|
Palmatine
Palmatine is a protoberberine alkaloid found in several plants including ''Phellodendron amurense'', ''Coptis Chinensis'' (Rhizoma coptidis, chinese goldthread) and '' Corydalis yanhusuo'', ''Tinospora cordifolia'' (gurjo, heart-leaved moonseed), ''Tinospora sagittata'', ''Phellodendron amurense'' (amur cork tree), '' Stephania yunnanensis.'' It is the major component of the protoberberine extract from ''Enantia chlorantha''. It has been studied for its potential use in the treatment of jaundice, dysentery, hypertension, inflammation, and liver-related diseases. This compound also has weak ''in vitro'' activity against flavivirus. Pharmacology Neuroprotective activity Palmatine can be used to treat Alzheimer’s disease, mainly by inhibiting the activity of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) and neuraminidase-1 (NA-1). It was found, that the positively charged nitrogen on palmatine binds in the gorge of active sire of AChE. Research show that palma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phellodendrine
Phellodendrine is an alkaloid isolated originally from ''Phellodendron amurense'' (Rutaceae). See also * Berberine * Jatrorrhizine * Palmatine Palmatine is a protoberberine alkaloid found in several plants including ''Phellodendron amurense'', ''Coptis Chinensis'' (Rhizoma coptidis, chinese goldthread) and '' Corydalis yanhusuo'', ''Tinospora cordifolia'' (gurjo, heart-leaved moonseed), ... References Benzylisoquinoline alkaloids Quaternary ammonium compounds Phenol ethers Isoquinolinoisoquinolines Phenols {{alkaloid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.Chemical Encyclopedia: alkaloids xumuk.ru Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms including , , Medicinal plant, plants, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out necrotic cells and tissues damaged from the original insult and the inflammatory process, and initiate tissue repair. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and Functio laesa, loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore it is considered as a mechanism of innate immune system, innate immunity, as compared to adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity, which is specific for each pathogen. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary Ammonium Compounds
In chemistry, quaternary ammonium cations, also known as quats, are positively charged polyatomic ions of the structure , R being an alkyl group or an aryl group. Unlike the ammonium ion () and the primary, secondary, or tertiary ammonium cations, the quaternary ammonium cations are permanently charged, independent of the pH of their solution. Quaternary ammonium salts or quaternary ammonium compounds (called quaternary amines in oilfield parlance) are salts of quaternary ammonium cations. Polyquats are a variety of engineered polymer forms which provide multiple quat molecules within a larger molecule. Quats are used in consumer applications including as antimicrobials (such as detergents and disinfectants), fabric softeners, and hair conditioners. As an antimicrobial, they are able to inactivate enveloped viruses (such as SARS-CoV-2). Quats tend to be gentler on surfaces than bleach-based disinfectants, and are generally fabric-safe. Synthesis Quaternary ammonium compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoquinoline Alkaloids
Isoquinoline alkaloids are natural products of the group of alkaloids, which are chemically derived from isoquinoline. They form the largest group among the alkaloids. Isoquinoline alkaloids can be further classified based on their different chemical basic structures. The most common structural types are the benzylisoquinolines and the aporphines.Bettina Ruff: ''Chemische und biochemische Methoden zur stereoselektiven Synthese von komplexen Naturstoffen.'' Verlag Logos, Berlin 2012, , S. 8. () According to current knowledge, a total of about 2500 isoquinoline alkaloids are known nowadays, which are mainly formed by plants.Jennifer M. Finefield, David H. Sherman, Martin Kreitman, Robert M. Williams: ''Enantiomere Naturstoffe: Vorkommen und Biogenese.'' In: ''Angewandte Chemie.'' Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2012, doi:10.1002/ange.201107204, S. 4905–4915. Known examples Morphin - Morphine.svg, Morphine Codein - Codeine.svg, Codeine Papaverin - Papaverine.svg, Papaverine Berbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jatrorrhizine
Jatrorrhizine is a protoberberine alkaloid found in some plant species, such as '' Enantia chlorantha'' (Annonaceae). Synonyms that may be encountered include jateorrhizine, neprotin, jatrochizine, jatrorhizine, and yatrorizine. Bioactive effects Jatrorrhizine has been reported to have antiinflammatory effect, and to improve blood flow and mitotic activity in thioacetamide-traumatized rat livers. It was found to have antimicrobial and antifungal activity. It binds and noncompetitively inhibits monoamine oxidase (IC50 = 4 μM for MAO-A and 62 μM for MAO-B) It interferes with multidrug resistance Multiple drug resistance (MDR), multidrug resistance or multiresistance is antimicrobial resistance shown by a species of microorganism to at least one antimicrobial drug in three or more antimicrobial categories. Antimicrobial categories are c ... by cancer cells ''in vitro'' when exposed to a chemotherapeutic agent. Large doses (50–100 mg/kg) reduced blood sugar levels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berberine
Berberine is a quaternary ammonium salt from the protoberberine group of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids found in such plants as ''Berberis vulgaris'' (barberry), ''Berberis aristata'' (tree turmeric), ''Mahonia aquifolium'' (Oregon grape), ''Hydrastis canadensis'' (goldenseal), ''Xanthorhiza simplicissima'' (yellowroot), ''Phellodendron amurense'' (Amur cork tree), ''Coptis chinensis'' (Chinese goldthread), ''Tinospora cordifolia'', ''Argemone mexicana'' (prickly poppy), and ''Eschscholzia californica'' (Californian poppy). Berberine is usually found in the roots, rhizomes, stems, and bark. Due to its yellow color, ''Berberis'' species were used to dye wool, leather, and wood. Under ultraviolet light, berberine shows a strong yellow fluorescence, making it useful in histology for staining heparin in mast cells. As a natural dye, berberine has a color index of 75160. Research and adverse effects The safety of using berberine for any condition is not adequately defined by high-qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
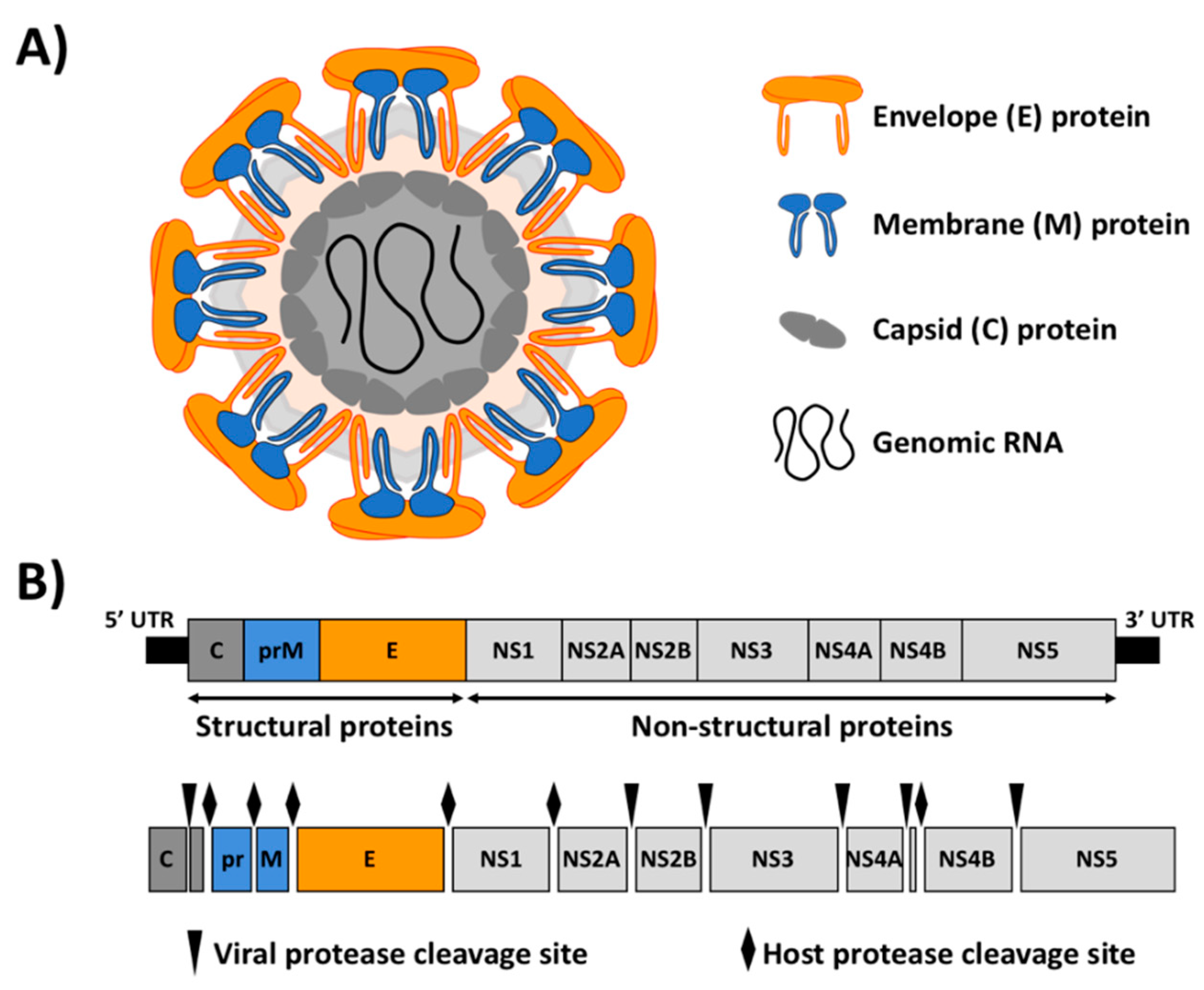
Flavivirus
''Flavivirus'' is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family ''Flaviviridae''. The genus includes the West Nile virus, dengue virus, tick-borne encephalitis virus, yellow fever virus, Zika virus and several other viruses which may cause encephalitis, as well as insect-specific flaviviruses (ISFs) such as cell fusing agent virus (CFAV), Palm Creek virus (PCV), and Parramatta River virus (PaRV). While dual-host flaviviruses can infect vertebrates as well as arthropods, insect-specific flaviviruses are restricted to their competent arthropods. The means by which flaviviruses establish persistent infection in their competent vectors and cause disease in humans depends upon several virus-host interactions, including the intricate interplay between flavivirus-encoded immune antagonists and the host antiviral innate immune effector molecules. Flaviviruses are named for the yellow fever virus; the word ''flavus'' means 'yellow' in Latin, and yellow fever in turn is named from i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from ''in vitro'' experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to ''in vitro'' experiments, ''in vivo'' studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, and whole plants. Definition ''In vitro'' ( la, in glass; often not italicized in English usage) studies are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high blood pressure, however, is a major risk factor for stroke, coronary artery disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, peripheral arterial disease, vision loss, chronic kidney disease, and dementia. Hypertension is a major cause of premature death worldwide. High blood pressure is classified as primary (essential) hypertension or secondary hypertension. About 90–95% of cases are primary, defined as high blood pressure due to nonspecific lifestyle and genetic factors. Lifestyle factors that increase the risk include excess salt in the diet, excess body weight, smoking, and alcohol use. The remaining 5–10% of cases are categorized as secondary high blood pressure, defined as high blood pressure due to an identifiable cause, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phellodendron Amurense
''Phellodendron amurense'' is a species of tree in the family Rutaceae, commonly called the Amur cork tree. It is a major source of '' huáng bò'' ( or 黄 檗), one of the 50 fundamental herbs used in traditional Chinese medicine. The Ainu people used this plant, called shikerebe-ni, as a painkiller. It is known as ''hwangbyeok'' in Korean and (キハダ) ''kihada'' in Japanese. It is native to eastern Asia: northern China, northeast China, Korea, Ussuri, Amur, and Japan, the Amur cork tree is considered invasive in many parts of North America. The State of Massachusetts lists it as a noxious weed.Bruce Marlin''Phellodendron amurense''/ref> Medicinal use It has been used as a Chinese traditional medicine for the treatment of meningitis, bacillary dysentery, pneumonia, tuberculosis, tumours, jaundice and liver cirrhosis. Used orally to treat abdominal pain, diarrhoea, gastroenteritis and urinary tract infections. ''Phellodendron amurense'' may protect cartilage against os ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysentery
Dysentery (UK pronunciation: , US: ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complications may include dehydration. The cause of dysentery is usually the bacteria from genus ''Shigella'', in which case it is known as shigellosis, or the amoeba ''Entamoeba histolytica''; then it is called amoebiasis. Other causes may include certain chemicals, other bacteria, other protozoa, or parasitic worms. It may spread between people. Risk factors include contamination of food and water with feces due to poor sanitation. The underlying mechanism involves inflammation of the intestine, especially of the colon. Efforts to prevent dysentery include hand washing and food safety measures while traveling in areas of high risk. While the condition generally resolves on its own within a week, drinking sufficient fluids such as oral rehydration s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |