|
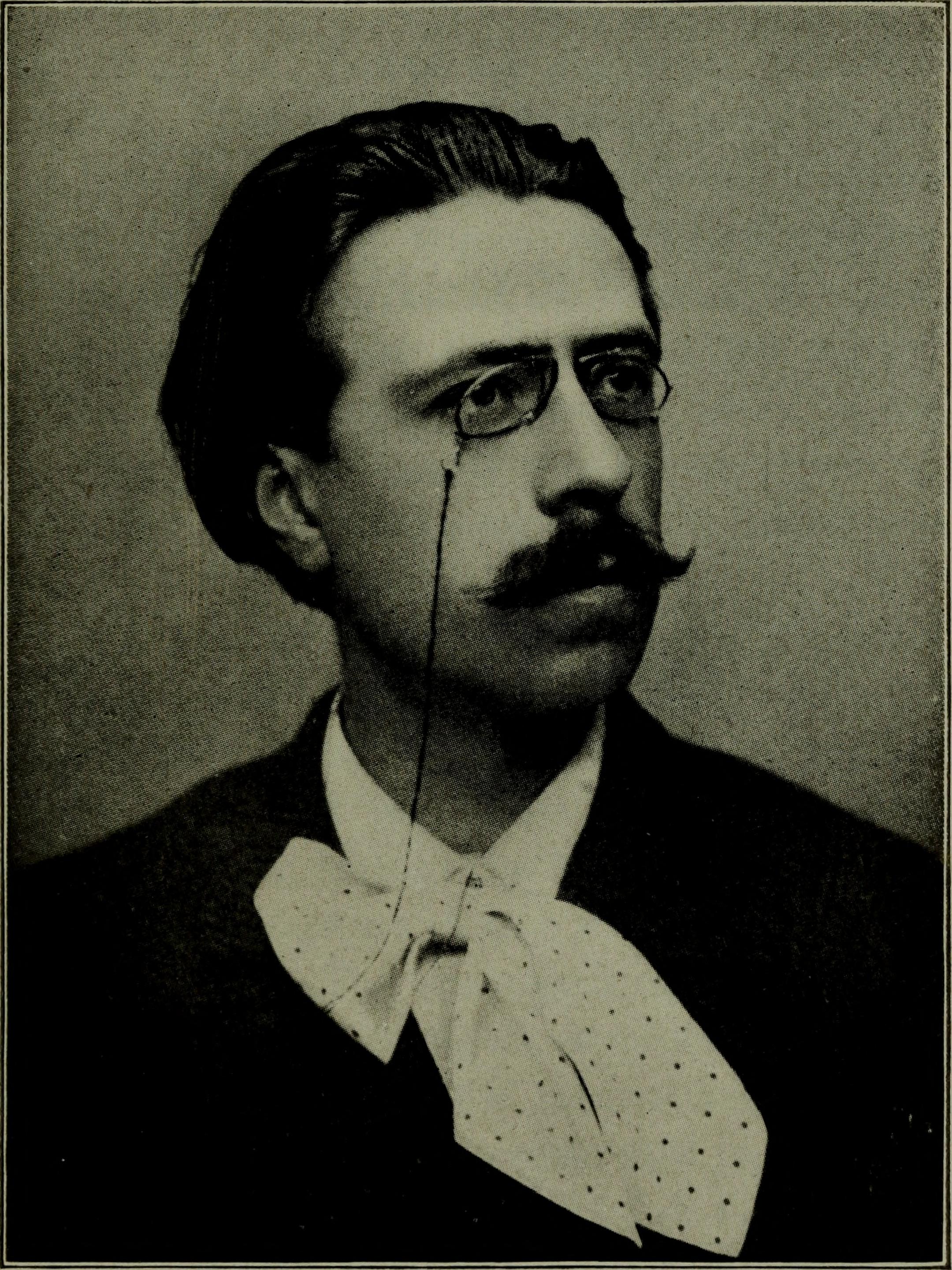
Paul Gilson
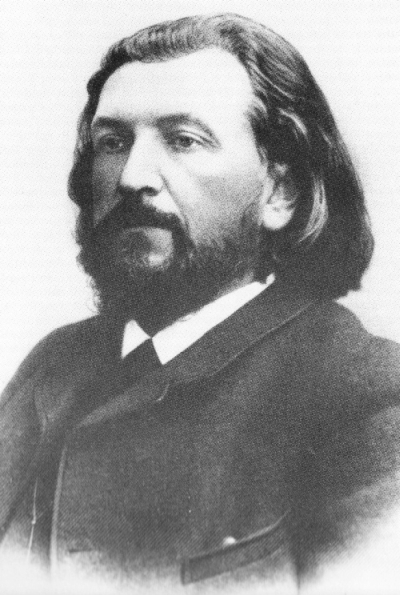
Paul Gilson (Brussels, 15 June 1865 – Brussels, 3 April 1942) was a Belgian musician and composer. Biography Paul Gilson was born in Brussels. In 1866, his family moved to Ruisbroek in the Belgian province of Brabant. There he studied theory with the organist and choir director Auguste Cantillon, and began writing works for orchestra and choir. His first official training came from 1887–1889 under François-Auguste Gevaert in composition and under Charles Duyck in harmony and counterpoint at the Brussels Conservatory, and in 1889, he was awarded the Belgian ''Prix de Rome'' for a cantata, ''Sinaï'', which was very well received. As the winner of the prize he was able to spend time in Bayreuth (1892), Paris (1893–4) and Italy (1895). A large orchestral work, ''La mer'', which was first performed in Brussels on 20 March 1892, established Gilson as a national musical figure and also gave him success abroad, though not in Paris. In 1899 he became professor of comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Gilson
Paul Gilson (Brussels, 15 June 1865 – Brussels, 3 April 1942) was a Belgian musician and composer. Biography Paul Gilson was born in Brussels. In 1866, his family moved to Ruisbroek in the Belgian province of Brabant. There he studied theory with the organist and choir director Auguste Cantillon, and began writing works for orchestra and choir. His first official training came from 1887–1889 under François-Auguste Gevaert in composition and under Charles Duyck in harmony and counterpoint at the Brussels Conservatory, and in 1889, he was awarded the Belgian ''Prix de Rome'' for a cantata, ''Sinaï'', which was very well received. As the winner of the prize he was able to spend time in Bayreuth (1892), Paris (1893–4) and Italy (1895). A large orchestral work, ''La mer'', which was first performed in Brussels on 20 March 1892, established Gilson as a national musical figure and also gave him success abroad, though not in Paris. In 1899 he became professor of comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Théo De Joncker
Théo De Joncker (11 April 1894, in Brussels – 12 July 1964, in Asse) was a Belgian composer. Biography Théo De Joncker was a student of August de Boeck and Paul Gilson. For years he conducted the orchestra of the Belgian National Radio (NIR), but he also enjoyed a conducting career outside of Belgium. As a composer, he belonged to the Brussels group ''Les Synthétistes''. This group was found by students of Paul Gilson as a way to celebrate their teacher's 60th birthday and included Francis de Bourguignon, Théo De Joncker, Marcel Poot, Maurice Schoemaker, Jules Strens, René Bernier, and Robert Otlet. Compositions Orchestral works * 1917 ''Filosofische gedachten van een draaiorgelspeler'' for orchestra * 1918 ''Hedda Gabler'' for orchestra * 1927 ''Breugeliaansche schets'' for orchestra * 1939 ''Sinfonia burlesca'' for orchestra * 1939 ''Sinfonie im klassischen Stil'' for orchestra * 1943 ''Symfonie nr.3'' for orchestra * 1944 ''Muzikaal portret van Bernard Shaw'' for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breitkopf & Härtel
Breitkopf & Härtel is the world's oldest music publishing house. The firm was founded in 1719 in Leipzig by Bernhard Christoph Breitkopf. The catalogue currently contains over 1,000 composers, 8,000 works and 15,000 music editions or books on music. The name "Härtel" was added when Gottfried Christoph Härtel took over the company in 1795. In 1807, Härtel began to manufacture pianos, an endeavour which lasted until 1870. The Breitkopf pianos were highly esteemed in the 19th century by pianists like Franz Liszt and Clara Schumann. In the 19th century the company was for many years the publisher of the ''Allgemeine musikalische Zeitung'', an influential music journal. The company has consistently supported contemporary composers and had close editorial collaboration with Beethoven, Haydn, Mendelssohn, Schumann, Chopin, Liszt, Wagner and Brahms. In the 19th century they also published the first "complete works" editions of various composers, for instance Bach (the Bach-Gesells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Mer (Debussy)
''La mer, trois esquisses symphoniques pour orchestre'' (French for ''The sea, three symphonic sketches for orchestra''), or simply ''La mer'' (''The Sea''), List of compositions by Claude Debussy by Lesure number, L. 109, CD. 111, is an orchestral composition by the French composer Claude Debussy. Composed between 1903 and 1905, the piece was premiered in Paris in October 1905. It was initially not well received. Even some who had been strong supporters of Debussy's work were unenthusiastic, even though ''La mer'' presented three key aspects of Debussy's aesthetic: Impressionism in music, Impressionism, Symbolism in music, Symbolism and Japonisme, Japonism. The work was performed in the US in 1907 and Britain in 1908; after its second performance in Paris, in 1908, it quickly became one of Debussy's most admired and frequently performed orchestral works. The first audio recording of the work was made in 1928. Since then, orchestras and conductors from around the world have set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonata Form
Sonata form (also ''sonata-allegro form'' or ''first movement form'') is a musical form, musical structure generally consisting of three main sections: an exposition, a development, and a recapitulation. It has been used widely since the middle of the 18th century (the early Classical music era, Classical period). While it is typically used in the first Movement (music), movement of multi-movement pieces, it is sometimes used in subsequent movements as well—particularly the final movement. The teaching of sonata form in music theory rests on a standard definition and a series of hypotheses about the underlying reasons for the durability and variety of the form—a definition that arose in the second quarter of the 19th century. There is little disagreement that on the largest level, the form consists of three main sections: an exposition, a development, and a recapitulation; however, beneath this general structure, sonata form is difficult to pin down to a single model. The st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impressionism In Music
Impressionism in music was a movement among various composers in Western classical music (mainly during the late 19th and early 20th centuries) whose music focuses on mood and atmosphere, "conveying the moods and emotions aroused by the subject rather than a detailed tone‐picture". "Impressionism" is a philosophical and aesthetic term borrowed from late 19th-century French painting after Monet's ''Impression, Sunrise''. Composers were labeled Impressionists by analogy to the Impressionist painters who use starkly contrasting colors, effect of light on an object, blurry foreground and background, flattening perspective, etc. to make the observer focus their attention on the overall impression.J. Peter Burkholder, Donald Jay Grout and Claude V. Palisca, ''A History of Western Music'', eighth edition (New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 2010). . The most prominent feature in musical Impressionism is the use of "color", or in musical terms, timbre, which can be achieved through or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Wagner
Wilhelm Richard Wagner ( ; ; 22 May 181313 February 1883) was a German composer, theatre director, polemicist, and conductor who is chiefly known for his operas (or, as some of his mature works were later known, "music dramas"). Unlike most opera composers, Wagner wrote both the libretto and the music for each of his stage works. Initially establishing his reputation as a composer of works in the romantic vein of Carl Maria von Weber and Giacomo Meyerbeer, Wagner revolutionised opera through his concept of the ''Gesamtkunstwerk'' ("total work of art"), by which he sought to synthesise the poetic, visual, musical and dramatic arts, with music subsidiary to drama. He described this vision in a series of essays published between 1849 and 1852. Wagner realised these ideas most fully in the first half of the four-opera cycle ''Der Ring des Nibelungen'' (''The Ring of the Nibelung''). His compositions, particularly those of his later period, are notable for their complex textures, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Leopold (Belgium)
The Order of Leopold ( nl, Leopoldsorde, french: Ordre de Léopold, ) is one of the three current Belgian national honorary orders of knighthood. It is the oldest and highest order of Belgium and is named in honour of its founder, King Leopold I. It consists of a military, a maritime and a civil division. The maritime division is only awarded to personnel of the merchant navy, and the military division to military personnel. The decoration was established on 11 July 1832 and is awarded by Royal order. History When Belgium became independent of the Netherlands, there was an urgent need to create a national honour system that could serve as a diplomatic gift. The national congress provided this exclusive right to the sovereign, this military honour system was written in Article 76. The first King of the Belgians, Leopold I of Belgium, used his constitutional right in a larger way than foreseen: not only military merit, but every service in honour of the Kingdom. Two years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitrofan Belyayev
Mitrofan Petrovich Belyayev (russian: Митрофа́н Петро́вич Беля́ев; old style 10/22 February 1836, St. Petersburg22 December 1903/ 4 January 1904) was an Imperial Russian music publisher, outstanding philanthropist, and the owner of a large wood dealership enterprise in Russia. He was also the founder of the Belyayev circle, a society of musicians in Russia whose members included Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov, Alexander Glazunov and Anatoly Lyadov. His surname is often transliterated as ''Belaieff'' or ''Belayev''. In 1886 the Russian painter Ilya Repin made a portrait of Belyayev. Biography Belyayev was the son of a rich Russian wood dealer and large land owner. Early on, he was established as a successful buyer in his father's company, whose line he took over after 30 years. His passion, at first private, was however for music. Belyayev had learned and played violin, viola and piano when in school, and played viola for many years in a string quartet. L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
César Cui
César Antonovich Cui ( rus, Це́зарь Анто́нович Кюи́, , ˈt͡sjezərʲ ɐnˈtonəvʲɪt͡ɕ kʲʊˈi, links=no, Ru-Tsezar-Antonovich-Kyui.ogg; french: Cesarius Benjaminus Cui, links=no, italic=no; 13 March 1918) was a Russian composer and music critic, member of the Belyayev circle and The Five – a group of composers combined by the idea of creating a specifically Russian type of music. As an officer of the Imperial Russian Army he rose to the rank of Engineer-General (equivalent to full General), taught fortifications in Russian military academies and wrote a number of monographs on the subject. Biography Upbringing and career Cesarius-Benjaminus Cui was born in Wilno, Vilna Governorate of the Russian Empire (now Vilnius, Lithuania) into a Roman Catholic family of French and Polish– Lithuanian descent, the youngest of five children. The original French spelling of his surname was "Queuille". His French father, Antoine (Anton Leonardovic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and shares Borders of Russia, land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than List of countries and territories by land borders, any other country but China. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, world's ninth-most populous country and List of European countries by population, Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city is Moscow, the List of European cities by population within city limits, largest city entirely within E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Otlet
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English, German, Dutch, Norwegian, Swedish, Scots, Danish, and Icelandic. It can be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |