|
Pavagadh
Pavagadh is a municipal operated region in Panchmahal district about away from Vadodara in Gujarat state in western India. It is known for a famous Mahakali temple which is one of the 51 Shaktipeeths and draws thousands of pilgrims every day. However, as per records, this was originally a Jain temple belonging to the Svetambara Achalgaccha sect, whose Adhistayika Mahakali's idol was installed here in the 12th century. This locality Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park was declared by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site in 2004. History Pavagadh was an Ancient Jain Pilgrimage. In 140 CE, Greek geographer Ptolemy during his tour to India stated that Pavagadh is very ancient & holy, which proves its antiquity. It is stated that Raja Gangasinh, a successor of Emperor Ashok got the fort & the temples of Pavagadh repaired. There have been several attempts to destroy the evidence of its Jain heritage. However, the court ordered against destruction of facts and heritage. The Jai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavagadh Hill
Pavagadh Hill is situated within a plain in Panchmahal district, Gujarat, western India. A volcanic eruption occurred in the region approximately 500 million years ago and the etymology of Pavagadh is associated with this eruption: ''Pav-gadh'' means "one fourth hill" or "fire-hill". At its base is the historical city of Champaner, while the hill station of Pavagadh was built upon the volcanic cone itself. With Champaner, Pavagadh hill forms the Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site which is spread over an area of more than . Known for its forts, there are also dozens of heritage structures on the hill. The site is east of Vadodara and south of Godhra. Faith based legend surrounding Pavagadh formation suggests that the right foot of Sati is believed to have fallen at Pavagadh, thus forming a deep valley and the God later on "sent a large hill as per the request of Rishi Vishwamitra to fill up this deep valley so that the sage's sacred cows do not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park
Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is located in Panchmahal district in Gujarat, India. It is located around the historical city of Champaner, a city which was founded by Vanraj Chavda, the most prominent king of the Chavda Dynasty, in the eighth century. He named it after the name of his friend and general Champa, also known later as Champaraj. The heritage site is studded with forts with bastions starting from the hills of Pavagadh, and extending into the city of Champaner. The park's landscape includes archaeological, historic and living cultural heritage monuments such as Chalcolithic sites, a hill fortress of an early Hindu capital, and remains of the 16th-century capital of the state of Gujarat. There are palaces, entrance gates and arches, mosques, tombs and temples, residential complexes, agricultural structures and water installations such as stepwells and tanks, dating from the eighth to the 14th centuries. The Kalika Mata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jain Temples, Pavagadh
Jain temples, Pavagadh is a group of seven Jain temples located in Pavagadh Hill in the state of Gujarat. These temples are part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site of Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park. Jain tradition Pavagadh hill is considered one of the four sacred regions where ''moksha'' can be attained. History This was a Jain pilgrimage. There were several attempts to destroy evidences of its Jain heritage. However, a court ordered against the destruction of facts and heritage. Its Jain history dates back to 3rd century BC. # King Samprati, in the 3rd century BC, constructed and installed the idol of Sambhavnatha which was consecrated by Svetambara Jain monk Acharya Suhastisuri. # In 1055 AD, Śvetāmbara monk Acharya Gunsagarsuri consecrated a new temple of Jirawala Parshvanath and reconstructed an ancient 52-shrine temple of Abhinandanswami. # In the 10th century AD, the Achalgacch of the Śvetāmbara sect of Jainism was established here by Acharya Aryar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalika Mata Temple, Pavagadh
Mahakali Mata Temple (or Mahakalimata; ) is a Hindu goddess temple complex and pilgrim centre at the summit of Pavagadh Hill in Panchmahal District, India, with in the Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park. Here, She is worshipped in the form of Durga or Chandi. In the temple, the Kali Yantra is worshipped which dates to 10th or 11th century. The temple has three images of goddesses: the central image is of Mahakali Mata, flanked by Kali on the right and Bahucharamata on the left. The idol of Mahakali originally belonged to the Achalgacch of Svetambara sect of Jains that was established on the hill in the 12th century, installing the Mahakali devi as the Adishtayika of the Achalgacch. Pavagadh was an ancient Jain pilgrimage centre. On Chitra sud 8, a fair is held at the temple which is attended by thousands of devotees. The temple is the site of one of the 51 Great holy Shakti Peethas. One can easily reach the temple by ropeway. Geography Kalika Mata Temple is situat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aryarakshitsuri
Aryarakshitsuri (c. 1080 CE1180 CE) was Śvetāmbara Jain monk and the founder of the Achal Gaccha of the Śvetāmbara sect of Jainism. He was a contemporary of Hemchandrasuri and is said to have met him. Early life He was born as Vayja Kumar to Dedi and Dron in the Pragwat community in a small village Dantani near Mount Abu, Rajasthan, India on 9th day of bright half of Shravan month in 1080 CE. He also had a younger brother named Solha. Initiation At the age of 6, on the 8th day of bright half of Vaishakh month in 1086 CE, Vayja Kumar was initiated as a Jain monk by Acharya Jaysinghsuri at Dantani, his birth place. He was named as Muni Vijayachandra by his preceptor Acharya Jaysinghsuri. After his initiation as a Jain monk, he studied Jain Aagams, Sanskrit and Prakrit grammar, poetries, law theories, prosody, lexicography, and philosophy under the guidance of his preceptor. He also learned different mantras, hymns, and other meditation techniques from Acharya Jays ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahakali
Mahakali () is the Hindu goddess of time and death in the goddess-centric tradition of Shaktism. She is also known as the supreme being in various tantras and Puranas. Similar to Kali, Mahakali is a fierce goddess associated with universal power, time, life, death, and both rebirth and liberation. She is the consort of Bhairava, the god of consciousness, the basis of reality and existence. Mahakali, in Sanskrit, is etymologically the feminised variant of Mahakala, or ''Great Time'' (which is also interpreted as ''Death''), Shiva in Hinduism. Meaning Mahakali's origin is found in various Puranic and Tantric Hindu scriptures (Shastras). In the texts of Shaktism, she is variously portrayed as the Adi-Shakti, the Primeval Force of the Universe, identical with the Ultimate Reality, or Brahman. She is also known as the (female) Prakriti or the world as opposed to the (male) Purusha or the consciousness, or as one of three manifestations of Mahadevi (The Great Goddess) that re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
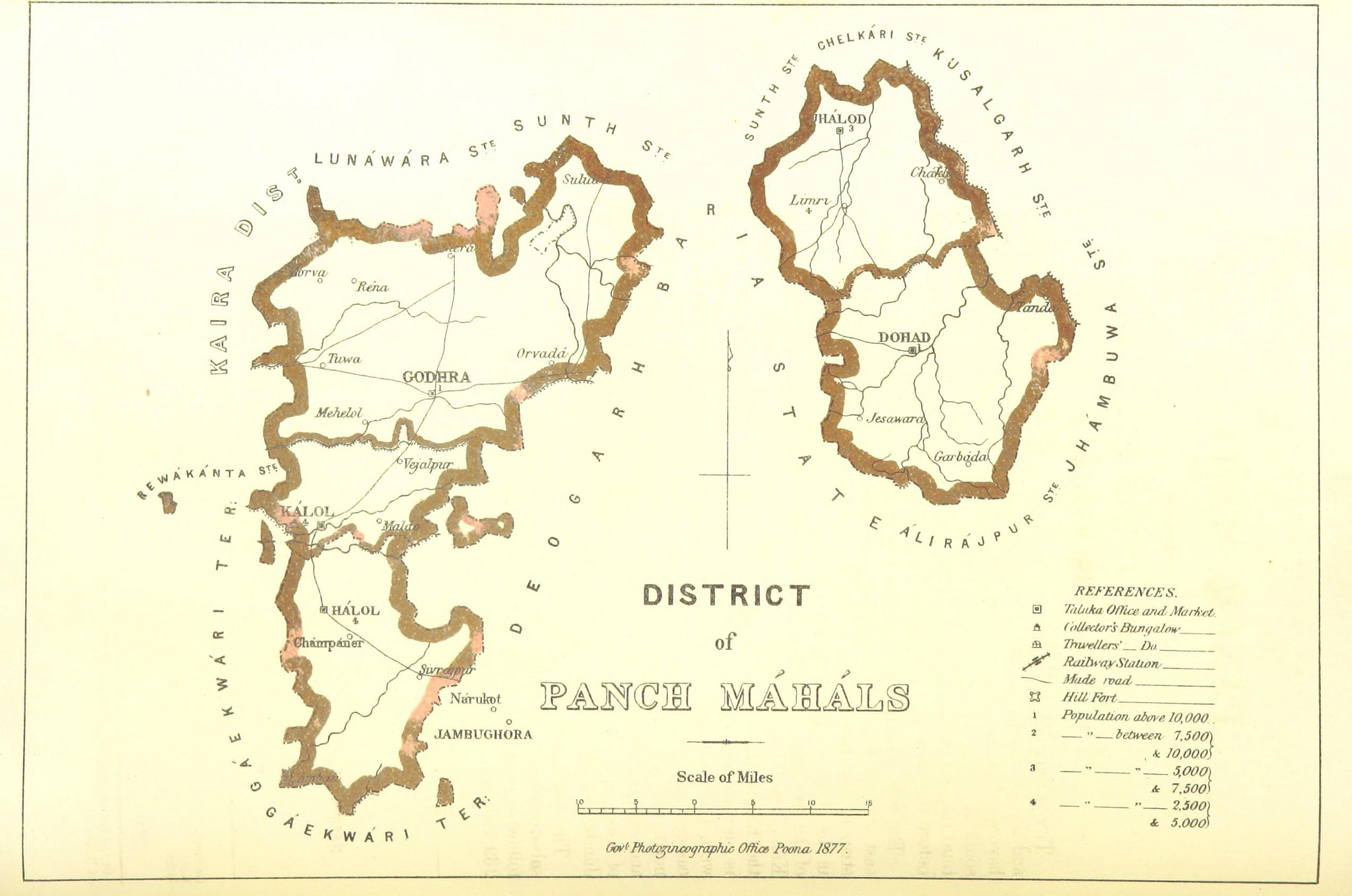
Panchmahal
Panchmahal, also rendered as Panch Mahal, is a district in the eastern portion of Gujarat State western India. ''Panch-mahal'' means "five tehsils/talukas" (5 sub-divisions), and refers to the five sub-divisions that were transferred by the Maharaja Jivajirao Scindia of Gwalior State to the British: Godhra, Dahod, Halol, Kalol and Jhalod, Devgadh Baria. The district had a population of 2,390,776 of which 12.51% were urban as of 2001. The district is located on the eastern end of the state. It is bordered by Dahod district to the north-east & east, Vadodara district to the southwest and Chhota Udaipur district to southeast, Kheda district to the west and Mahisagar district to the north. Name ''Panch-mahal'' is a Hindustani or Gujarati word derived from Panch ("five") and Mahal which adopted from its original usage in Arabic for a place or type of building, later adopted in Hindi to refer to a province, district or its division, an estate etc. The district was originall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achal Gaccha
Achal Gaccha, also known as the ''Vidhipakṣa'' or ''Anchal Gaccha'' () is one of the four existing Gacchas and one of the 84 ''gacchas'' of the Śvetāmbara Murtipujaka sect of Jainism. It was founded by Acharya Aryarakshitsuri in 1079 CE in response to the laxity that had crept into monasticism. Except for some minors differences, the rules and rituals of Achal Gaccha are similar to all the other existing ''gacchas'' of the Śvetāmbara Murtipujaka sect. Currently, Acharya Kalāprabhasāgarsuri is the ''gacchadhipati'' of Achal Gaccha who was declared as Gunodayasāgarsuri's successor after his demise in 2020. Acharya Kalāprabhasāgarsuri was formally coronated as the ''gacchadhipati'' of Achal Gaccha in 2022 in Mulund. History and origin Akin to the remaining three, Achal Gaccha traces its roots to the then ''Vada Gachha'' which was the unbroken lineage of monks, starting with one of Mahavira's 11 Ganadharas, Sudharmaswami. Initially, the name of Achal Gaccha was ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalyansagarsuri
Kalyansagarsuri ( – 1661 CE) was a 16th century Jain ascetic, reformer, philosopher, and researcher belonging to the Achal Gaccha of the Śvetāmbara Murtipujaka sect of Jainism. Early life Kodan Kumar was born to Naning (father) of Bhinmal, Shrimali clan and Namilde (mother) on the 2nd day of the bright half of Ashadha month in 1577 CE in the town of Lolada in Patan, Gujarat, Patan, Gujarat. The town is situated roughly 19 km away from Shankheshwar Jain Temple. Initiation With permission from his parents, at the age of 9 years, he was initiated as a Jainism, Jain monk on 4th day of the bright half of Phalguna, Falguna month in 1586 CE by Acharya Dharmamurtisuri of Achal Gaccha of the Śvetāmbara sect of Jainism in the town of Dholka, Gujarat and was renamed as Kalyansagar. Ascetic life Consecration as an ''Acharya'' After initiation, Kalyansagar began studying the Jain literature, Aagamas, law, poetry, grammar and other scholarly disciplines under his preceptor Dharmamurt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sallekhana
(IAST: ), also known as ''samlehna'', ''santhara'', ''samadhi-marana'' or ''sanyasana-marana'', is a supplementary vow to the ethical code of conduct of Jainism. It is the religious practice of voluntarily fasting to death by gradually reducing the intake of food and liquids. It is viewed in Jainism as the thinning of human passions and the body, and another means of destroying rebirth-influencing karma by withdrawing all physical and mental activities. It is not considered a suicide by Jain scholars because it is not an act of passion, nor does it employ poisons or weapons. After the ''sallekhana'' vow, the ritual preparation and practice can extend into years. is a vow available to both Jain ascetics and householders. Historic evidence such as ''nishidhi'' engravings suggest was observed by both men and women, including queens, in Jain history. However, in the modern era, death through ''sallekhana'' has been a relatively uncommon event. There is debate about the prac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yati
Yati, historically was the general term for a monk or pontiff in Jainism. Jainism In the late medieval period, yati came to represent a stationary monk, who lived in one place rather than wandering as required for a Jain monk. The term was more common for the Śvētāmbara monastics, but was also used by the Digambaras. The term has also been occasionally for ascetics from other traditions. Some scholars married and were termed ''sansari yati'' or mahātmās. Some ruling dynasties in Rajasthan had a close relationship with yatis. Abu'l-Fazl ibn Mubarak mentions that yatis were invited to participate in the discussion on religions. The stationary yatis often managed institutions and properties. Some of their residences are termed ''jatiji'' in their memory. With the re-establishment of orders of wandering (') monks since late 19th and early 20th century, the number of yatis have declined significantly. Shripujya The heads of the institutions of Śvetāmbara yatis were ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |