|
PR-199
Puerto Rico Highway 199 (PR-199) is a main highway, mostly divided, in San Juan, Puerto Rico and Guaynabo, Puerto Rico. It is one of the few highways in Puerto Rico with discontinuity, as there is also another Puerto Rico Highway 199 in Bayamón. Route description San Juan to Guaynabo In San Juan, near Trujillo Alto, it begins near PR-850 and PR-181 and goes through the exclusive Paseos area, goes west, intersecting Puerto Rico Highway 1, Puerto Rico Highway 52 and Puerto Rico Highway 20. It approaches downtown Guaynabo. Several schools can be found along the way. Carretera PR-199, intersección con la carretera PR-1, San Juan, Puerto Rico.jpg, PR-199 west at PR-1 interchange in Caimito, San Juan Bayamón Puerto Rico Highway 199 begins again at Puerto Rico Highway 5 and ends near Puerto Rico Highway 167. The segment is likely to be renumbered as Puerto Rico Highway 5 since the latter is being built into a tollway to Naranjito and Comerío and it shows to be not probabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puerto Rico Highway 5
Puerto Rico Highway 5 (PR-5) is a main highway in the San Juan Metropolitan area which connects the cities of Cataño to Bayamón and is being extended and converted to a tollway (it has a toll plaza in Bayamón near PR-2 and PR-174) to access the municipalities of Naranjito and Comerío. It is a short freeway from south Cataño to the business area in Bayamón. It makes intersections with PR-22, PR-6, PR-2 and PR-199, where it ends at this time. The highway will parallel Puerto Rico Highway 167 and will contain the new cable-stayed bridge being built between Bayamón and Naranjito. It will probably end in Puerto Rico highway 152 when completed. Route description Cataño to Bayamón PR-5 begins in a dead end in downtown Cataño, on a peninsula overlooking San Juan Bay. It crosses downtown Cataño on an urban street, passing through the main square. Shortly after an intersection with PR-165, it becomes a divided avenue until reaching PR-22 at the Bayamon city limit. After th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cupey, San Juan, Puerto Rico
Cupey is one of the 18 barrios of the municipality of San Juan, Puerto Rico located in the mountainous area of the municipality. It is the largest barrio or district in the San Juan and the third most populous with 36,058 inhabitants according to the 2010 US Census. The territorial land area of Cupey is 7.49 square miles (19.40 km2). It is bound by the municipality of Caguas to the South, by the municipality of Trujillo Alto to the East, by the barrios of Caimito and Monacillo to the West, and by the barrios of El Cinco and Sabana Llana Sur to the North. Between 1990 and 2000 Cupey had a 17.98% increase in population, more than any other barrio in San Juan. History Established in 1878, this barrio was a former ward of the now defunct town of Río Piedras. It was divided into the subbarrios of Cupey Alto and Cupey Bajo. It is named for the Cupey tree, sometimes spelled copey (''Clusia rosea''), which is indigenous to the Caribbean. It belongs to the family Clusiaceae. Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caimito, San Juan, Puerto Rico
Caimito is one of the 18 barrios of the municipality of San Juan, Puerto Rico located in the mountainous part of the municipality. With a land area of , Caimito is the second largest barrio in the municipality of San Juan, Puerto Rico. In 2010 it had 21,825 inhabitants and a population density of 4,034.2 per sq.mi. Located in the southern part of San Juan, Caimito is bordered by barrios Tortugo and Quebrada Arenas to the west, by Monacillo to the north, by Cupey to the east and by the municipality of Caguas to the south. History The name Caimito comes from the Caimito tree, which is common in the region. The word ''caimito'' is possibly a Spanish adaptation (''-ito'' being the Spanish diminutive) of the Taino word ''caima'', possibly related to the Carib ''acayouman'', meaning crocodile (see caiman). Assigned as a suburb of Río Piedras in 1835 by Pedro Tomás de Córdova, who was Captain General of Puerto Rico from 1816 to 1836, Caimito consisted of 3,595.30 acres or la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puerto Rico Highway 20
Puerto Rico Highway 20 (PR-20) or Expreso Rafael Martínez Nadal is a short tollway located entirely in the municipality of Guaynabo, Puerto Rico. Route description It used to be divided highway with traffic signals, which even turned into a rural road near its south end, but due to the traffic congestion in parallel freeway PR-18, and also in PR-1 and PR-52, it had to be converted and is now 9.5 kilometers long. Departamento de Transportación y Obras Publicas de Puerto Rico. Accessed 3 May 2019. It has few exits; the first being to PR-169, a road to the rural area of Guaynabo and part of |
Puerto Rico Department Of Transportation And Public Works
The Department of Transportation and Public Works (DTOP; es, Departamento de Transportación y Obras Públicas)— is the Executive Department of the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico that regulates transportation and public works in Puerto Rico.Transportation Improvement Program (TIP) Fiscal Years 2010-2013 Aguadilla Urbanized Area (AUA) (UA > 200,000 in Population) Puerto Rico Department of Transportation and Public Works. Retrieved on March 11, 2010. The agency's headquarters are located in San Juan. Agencies The following agencies are involved in transportation issues of Puerto Rico. style="margin: 0 auto" ! scope=col style="text-align: left" , Name in English ! scope=col style="text-align: left" , Name in Spanish ! scope=col style="text-align: left" , Abbreviation in Spanish , - , Commission on Traffic Safety , '' Comisión para la Seguridad en el Tránsito'' , CST , - , Highways and Transportation Authority , '' Autoridad de Carreteras y Transportación'' , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puerto Rico Highway 181
Puerto Rico Highway 181 (PR-181), also known as ''Expreso Trujillo Alto'', is a road that connects the towns of San Juan, Puerto Rico (very close to Carolina) in the north/northeast coast of Puerto Rico with Patillas in the southeast, passing through the municipalities of San Juan (very small part) at Jesus de Piñero Avenue (PR-17) as it approaches the Teodoro Moscoso Bridge and the Luis Muñoz Marín International Airport, Trujillo Alto, Gurabo, San Lorenzo, Yabucoa and Patillas in the center of the town district near PR-3. Along with PR-10, PR-149, PR-1 and PR-52, it is one of the longest highways crossing the island from north to south through the central mountainous region. In the north part of Trujillo Alto it is a four-lane highway, turning completely rural on the way to Patillas with the exception of a small tract in Gurabo where it intersects PR-30. Route description Rural road In Trujillo Alto, near Gurabo, it turns into a rural road with very narrow lanes per d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond Interchange
A diamond interchange is a common type of road junction, used where a controlled-access highway crosses a minor road. Design The freeway itself is grade-separated from the minor road, one crossing the other over a bridge. Approaching the interchange from either direction, an off-ramp diverges only slightly from the freeway and runs directly across the minor road, becoming an on-ramp that returns to the freeway in similar fashion. The two places where the ramps meet the road are treated as conventional intersections. In the United States, where this form of interchange is very common, particularly in rural areas, traffic on the off-ramp typically faces a stop sign at the minor road, while traffic turning onto the freeway is unrestricted. The diamond interchange uses less space than most types of freeway interchange, and avoids the interweaving traffic flows that occur in interchanges such as the cloverleaf. Thus, diamond interchanges are most effective in areas where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Cloverleaf Interchange
A partial cloverleaf interchange or parclo is a modification of a cloverleaf interchange. The design has been well received, and has since become one of the most popular freeway-to-arterial interchange designs in North America. It has also been used occasionally in some European countries, such as Germany, Hungary, Italy, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom. Comparison with other interchanges *A diamond interchange has four ramps. *A cloverleaf interchange has eight ramps, as does a stack interchange. They are fully grade separated, unlike a parclo, and have traffic flow without stops on all ramps and throughways. *A parclo generally has either four or six ramps but less commonly has five ramps. Naming In Ontario, the specific variation is identified by a letter/number suffix after the name. Ontario's naming conventions are used in this article. The letter ''A'' designates that two ramps meet the freeway ''ahead'' of the arterial road, while ''B'' designates that two ram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
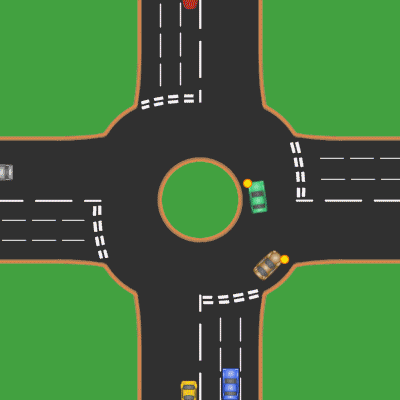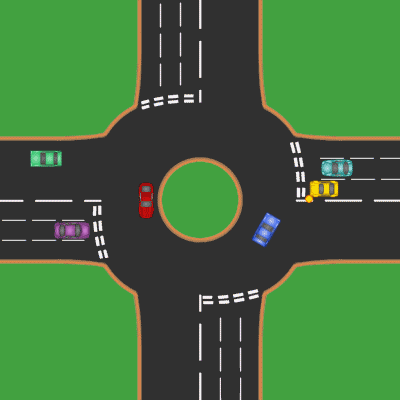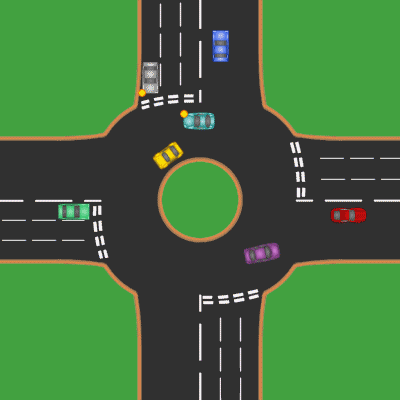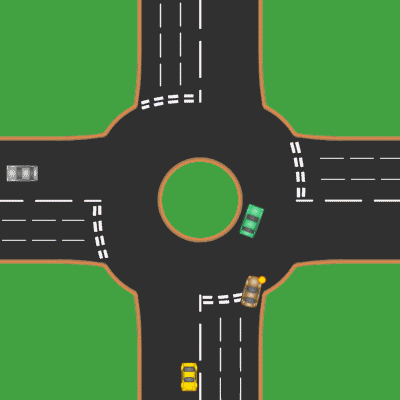
Roundabout
A roundabout is a type of circular intersection or junction in which road traffic is permitted to flow in one direction around a central island, and priority is typically given to traffic already in the junction.''The New Shorter Oxford English Dictionary,'' Volume 2, Clarendon Press, Oxford (1993), page 2632 Engineers use the term modern roundabout to refer to junctions installed after 1960 that incorporate various design rules to increase safety. Both modern and non-modern roundabouts, however, may bear street names or be identified colloquially by local names such as rotary or traffic circle. Compared to stop signs, traffic signals, and earlier forms of roundabouts, modern roundabouts reduce the likelihood and severity of collisions greatly by reducing traffic speeds and minimizing T-bone and head-on collisions. Variations on the basic concept include integration with tram or train lines, two-way flow, higher speeds and many others. For pedestrians, traffic exiting th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seagull Intersection
A seagull intersectionJohn Harper, Wal Smart, Michael de Roos''Seagull Intersection Layout. Island Point Road – A Case Study'' 2000 – 2010 or continuous green T-intersection (also known as a turbo-T (in Florida) or High-T intersection (in Nevada and Utah)Nevada DOT''US93 Lakeshore v4 Handouts''/ref>) is a type of three-way road intersection, usually used on high traffic volume roads and dual carriageways. This form of intersection is popular in Australia and New Zealand, and sometimes used in the United States and other countries. Design Seagull intersections get their name from the pattern that the two cross-traffic turn lanes make when looking down at them from the air. In a seagull intersection, one or more lanes of traffic on the arterial road, on the carriageway opposite the intersecting side road, are free flowing, that is, one direction of traffic on the arterial is allowed to travel straight through without stopping. The free-flowing lane(s) are called "continuou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comerío, Puerto Rico
Comerío () is a town and municipality of Puerto Rico in the center-eastern region of island, north of Aibonito; south of Naranjito and Bayamón; east of Barranquitas; and west of Cidra and Aguas Buenas. Comerío is spread over 7 barrios and Comerío Pueblo (the downtown area and the administrative center of the city). It is part of the San Juan-Caguas-Guaynabo Metropolitan Statistical Area. History Comerío was founded on June 12, 1826. Originally named Sabana del Palmar, but later changed to ''Comerío''. In 1854, nearly 1000 acres (1000 ) of land were being used for agriculture. In 1894, there was one sugar and two coffee plantations ( estates) in Comerío. In the early 20th century, Comerio residents, had a short but legendary territory war with residents of the city of Barranquitas. Puerto Rico was ceded by Spain in the aftermath of the Spanish–American War under the terms of the Treaty of Paris of 1898 and became a territory of the United States. In 1899, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naranjito, Puerto Rico
Naranjito (, ) is a town and municipality of Puerto Rico located in the central region of the island, south of Toa Alta; north of Barranquitas and Comerío; east of Corozal; and west of Bayamón. Naranjito is spread over 7 barrios and Naranjito Pueblo (the downtown area and the administrative center). It is part of the San Juan-Caguas-Guaynabo Metropolitan Statistical Area. History The intention to form the municipality of Naranjito began in 1810. After a series of major incidents with powerful political interests of the time, on December 3, 1824, Don Braulio Morales successfully founded the town of Naranjito. The town was founded in the neighborhood of the same name, on a land donated by Doña Manuela Rivera and Don Braulio Morales. Morales was named "Captain Settler" and at the same time was appointed mayor of the town in development. The name "Naranjito" is derived from a small orange tree that served as a reference point for travelers looking for in the shortest way to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |