|
Pediococcus
''Pediococcus'' is a genus of gram-positive lactic acid bacteria, placed within the family of Lactobacillaceae. They usually occur in pairs or tetrads, and divide along two planes of symmetry, as do the other lactic acid cocci genera ''Aerococcus'' and '' Tetragenococcus''. They are purely homofermentative. '' Pediococcus dextrinicus'' has recently been reassigned to the genus ''Lapidilactobacillus''. Food processing ''Pediococcus'' is, along with other lactic acid bacteria such as '' Leuconostoc'' and ''Lactobacillus'', responsible for the fermentation of cabbage, making it sauerkraut. In this process, the sugars in fresh cabbage are fermented to lactic acid, which gives sauerkraut a sour flavour and good keeping qualities. ''Pediococcus'' bacteria are usually considered contaminants of beer and wine, although their presence is sometimes desired in beer styles such as lambic and Berliner Weisse. Certain ''Pediococcus'' isolates produce diacetyl which gives a buttery or butt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediococcus Acidilactici
''Pediococcus acidilactici'' is a species of Gram-positive cocci that is often found in pairs or tetrads. ''P. acidilactici'' is a homofermentative bacterium that can grow in a wide range of pH, temperature, and osmotic pressure, therefore being able to colonize the digestive tract. It has emerged as a potential probiotic that has shown promising results in animal and human experiments, though some of the results are limited. They are commonly found in fermented vegetables, fermented dairy products, and meat.Barros R.R., Carvalho G.S., Peralta J.M., Facklam R.R., Teixeira L.M. 2001. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Pediococcus strains isolated from human clinical sources. J. Clin Microbiol. April;39(4): 1241–1246. ''Pediococcus acidilactici'' is a facultative anaerobe that grows well on de Man, Rogosa, Sharpe agar of an optimum pH of 6.2, with an overnight incubation at 37 and 45 °C. It is also viable at higher temperatures up to 65 °C.Lin J.J. 2006. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
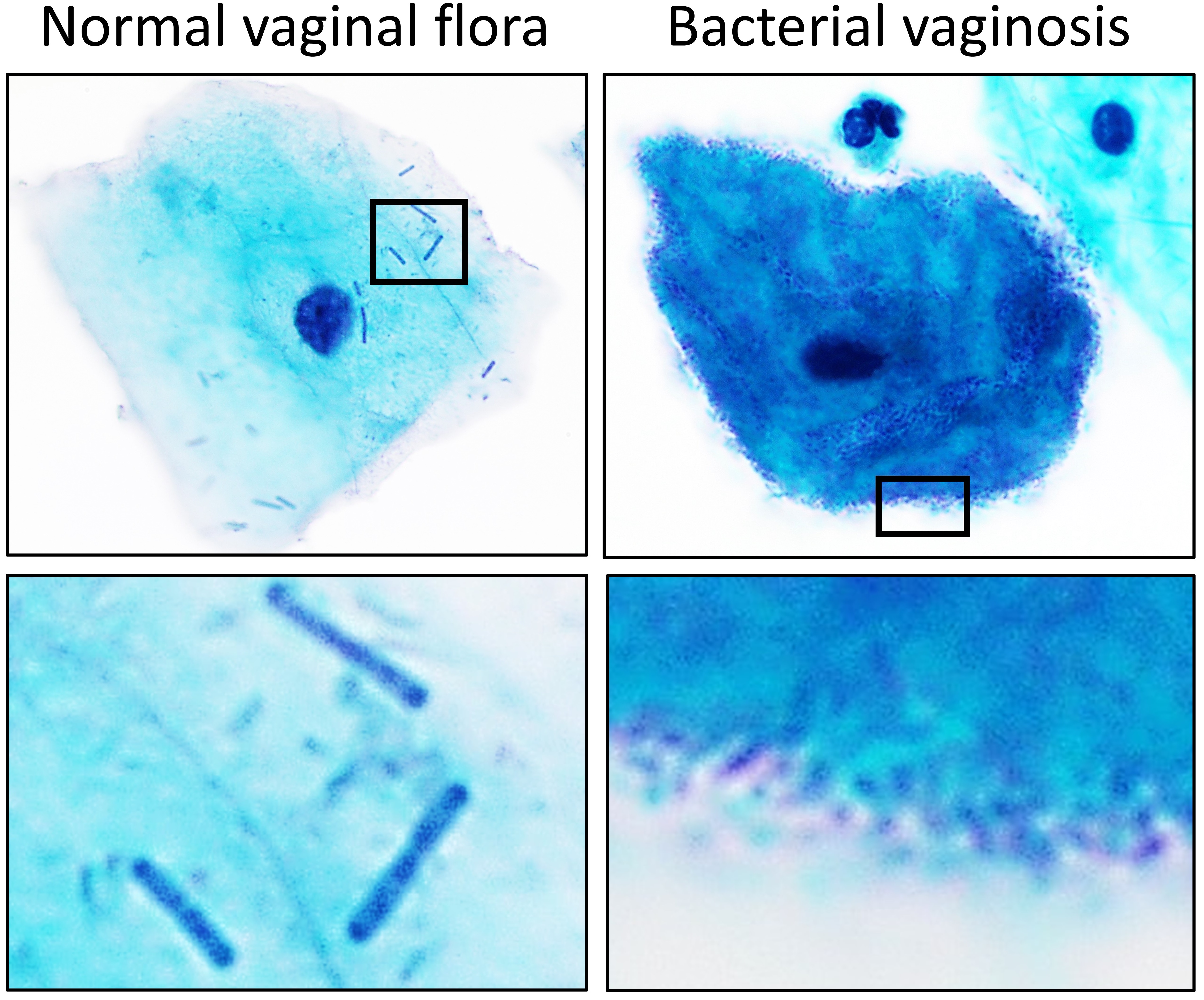
Pediococcus Claussenii
''Pediococcus claussenii'' is a species of Gram-positive bacteria. Like other ''Pediococcus'' species, ''P. claussenii'' is implicated in the spoilage of fermented beverages due to its production of diacetyl. Strains of this species were originally isolated from spoiled beer Beer is one of the oldest and the most widely consumed type of alcoholic drink in the world, and the third most popular drink overall after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches, mainly derived from cer .... The genome of ''P. claussenii'' strain ATCC BAA-344 has been sequenced. References External linksType strain of ''Pediococcus claussenii'' at Bac''Dive'' - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase Lactobacillaceae Bacteria described in 2002 {{lactobacilli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediococcus Cellicola
''Pediococcus cellicola'' is a species of Gram-positive bacteria. Strains of this species were originally isolated from a fermenting cellar in Hebei Province Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and ..., China. References External linksType strain of ''Pediococcus cellicola'' at Bac''Dive'' - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase Lactobacillaceae Bacteria described in 2005 {{lactobacilli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillales
Lactobacillales are an order of gram-positive, low-GC, acid-tolerant, generally nonsporulating, nonrespiring, either rod-shaped ( bacilli) or spherical ( cocci) bacteria that share common metabolic and physiological characteristics. These bacteria, usually found in decomposing plants and milk products, produce lactic acid as the major metabolic end product of carbohydrate fermentation, giving them the common name lactic acid bacteria (LAB). Production of lactic acid has linked LAB with food fermentations, as acidification inhibits the growth of spoilage agents. Proteinaceous bacteriocins are produced by several LAB strains and provide an additional hurdle for spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms. Furthermore, lactic acid and other metabolic products contribute to the organoleptic and textural profile of a food item. The industrial importance of the LAB is further evidenced by their generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status, due to their ubiquitous appearance in food and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactic Acid Bacteria
Lactobacillales are an order of gram-positive, low-GC, acid-tolerant, generally nonsporulating, nonrespiring, either rod-shaped ( bacilli) or spherical ( cocci) bacteria that share common metabolic and physiological characteristics. These bacteria, usually found in decomposing plants and milk products, produce lactic acid as the major metabolic end product of carbohydrate fermentation, giving them the common name lactic acid bacteria (LAB). Production of lactic acid has linked LAB with food fermentations, as acidification inhibits the growth of spoilage agents. Proteinaceous bacteriocins are produced by several LAB strains and provide an additional hurdle for spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms. Furthermore, lactic acid and other metabolic products contribute to the organoleptic and textural profile of a food item. The industrial importance of the LAB is further evidenced by their generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status, due to their ubiquitous appearance in food and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillus
''Lactobacillus'' is a genus of Gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus ''Lactobacillus'' comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically diverse species; a taxonomic revision of the genus assigned lactobacilli to 25 genera (see below). ''Lactobacillus'' species constitute a significant component of the human and animal microbiota at a number of body sites, such as the digestive system, and the female genital system. In women of European ancestry, ''Lactobacillus'' species are normally a major part of the vaginal microbiota. ''Lactobacillus'' forms biofilms in the vaginal and gut microbiota, allowing them to persist during harsh environmental conditions and maintain ample populations. ''Lactobacillus'' exhibits a mutualistic relationship with the human body, as it protects the host against potential invasions by pathogens, and in turn, the host provides a source of nutri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillaceae
The ''Lactobacillaceae'' are a family of lactic acid bacteria. It is the only family in the lactic acid bacteria which includes homofermentative and heterofermentative organisms; in the ''Lactobacillaceae,'' the pathway used for hexose fermentation is a genus-specific trait. ''Lactobacillaceae'' include the homofermentative lactobacilli ''Lactobacillus'', ''Holzapfelia'', ''Amylolactobacillus'', ''Bombilactobacillus'', ''Companilactobacillus'', ''Lapidilactobacillus'', ''Agrilactobacillus'', ''Schleiferilactobacillus'', ''Loigolactobacillus'', ''Lacticaseibacillus'', ''Latilactobacillus'', ''Dellaglioa'', ''Liquorilactobacillus'', ''Ligilactobacillus'', and ''Lactiplantibacillus''; the heterofermentative lactobacilli ''Furfurilactobacillus'', ''Paucilactobacillus'', ''Limosilactobacillus'', ''Fructilactobacillus'', ''Acetilactobacillus'', ''Apilactobacillus'', ''Levilactobacillus'', ''Secundilactobacillus'', and ''Lentilactobacillus,'' which were previously classified in the genus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leuconostoc
''Leuconostoc'' is a genus of gram-positive bacteria, placed within the family of Lactobacillaceae. They are generally ovoid cocci often forming chains. ''Leuconostoc'' spp. are intrinsically resistant to vancomycin and are catalase-negative (which distinguishes them from staphylococci). All species within this genus are heterofermentative and are able to produce dextran from sucrose. They are generally slime-forming. Blamed for causing the 'stink' when creating a sourdough starter, some species are also capable of causing human infection. Because they are an uncommon cause of disease in humans, standard commercial identification kits are often unable to identify the organism. ''Leuconostoc'' spp., along with other lactic acid bacteria such as '' Pediococcus'' and ''Lactobacillus'', are responsible for the fermentation of cabbage, making it sauerkraut. In this process, fresh cabbage is fermented in a light brine, where the sugars in the cabbage are transformed by lactofer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silage
Silage () is a type of fodder made from green foliage crops which have been preserved by fermentation to the point of acidification. It can be fed to cattle, sheep and other such ruminants ( cud-chewing animals). The fermentation and storage process is called ''ensilage'', ''ensiling'' or ''silaging''. Silage is usually made from grass crops, including maize, sorghum or other cereals, using the entire green plant (not just the grain). Silage can be made from many field crops, and special terms may be used depending on type: ''oatlage'' for oats, ''haylage'' for alfalfa (''haylage'' may also refer to high dry matter silage made from hay). Silage can be made using several methods, largely dependent on available technology, local tradition or prevailing climate. Production The crops most often used for ensilage are the ordinary grasses, clovers, alfalfa, vetches, oats, rye and maize. Many crops have ensilaging potential, including potatoes and various weeds, notably spu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauerkraut
Sauerkraut (; , "sour cabbage") is finely cut raw cabbage that has been fermented by various lactic acid bacteria. It has a long shelf life and a distinctive sour flavor, both of which result from the lactic acid formed when the bacteria ferment the sugars in the cabbage leaves.Gil MarksEncyclopedia of Jewish Food p. 1052.Joseph Mercola, Brian Vaszily, Kendra Pearsall, Nancy Lee BentleyDr. Mercola's Total Health Cookbook & Program p. 227. It is one of the best-known national dishes in Germany. Although in English-speaking countries it is known under its German name, it is also widely known in Eastern Europe and other places (see below). For example, in Russia, () 'sour cabbage' or () 'fermented cabbage' has been a traditional and ubiquitous dish from ancient times. Overview and history Fermented foods have a long history in many cultures, with sauerkraut being one of the most well-known instances of traditional fermented moist cabbage side dishes. The Roman writers C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |