|
Impressionism In Music
Impressionism in music was a movement among various composers in Western classical music (mainly during the late 19th and early 20th centuries) whose music focuses on mood and atmosphere, "conveying the moods and emotions aroused by the subject rather than a detailed tone‐picture". "Impressionism" is a philosophical and aesthetic term borrowed from late 19th-century French painting after Monet's '' Impression, Sunrise''. Composers were labeled Impressionists by analogy to the Impressionist painters who use starkly contrasting colors, effect of light on an object, blurry foreground and background, flattening perspective, etc. to make the observer focus their attention on the overall impression.J. Peter Burkholder, Donald Jay Grout and Claude V. Palisca, ''A History of Western Music'', eighth edition (New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 2010). . The most prominent feature in musical Impressionism is the use of "color", or in musical terms, timbre, which can be achieved through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expressionist Music
The term expressionism "was probably first applied to music in 1918, especially to Schoenberg", because like the painter Wassily Kandinsky (1866–1944) he avoided "traditional forms of beauty" to convey powerful feelings in his music. Theodor Adorno interprets the expressionist movement in music as seeking to "eliminate all of traditional music's conventional elements, everything formulaically rigid". This he sees as analogous "to the literary ideal of the 'scream' ". As well Adorno sees expressionist music as seeking "the truthfulness of subjective feeling without illusions, disguises or euphemisms". Adorno also describes it as concerned with the unconscious, and states that "the depiction of fear lies at the centre" of expressionist music, with dissonance predominating, so that the "harmonious, affirmative element of art is banished". Expressionist music would "thus reject the depictive, sensual qualities that had come to be associated with impressionist music. It would endeavo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arbie Orenstein
Arbie Orenstein (born 1937) is an American musicologist, author, academic and pianist, known as a scholar of the life and works of the composer Maurice Ravel and, more generally, as an expert on Jewish music. Life and career Orenstein was born in New York and was educated at the High School of Music and Art, Queens College, and Columbia University, receiving a doctorate in musicology."Arbie Orenstein" , retrieved 2 April 2015 He is known as a scholar, and his books include ''The Vocal Works of Maurice Ravel'' (19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Scriabin
Alexander Nikolayevich Scriabin (; russian: Александр Николаевич Скрябин ; – ) was a Russian composer and virtuoso pianist. Before 1903, Scriabin was greatly influenced by the music of Frédéric Chopin and composed in a relatively tonal, late Romantic idiom. Later, and independently of his influential contemporary, Arnold Schoenberg, Scriabin developed a much more dissonant musical language that had transcended usual tonality but was not atonal, which accorded with his personal brand of metaphysics. Scriabin found significant appeal in the concept of Gesamtkunstwerk as well as synesthesia, and associated colours with the various harmonic tones of his scale, while his colour-coded circle of fifths was also inspired by theosophy. He is often considered the main Russian Symbolist composer and a major representative of the Russian Silver Age. Scriabin was an innovator as well as one of the most controversial composer-pianists of the early 20th centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Dukas
Paul Abraham Dukas ( or ; 1 October 1865 – 17 May 1935) was a French composer, critic, scholar and teacher. A studious man of retiring personality, he was intensely self-critical, having abandoned and destroyed many of his compositions. His best-known work is the orchestral piece ''The Sorcerer's Apprentice'' (''L'apprenti sorcier''), the fame of which has eclipsed that of his other surviving works. Among these are the opera '' Ariane et Barbe-bleue'', his Symphony in C and Piano Sonata in E-flat minor, the '' Variations, Interlude and Finale on a Theme by Rameau'' (for solo piano), and a ballet, '' La Péri''. At a time when French musicians were divided into conservative and progressive factions, Dukas adhered to neither but retained the admiration of both. His compositions were influenced by composers including Beethoven, Berlioz, Franck, d'Indy and Debussy. In tandem with his composing career, Dukas worked as a music critic, contributing regular reviews to at le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Delius
file:Fritz Delius (1907).jpg, Delius, photographed in 1907 Frederick Theodore Albert Delius ( 29 January 1862 – 10 June 1934), originally Fritz Delius, was an English composer. Born in Bradford in the north of England to a prosperous mercantile family, he resisted attempts to recruit him to commerce. He was sent to Florida in the United States in 1884 to manage an orange plantation. He soon neglected his managerial duties and in 1886 returned to Europe. Having been influenced by African-American music during his short stay in Florida, he began composing. After a brief period of formal musical study in Germany beginning in 1886, he embarked on a full-time career as a composer in Paris and then in nearby Grez-sur-Loing, where he and his wife Jelka Rosen, Jelka lived for the rest of their lives, except during the First World War. Delius's first successes came in Germany, where Hans Haym and other conductors promoted his music from the late 1890s. In Delius's native Britain, hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Albéniz
Isaac Manuel Francisco Albéniz y Pascual (; 29 May 1860 – 18 May 1909) was a Spanish virtuoso pianist, composer, and conductor. He is one of the foremost composers of the Post-Romantic era who also had a significant influence on his contemporaries and younger composers. He is best known for his piano works based on Spanish folk music idioms. Isaac Albéniz was close to the Generation of '98. Transcriptions of many of his pieces, such as '' Asturias (Leyenda)'', ''Granada'', ''Sevilla'', '' Cadiz'', ''Córdoba'', ''Cataluña'', ''Mallorca'', and Tango in D, are important pieces for classical guitar, though he never composed for the guitar. The personal papers of Albéniz are preserved in, among other institutions, the Library of Catalonia. Life Born in Camprodon, province of Girona, to Ángel Albéniz (a customs official) and his wife, Maria de los Dolores Pascual, Albéniz was a child prodigy who first performed at the age of four. At age seven, after apparently t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lili Boulanger
Marie Juliette "Lili" Boulanger (; 21 August 189315 March 1918) was a French composer and the first female winner of the Prix de Rome composition prize. Her older sister was the noted composer and composition teacher Nadia Boulanger. Biography Early years As a Parisian-born child prodigy, Boulanger's talent was apparent at the age of two, when Gabriel Fauré, a friend of the family, discovered she had perfect pitch. Her parents, both of whom were musicians, encouraged their daughter's musical education. Her mother, Raissa Myshetskaya (Mischetzky), was a Russian princess who married her Paris Conservatoire teacher, Ernest Boulanger (1815–1900), who won the Prix de Rome in 1835. Her father was 77 years old when she was born and she became very attached to him. Her grandfather Frédéric Boulanger had been a noted cellist and her grandmother Juliette a singer. Boulanger accompanied her ten-year-old sister Nadia to classes at the Paris Conservatoire before she was five, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hector Berlioz
In Greek mythology, Hector (; grc, Ἕκτωρ, Hektōr, label=none, ) is a character in Homer's Iliad. He was a Trojan prince and the greatest warrior for Troy during the Trojan War. Hector led the Trojans and their allies in the defense of Troy, killing countless Greek warriors. He was ultimately killed in single combat by Achilles, who later dragged his dead body around the city of Troy behind his chariot. Etymology In Greek, is a derivative of the verb ἔχειν ''ékhein'', archaic form * grc, ἕχειν, hékhein, label=none ('to have' or 'to hold'), from Proto-Indo-European *'' seɡ́ʰ-'' ('to hold'). , or as found in Aeolic poetry, is also an epithet of Zeus in his capacity as 'he who holds verything together. Hector's name could thus be taken to mean 'holding fast'. Description Hector was described by the chronicler Malalas in his account of the ''Chronography'' as "dark-skinned, tall, very stoutly built, strong, good nose, wooly-haired, good beard, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Liszt
Franz Liszt, in modern usage ''Liszt Ferenc'' . Liszt's Hungarian passport spelled his given name as "Ferencz". An orthographic reform of the Hungarian language in 1922 (which was 36 years after Liszt's death) changed the letter "cz" to simply "c" in all words except surnames; this has led to Liszt's given name being rendered in modern Hungarian usage as "Ferenc". From 1859 to 1867 he was officially Franz Ritter von Liszt; he was created a ''Ritter'' (knight) by Emperor Francis Joseph I in 1859, but never used this title of nobility in public. The title was necessary to marry the Princess Carolyne zu Sayn-Wittgenstein without her losing her privileges, but after the marriage fell through, Liszt transferred the title to his uncle Eduard in 1867. Eduard's son was Franz von Liszt., group=n (22 October 1811 – 31 July 1886) was a Hungarian composer, pianist and teacher of the Romantic period. With a diverse body of work spanning more than six decades, he is considered to be o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
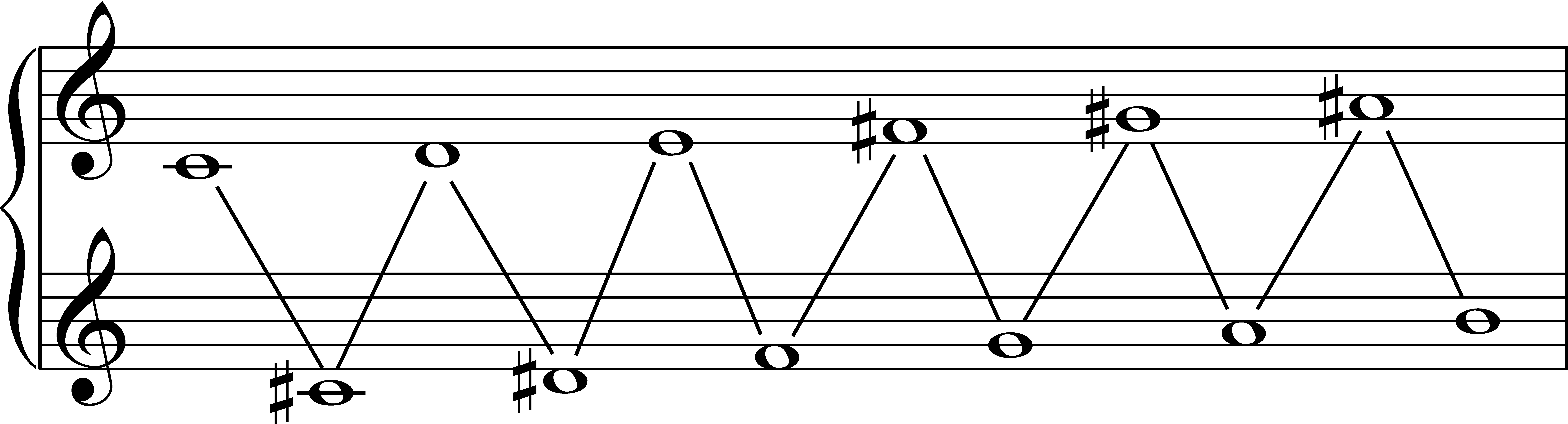
Whole-tone Scale
In music, a whole-tone scale is a scale in which each note is separated from its neighbors by the interval of a whole tone. In twelve-tone equal temperament, there are only two complementary whole-tone scales, both six-note or '' hexatonic'' scales. A single whole-tone scale can also be thought of as a "six-tone equal temperament". : : The whole-tone scale has no leading tone and because all tones are the same distance apart, "no single tone stands out, ndthe scale creates a blurred, indistinct effect". This effect is especially emphasised by the fact that triads built on such scale tones are all augmented triads. Indeed, all six tones of a whole-tone scale can be played simply with two augmented triads whose roots are a major second apart. Since they are symmetrical, whole-tone scales do not give a strong impression of the tonic or tonality. The composer Olivier Messiaen called the whole-tone scale his first mode of limited transposition. The composer and music t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended Chord
In music, extended chords are certain chords (built from thirds) or triads with notes ''extended'', or added, beyond the seventh. Ninth, eleventh, and thirteenth chords are extended chords. The thirteenth is the farthest extension diatonically possible as, by that point, all seven tonal degrees are represented within the chord (the next extension, the fifteenth, is the same as the root of the chord). In practice however, extended chords do not typically use all the chord members; when it is not altered, the fifth is often omitted, as are notes between the seventh and the highest note (i.e., the ninth is often omitted in an eleventh chord; the ninth and eleventh are usually omitted in a thirteenth chord), unless they are altered to give a special texture. Chords extended beyond the seventh are rarely seen in the Baroque era, and are used more frequently in the Classical era. The Romantic era saw greatly increased use of extended harmony. Extended harmony prior to the 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symphonic Poem
A symphonic poem or tone poem is a piece of orchestral music, usually in a single continuous movement, which illustrates or evokes the content of a poem, short story, novel, painting, landscape, or other (non-musical) source. The German term ''Tondichtung (tone poem)'' appears to have been first used by the composer Carl Loewe in 1828. The Hungarian composer Franz Liszt first applied the term ''Symphonische Dichtung'' to his 13 works in this vein. While many symphonic poems may compare in size and scale to symphonic movements (or even reach the length of an entire symphony), they are unlike traditional classical symphonic movements, in that their music is intended to inspire listeners to imagine or consider scenes, images, specific ideas or moods, and not (necessarily) to focus on following traditional patterns of musical form such as sonata form. This intention to inspire listeners was a direct consequence of Romanticism, which encouraged literary, pictorial and dramati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |