and subspecies, but above that of Form (botany), form. As such, it gets a three-part Infraspecific name (botany), infraspecific name. It is sometimes recommended that the subspecies rank should be used to recognize geographic distinctiveness, whereas the variety rank is appropriate if the taxon is seen throughout the geographic range of the species. Example The pincushion cactus, ''Escobaria vivipara'' (Nutt.) Buxb., is a wide-ranging variable species occurring from Canada to Mexico, and found throughout New Mexico below about . Nine varieties have been described. Where the varieties of the pincushion cactus meet, they intergrade. The variety ''Escobaria vivipara'' var. ''arizonica'' is from Arizona, while ''Escobaria vivipara'' var. ''neo-mexicana'' is from New Mexico. See also ''Capsicum annuum var. glabriusculum'' Definitions The term is defined in different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sepal
A sepal () is a part of the flower of angiosperms (flowering plants). Usually green, sepals typically function as protection for the flower in bud, and often as support for the petals when in bloom., p. 106 The term ''sepalum'' was coined by Noël Martin Joseph de Necker in 1790, and derived . Collectively the sepals are called the calyx (plural calyces), the outermost whorl of parts that form a flower. The word ''calyx'' was adopted from the Latin ,Jackson, Benjamin, Daydon; A Glossary of Botanic Terms with their Derivation and Accent; Published by Gerald Duckworth & Co. London, 4th ed 1928 not to be confused with 'cup, goblet'. ''Calyx'' is derived from Greek 'bud, calyx, husk, wrapping' ( Sanskrit 'bud'), while is derived from Greek 'cup, goblet', and the words have been used interchangeably in botanical Latin. After flowering, most plants have no more use for the calyx which withers or becomes vestigial. Some plants retain a thorny calyx, either dried or live, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flower
A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants (plants of the division Angiospermae). The biological function of a flower is to facilitate reproduction, usually by providing a mechanism for the union of sperm with eggs. Flowers may facilitate outcrossing (fusion of sperm and eggs from different individuals in a population) resulting from cross-pollination or allow selfing (fusion of sperm and egg from the same flower) when self-pollination occurs. There are two types of pollination: self-pollination and cross-pollination. Self-pollination occurs when the pollen from the anther is deposited on the stigma of the same flower, or another flower on the same plant. Cross-pollination is when pollen is transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower on a different individual of the same species. Self-pollination happens in flowers where the stamen and carpel mature at the same time, and are positi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Rehder
Alfred Rehder (4 September 1863 in Waldenburg, Saxony – 25 July 1949 in Jamaica Plain, Massachusetts) was a German-American botanical taxonomist and dendrologist who worked at the Arnold Arboretum of Harvard University. He is generally regarded as the foremost dendrologist of his generation. Life Georg Alfred Rehder was born in the castle of Waldenburg to Thekla née Schmidt (1839–1897) and Paul Julius Rehder (1833–1917), the superintendent of parks and gardens of the principality of Schönburg-Waldenburg. Through his father, Rehder was introduced to the gardening profession. On his mother's side of the family, Rehder was likely descended from Henry, Duke of Anhalt-Köthen (1778–1847). Rehder broke off his attendance at the gymnasium in Zwickau in 1881 and did not pursue university studies, instead working for three years as an apprentice under the tutelage of his father. His professional career began in 1884 at the Berlin Botanical Garden. Here he was able to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaf
A leaf ( : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, stem, flower, and fruit collectively form the shoot system. In most leaves, the primary photosynthetic tissue is the palisade mesophyll and is located on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of ''Eucalyptus'', palisade mesophyll is present on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral. Most leaves are flattened and have distinct upper (adaxial) and lower ( abaxial) surfaces that differ in color, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases), the amount and structure of epicuticular wax and other features. Leaves are mostly green in color due to the presence of a compound called chlorophyll that is essential for photosynthesis as it absorbs light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrub
A shrub (often also called a bush) is a small-to-medium-sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. Shrubs can be either deciduous or evergreen. They are distinguished from trees by their multiple stems and shorter height, less than tall. Small shrubs, less than 2 m (6.6 ft) tall are sometimes termed as subshrubs. Many botanical groups have species that are shrubs, and others that are trees and herbaceous plants instead. Some definitions state that a shrub is less than and a tree is over 6 m. Others use as the cut-off point for classification. Many species of tree may not reach this mature height because of hostile less than ideal growing conditions, and resemble a shrub-sized plant. However, such species have the potential to grow taller under the ideal growing conditions for that plant. In terms of longevity, most shrubs fit in a class between perennials and trees; some may only last about five y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
.png)
