|
PSI-BLAST
In bioinformatics, BLAST (basic local alignment search tool) is an algorithm and program for comparing Primary structure, primary biological sequence information, such as the amino acid, amino-acid sequences of proteins or the nucleotides of DNA sequence, DNA and/or RNA sequences. A BLAST search enables a researcher to compare a subject protein or nucleotide sequence (called a query) with a library or database of sequences, and identify database sequences that resemble the query sequence above a certain threshold. For example, following the discovery of a previously unknown gene in the Mus musculus, mouse, a scientist will typically perform a BLAST search of the human genome to see if humans carry a similar gene; BLAST will identify sequences in the human genome that resemble the mouse gene based on similarity of sequence. Background BLAST is one of the most widely used bioinformatics programs for sequence searching. It addresses a fundamental problem in bioinformatics research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Lipman
David J. Lipman is an American biologist who from 1989 to 2017 was the director of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) at the National Institutes of Health. NCBI is the home of GenBank, the U.S. node of the INSDC, International Sequence Database Consortium, and PubMed, one of the most heavily used sites in the world for the search and retrieval of biomedical information. Lipman is one of the original authors of the BLAST (biotechnology), BLAST sequence alignment program, and a respected figure in bioinformatics. In 2017, he left NCBI and became Chief Science Officer at Impossible Foods. Education Lipman received his undergraduate degree from Brown University and his Doctor of Medicine, M.D. in 1980 from the University at Buffalo, The State University of New York Career Lipman was the founding director of the National Center for Biotechnology Information, part of the National Library of Medicine at the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Under his leadership, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Altschul
Stephen Frank Altschul (born February 28, 1957) is an American mathematician who has designed algorithms that are used in the field of bioinformatics (the Karlin–Altschul algorithm and its successors). Altschul is the co-author of the BLAST algorithm used for sequence analysis of proteins and nucleotides. Education Altschul graduated summa cum laudeNew York Times: "Weddings; Caroline James, Stephen Altschul" April 17, 1994 from , where he was elected to in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Webb Miller
Webb Colby Miller (born 1943) is an American bioinformatician who is professor in the Department of Biology and the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at The Pennsylvania State University. Education Miller attended Whitman College, and received his Ph.D. in mathematics from the University of Washington in 1969. Research and career He joined Penn State in September 1985. Prior to that, he had held a position as permanent staff member at the IBM Thomas J. Watson Research Center and served on the faculty at the University of California, Santa Barbara, and the University of Arizona. He is a fellow of the ISCB (International Society for Computational Biology). Miller has been developing algorithms and software for analyzing DNA sequences and related types of data from molecular genetics. He is one of the authors of BLAST. He also develops methods for aligning long DNA sequences and extracting functional information from them. Webb Miller has made important contributions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit the air, soil, water, Hot spring, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria play a vital role in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients and the nitrogen fixation, fixation of nitrogen from the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of cadaver, dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Needleman–Wunsch Algorithm
The Needleman–Wunsch algorithm is an algorithm used in bioinformatics to align protein or nucleotide sequences. It was one of the first applications of dynamic programming to compare biological sequences. The algorithm was developed by Saul B. Needleman and Christian D. Wunsch and published in 1970. The algorithm essentially divides a large problem (e.g. the full sequence) into a series of smaller problems, and it uses the solutions to the smaller problems to find an optimal solution to the larger problem. It is also sometimes referred to as the optimal matching algorithm and the global alignment technique. The Needleman–Wunsch algorithm is still widely used for optimal global alignment, particularly when the quality of the global alignment is of the utmost importance. The algorithm assigns a score to every possible alignment, and the purpose of the algorithm is to find all possible alignments having the highest score. Introduction This algorithm can be used for any two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
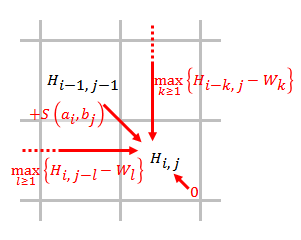
Smith–Waterman Algorithm
The Smith–Waterman algorithm performs local sequence alignment; that is, for determining similar regions between two strings of nucleic acid sequences or protein sequences. Instead of looking at the entire sequence, the Smith–Waterman algorithm compares segments of all possible lengths and optimizes the similarity measure. The algorithm was first proposed by Temple F. Smith and Michael S. Waterman in 1981. Like the Needleman–Wunsch algorithm, of which it is a variation, Smith–Waterman is a dynamic programming algorithm. As such, it has the desirable property that it is guaranteed to find the optimal local alignment with respect to the scoring system being used (which includes the substitution matrix and the gap-scoring scheme). The main difference to the Needleman–Wunsch algorithm is that negative scoring matrix cells are set to zero. Traceback procedure starts at the highest scoring matrix cell and proceeds until a cell with score zero is encountered, yielding the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Molecular Biology
The ''Journal of Molecular Biology'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all aspects of molecular biology. It was established in 1959 by Academic Press in London. It is currently published by Elsevier. The editor-in-chief was Peter Wright ( The Scripps Research Institute) for the last 33 years. He has been succeeded by Michael F. Summers ( University of Maryland Baltimore County). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor of 4.7. Notable articles Some of the most highly cited articles that have appeared in the journal are: *, in which Jacques Monod, Jeffries Wyman, and Jean-Pierre Changeux presented the MWC model, that explained the cooperativity exhibited by allosteric proteins, such as hemoglobin Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Karlin
Samuel Karlin (June 8, 1924 – December 18, 2007) was an American mathematician at Stanford University in the late 20th century. Education and career Karlin was born in Janów, Poland and immigrated to Chicago as a child. Raised in an Orthodox Jewish household, Karlin became an atheist in his teenage years and remained an atheist for the rest of his life. Later in life he told his three children, who all became scientists, that walking down the street without a yarmulke on his head for the first time was a milestone in his life. Karlin earned his undergraduate degree from Illinois Institute of Technology; and then his doctorate in mathematics from Princeton University in 1947 (at the age of 22) under the supervision of Salomon Bochner. He was on the faculty of Caltech from 1948 to 1956, before becoming a professor of mathematics and statistics at Stanford. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FASTA
FASTA is a DNA and protein sequence alignment software package first described by David J. Lipman and William R. Pearson in 1985. Its legacy is the FASTA format which is now ubiquitous in bioinformatics. History The original FASTA program was designed for protein sequence similarity searching. Because of the exponentially expanding genetic information and the limited speed and memory of computers in the 1980s heuristic methods were introduced aligning a query sequence to entire data-bases. FASTA, published in 1987, added the ability to do DNA:DNA searches, translated protein:DNA searches, and also provided a more sophisticated shuffling program for evaluating statistical significance. There are several programs in this package that allow the alignment of protein sequences and DNA sequences. Nowadays, increased computer performance makes it possible to perform searches for local alignment detection in a database using the Smith–Waterman algorithm. FASTA is pronounced "f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heuristic
A heuristic or heuristic technique (''problem solving'', '' mental shortcut'', ''rule of thumb'') is any approach to problem solving that employs a pragmatic method that is not fully optimized, perfected, or rationalized, but is nevertheless "good enough" as an approximation or attribute substitution. Where finding an optimal solution is impossible or impractical, heuristic methods can be used to speed up the process of finding a satisfactory solution. Heuristics can be mental shortcuts that ease the cognitive load of making a decision. Context Gigerenzer & Gaissmaier (2011) state that sub-sets of ''strategy'' include heuristics, regression analysis, and Bayesian inference. Heuristics are strategies based on rules to generate optimal decisions, like the anchoring effect and utility maximization problem. These strategies depend on using readily accessible, though loosely applicable, information to control problem solving in human beings, machines and abstract i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Genome
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as the DNA within each of the 23 distinct chromosomes in the cell nucleus. A small DNA molecule is found within individual Mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria. These are usually treated separately as the nuclear genome and the Human mitochondrial genetics, mitochondrial genome. Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA sequences and various types of non-coding DNA, DNA that does not encode proteins. The latter is a diverse category that includes DNA coding for non-translated RNA, such as that for ribosomal RNA, transfer RNA, ribozymes, small nuclear RNAs, and several types of RNA#Regulatory RNA, regulatory RNAs. It also includes Promoter (biology), promoters and their associated Cis-regulatory element, gene-regulatory elements, DNA playing structural and replicatory roles, such as Scaffold/matrix attachment region, scaffolding regions, telomeres, centromeres, and Origin of replication, origins of repl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |