|
Paemani
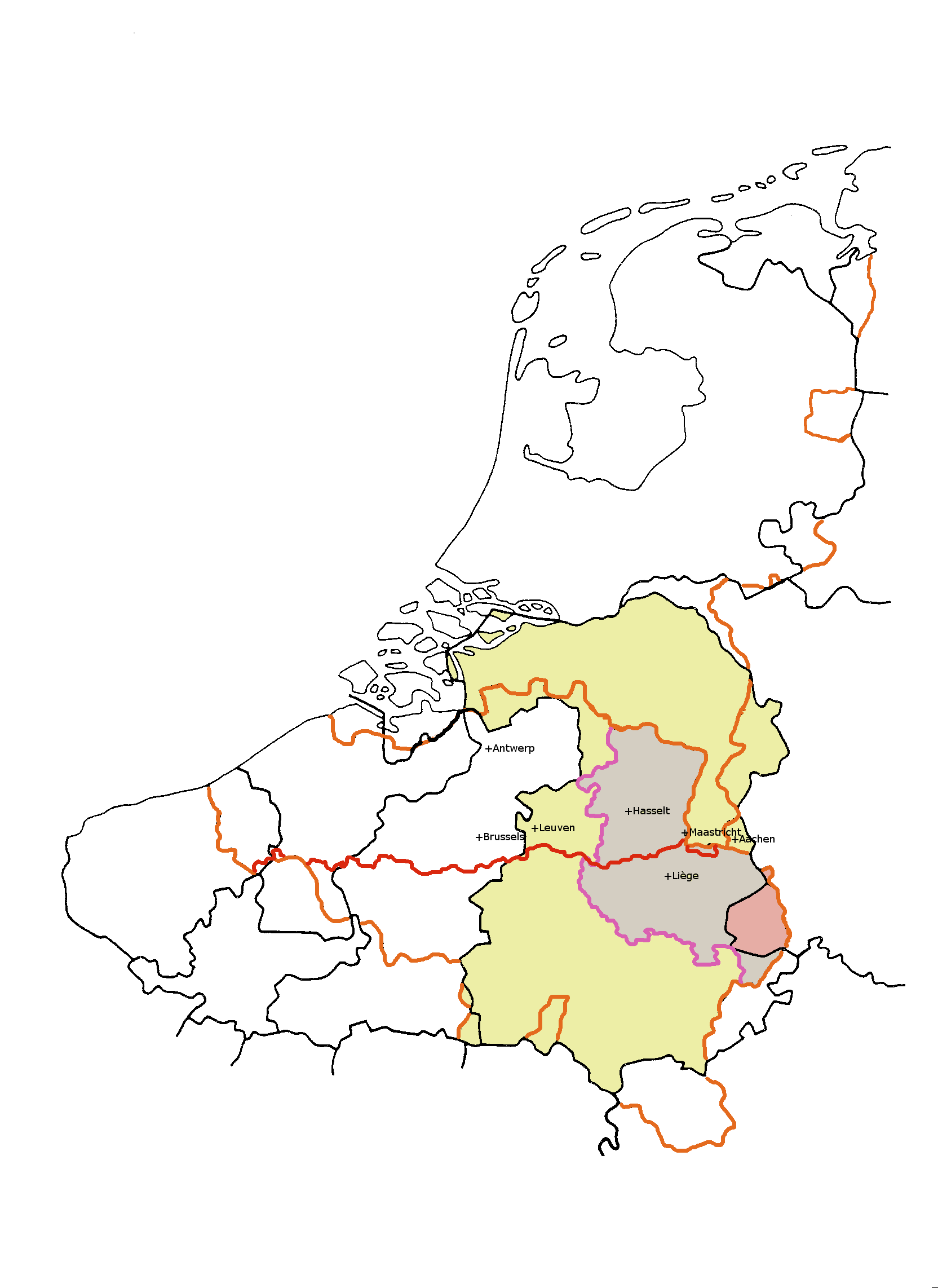
The Paemani (also Poemani or Caemani) were a small Belgic- Germanic tribe dwelling in Gallia Belgica during the Iron Age. Their ethnic identity remains uncertain. Caesar described them as part of the Germani Cisrhenani, but a number of scholars have argued that their name may be of Celtic origin. Like other Germani Cisrhenani tribes, it is possible that their old Germanic endonym came to be abandoned after a tribal reorganization, that they received their names from their Celtic neighbours, or else that they were fully or partially assimilated to Celtic culture at the time of the Roman invasion of the region in 57 BC. Name Attestations The name appears as ''Caemani'' in Caesar's accounts (mid-1st c. BC), along with the variant ''Paemani'' or ''Paemanes''. One of the two variants may be a scribal error. Alternatively, scholar Peter E. Busse has proposed to interpret the forms as Q-Celtic/P-Celtic equivalents: "that Caesar wrote Q-Celtic ''Caemanes'', with ''C-'' rather t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germani Cisrhenani
The ''Germani cisrhenani'' (Latin '' cis- rhenanus'' "on this side of the Rhine", referring to the Roman or western side), or "Left bank ''Germani''", were a group of Germanic peoples who lived west of the Lower Rhine at the time of the Gallic Wars in the mid-1st century BC. These ''Germani'' were first described by Julius Caesar, who was writing specifically about tribes near the Meuse river, who had settled among the Belgae before Roman intrusion into the area. Tribes who Caesar named as being among the ''Germani cisrhenani'' included the Eburones, the Condrusi, the Caeraesi, the Segni and the Paemani. Tacitus, writing around 100 AD when the region had been part of the Roman Empire, referred to these ''Germani'' next, saying that they were by his time called the Tungri. The "''Germani''" name had by this time become a term used more commonly to refer to many other peoples. Name and terminology Starting with Caesar, Roman historians described the Rhine as an important natura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eburones
The Eburones (Greek: ) were a Gallic- Germanic tribe dwelling in the northeast of Gaul, in what is now the southern Netherlands, eastern Belgium and the German Rhineland, in the period immediately preceding the Roman conquest of the region. Though living in Gaul, they were also described as being both Belgae and Germani (for a discussion of these terms, see below). The Eburones played a major role in Julius Caesar's account of his "Gallic Wars", as the most important tribe within the ''Germani cisrhenani'' group of tribes — ''Germani'' living west of the Rhine amongst the Belgae. Caesar claimed that the name of the Eburones was wiped out after their failed revolt against his forces during the Gallic Wars, and that the tribe was largely annihilated. Whether any significant part of the population lived on in the area as Tungri, the tribal name found here later, is uncertain but considered likely. Name Attestations They are mentioned as ''Eburones'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgae
The Belgae () were a large confederation of tribes living in northern Gaul, between the English Channel, the west bank of the Rhine, and the northern bank of the river Seine, from at least the third century BC. They were discussed in depth by Julius Caesar in his account of his wars in Gaul. Some peoples in Britain were also called Belgae, and O'Rahilly equated them with the Fir Bolg in Ireland. The Belgae gave their name to the Roman province of Gallia Belgica and, much later, to the modern country of Belgium; today "Belgae" is also Latin for "Belgians". Etymology The consensus among linguists is that the ethnic name ''Belgae'' comes from the Proto-Celtic root ''*belg-'' or ''*bolg-'' meaning "to swell (particularly with anger/battle fury/etc.)", cognate with the Dutch adjective ''gebelgd'' "very angry" (weak perfect participle of the verb ''belgen'' "to become angry") and ''verbolgen'' "being angry" (strong perfect participle of obsolete ''verbelgen'' "to make angry"), as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungri
The Tungri (or Tongri, or Tungrians) were a tribe, or group of tribes, who lived in the Belgic part of Gaul, during the times of the Roman Empire. Within the Roman Empire, their territory was called the ''Civitas Tungrorum''. They were described by Tacitus as being the same people who were first called "''Germani''" ( Germanic), meaning that all other tribes who were later referred to this way, including those in Germania east of the river Rhine, were named after them. More specifically, Tacitus was thereby equating the Tungri with the "''Germani Cisrhenani''" described generations earlier by Julius Caesar. Their name is the source of several place names in Belgium, Germany and the Netherlands, including Tongeren, Tongerlo Abbey, and Tongelre. image:Germanie-inferieure.jpg, 301x301px, The Roman province of Germania Inferior, showing Atuatuca, modern Tongeren, the capital of the Tungri (Tongres). Places associated with the Tungri are in bright green. It was on the road between Amiens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caerosi
The Caerosi (or Caeroesi) were a small Belgic- Germanic tribe dwelling in Gallia Belgica during the Iron Age and the Roman period. Their ethnic identity remains uncertain. Caesar described them as part of the Germani Cisrhenani, but their tribal name is probably of Celtic origin. Like other Germani Cisrhenani tribes, it is possible that their old Germanic endonym came to be abandoned after a tribal reorganization, that they received their names from their Celtic neighbours, or else that they were fully or partially assimilated into Celtic culture at the time of the Roman invasion of the region in 57 BC. Name They are mentioned as ''Caerosos'' (var. ''ceroesos'', ''caeroesos'', ''cerosos'') by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC), and as ''Caerosi'' by Orosius (early 5th c. AD)., s.v. ''Caerosi''. The ethnonym ''Caerosi'' probably derives from a Proto-Celtic root reconstructed as ''*caer-'' ('sheep'; cf. Old Irish ''caera''), itself from an earlier ''*caper-'' (cf. Latin ''caper'', Old Norse '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
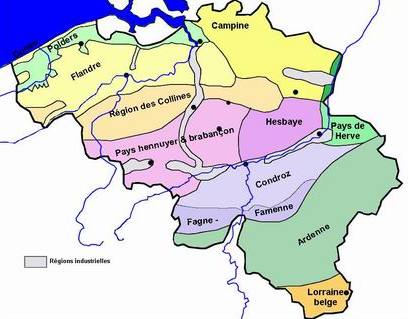
Famenne
Famenne (; wa, Fåmene, ) is a natural region in Wallonia (southern Belgium). Together with The Fagne or la Fagne, west of the river Meuse, it is part of the Fagne-Famenne natural region. The two regions are often grouped together because they are quite similar both geographically and naturally. Etymology The hypothesis that the name of the ''Famenne'' region may derive from ''Paemani'', an ancient Germanic tribe, following the influence of the Germanic sound shift from ''p-'' to ''f-'', is now considered doubtful by most scholars. In the first medieval mentions, the Famenne is spelled in Latin in forms with an "l", for example Falmenna. History The oldest known definitions of the medieval version of the Condroz ''pagus'' also included the Famenne. Compared to the late medieval archdeaconries of Condroz and Fammene, the early medieval ''pagi'' did not include the deaneries of St Remacle, Hanret, or Chimay. Chimay had been part of the Lomme ''pagus'', like most of the area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, English, is also the world's most widely spoken language with an estimated 2 billion speakers. All Germanic languages are derived from Proto-Germanic, spoken in Iron Age Scandinavia. The West Germanic languages include the three most widely spoken Germanic languages: English with around 360–400 million native speakers; German language, German, with over 100 million native speakers; and Dutch language, Dutch, with 24 million native speakers. Other West Germanic languages include Afrikaans, an offshoot of Dutch, with over 7.1 million native speakers; Low German, considered a separate collection of Standard language, unstandardized dialects, with roughly 4.35–7.15 million native speakers and probably 6.7–10 million people who can understand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribes Of Pre-Roman Gaul
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to conflicting theoretical understandings of social and kinship structures, and also reflecting the problematic application of this concept to extremely diverse human societies. The concept is often contrasted by anthropologists with other social and kinship groups, being hierarchically larger than a lineage or clan, but smaller than a chiefdom, nation or state. These terms are equally disputed. In some cases tribes have legal recognition and some degree of political autonomy from national or federal government, but this legalistic usage of the term may conflict with anthropological definitions. In the United States, Native American tribes are legally considered to have "domestic dependent nation" status within the territorial United States, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Germanic Peoples
Early Germanic culture refers to the culture of the early Germanic peoples. Largely derived from a synthesis of Proto-Indo-European and indigenous Northern European elements, the Germanic culture started to exist in the Jastorf culture that developed out of the Nordic Bronze Age. It came under significant external influence during the Migration Period, particularly from ancient Rome. The Germanic peoples eventually overwhelmed the Western Roman Empire, which by the Middle Ages facilitated their conversion from paganism to Christianity and the abandonment of their tribal way of life. Certain traces of early Germanic culture have survived among the Germanic peoples up to the present day. Languages Linguists postulate that an early Proto-Germanic language existed and was distinguishable from the other Indo-European languages as far back as 500 BCE. From what is known, the early Germanic tribes may have spoken mutually intelligible dialects derived from a common parent lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atuatuci
The Atuatuci (or Aduatuci) were a Gallic- Germanic tribe, dwelling in the eastern part of modern-day Belgium during the Iron Age. They fought the Roman armies of Julius Caesar during the Gallic Wars (58–50 BC). In the Battle of the Sabis (57 BC), the Atuatuci sent troops to assist their Belgic neighbours, the Nervii, Atrebates and Viromandui, but were too late to avoid an eventual Roman victory. After they withdrew to their oppidum (fortress), the Atuatuci were later defeated by the Romans during the siege of the Atuatuci (57 BC). According to Caesar, 4,000 of the Atuatici perished in the seizure of their stronghold, and 53,000 of them were reduced to slavery. Several years later in 54 BC the Atuatuci suffered further retribution when they were involved with their neighbours in a failed rebellion against the Romans. Following the devastation of the tribe, which left only a number of small groups, the Atuatuci disappeared from historical records and likely assimilated into neig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meuse
The Meuse ( , , , ; wa, Moûze ) or Maas ( , ; li, Maos or ) is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a total length of . History From 1301 the upper Meuse roughly marked the western border of the Holy Roman Empire with the Kingdom of France, after Count Henry III of Bar had to receive the western part of the County of Bar (''Barrois mouvant'') as a French fief from the hands of King Philip IV. In 1408, a Burgundian army led by John the Fearless went to the aid of John III against the citizens of Liège, who were in open revolt. After the battle which saw the men from Liège defeated, John ordered the drowning in the Meuse of suspicious burghers and noblemen in Liège. The border remained stable until the annexation of the Three Bishoprics Metz, Toul and Verdun by King Henry II in 1552 and the occupation of the Duchy of Lorraine by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhône
The Rhône ( , ; wae, Rotten ; frp, Rôno ; oc, Ròse ) is a major river in France and Switzerland, rising in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and southeastern France before discharging into the Mediterranean Sea. At Arles, near its mouth, the river divides into the Great Rhône (french: le Grand Rhône, links=no) and the Little Rhône (). The resulting delta forms the Camargue region. The river's source is the Rhône Glacier, at the east edge of the Swiss canton of Valais. The glacier is part of the Saint-Gotthard Massif, which gives rise to three other major rivers: the Reuss, Rhine and Ticino. The Rhône is, with the Po and Nile, one of the three Mediterranean rivers with the largest water discharge. Etymology The name ''Rhône'' continues the Latin name (Greek ) in Greco-Roman geography. The Gaulish name of the river was or (from a PIE root *''ret-'' "to run, roll" frequently found in river names). Names in other languages include german: R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)