|
Oviraptorid
Oviraptoridae is a group of bird-like, herbivorous and omnivorous maniraptoran dinosaurs. Oviraptorids are characterized by their toothless, parrot-like beaks and, in some cases, elaborate crests. They were generally small, measuring between one and two metres long in most cases, though some possible oviraptorids were enormous. Oviraptorids are currently known only from the Late Cretaceous of Asia, with the most well-known species and complete specimens found only in the Gobi Desert of Mongolia and northwestern China. Description The most characteristic feature of this group is the skull structure. Oviraptorids had short snouts and very deep mandibles. Some taxa (such as '' Citipati'', '' Corythoraptor'', ''Rinchenia'') had a midline crest on top of the skull, resembling that of a cassowary. Other distinguishing characteristics include a bony spike intruding on the mandibular fenestra, nostrils placed very high and far back on the snout, an extremely thin bony bar beneath th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oviraptor
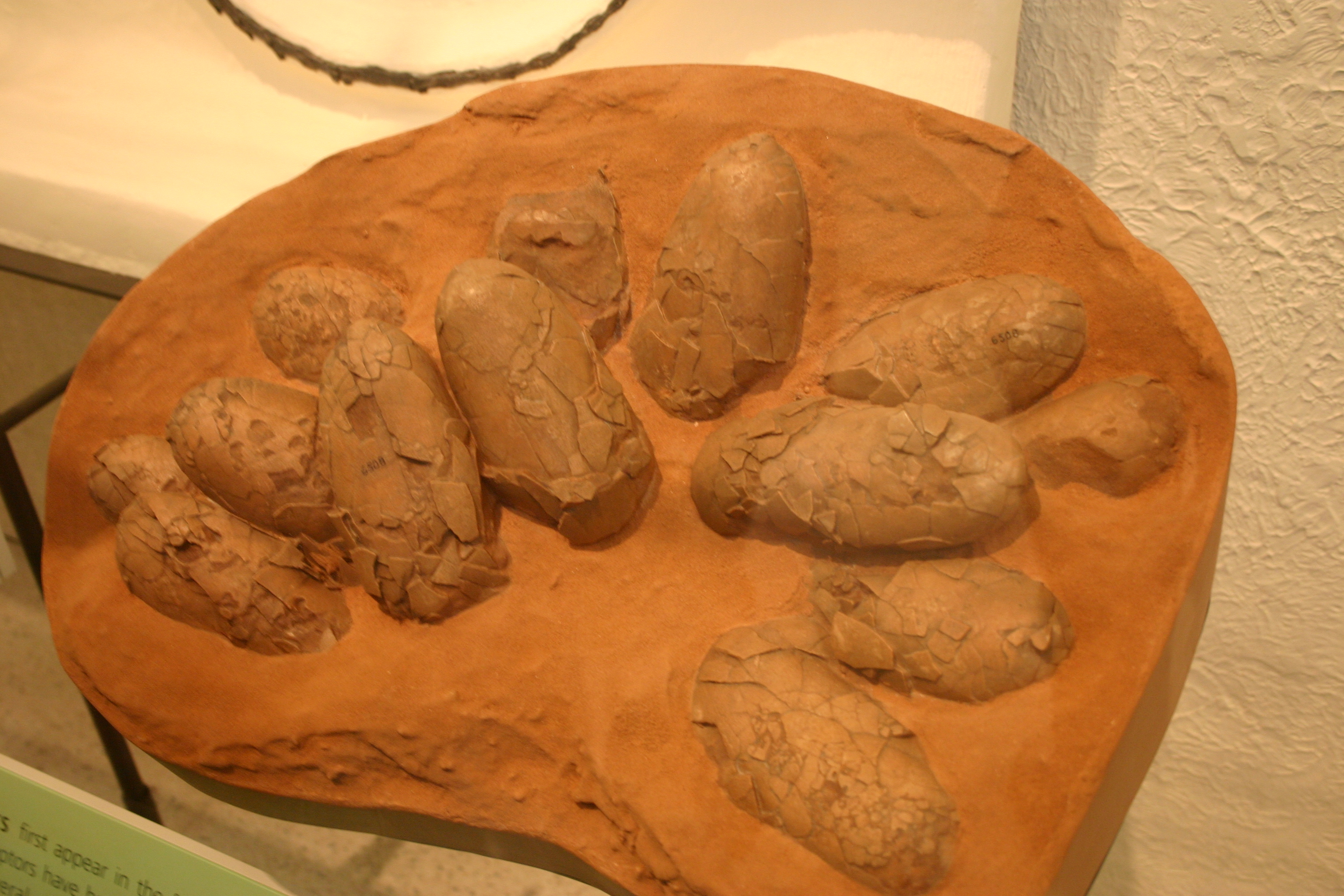
''Oviraptor'' (; ) is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period. The first remains were collected from the Djadokhta Formation of Mongolia in 1923 during a paleontological expedition led by Roy Chapman Andrews, and in the following year the genus and type species ''Oviraptor philoceratops'' were named by Henry Fairfield Osborn. The genus name refers to the initial thought of egg-stealing habits, and the specific name was intended to reinforce this view indicating a preference over ceratopsian eggs. Despite the fact that numerous specimens have been referred to the genus, ''Oviraptor'' is only known from a single partial skeleton regarded as the holotype, as well as a nest of about fifteen eggs and several small fragments from a juvenile. ''Oviraptor'' was a rather small feathered oviraptorid, estimated at long with a weight between . It had a wide lower jaw with a skull that likely had a crest. Both upper and lower jaws were toothle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oviraptor Philoceratops
''Oviraptor'' (; ) is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period. The first remains were collected from the Djadokhta Formation of Mongolia in 1923 during a paleontological expedition led by Roy Chapman Andrews, and in the following year the genus and type species ''Oviraptor philoceratops'' were named by Henry Fairfield Osborn. The genus name refers to the initial thought of egg-stealing habits, and the specific name was intended to reinforce this view indicating a preference over ceratopsian eggs. Despite the fact that numerous specimens have been referred to the genus, ''Oviraptor'' is only known from a single partial skeleton regarded as the holotype, as well as a nest of about fifteen eggs and several small fragments from a juvenile. ''Oviraptor'' was a rather small feathered oviraptorid, estimated at long with a weight between . It had a wide lower jaw with a skull that likely had a crest. Both upper and lower jaws were toothless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nemegtomaia
''Nemegtomaia'' is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaur from what is now Mongolia that lived in the Late Cretaceous Period, about 70million years ago. The first specimen was found in 1996, and became the basis of the new genus and species ''N. barsboldi'' in 2004. The original genus name was '' Nemegtia'', but this was changed to ''Nemegtomaia'' in 2005, as the former name was preoccupied. The first part of the generic name refers to the Nemegt Basin, where the animal was found, and the second part means "good mother", in reference to the fact that oviraptorids are known to have brooded their eggs. The specific name honours the palaeontologist Rinchen Barsbold. Two more specimens were found in 2007, one of which was found on top of a nest with eggs, but the dinosaur had received its genus name before it was found associated with eggs. ''Nemegtomaia'' is estimated to have been around 2 m (7 ft) in length, and to have weighed 40 kg (85 lb). As an oviraptorosaur, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citipati
''Citipati'' (; meaning "funeral pyre lord") is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period, about 75 million to 71 million years ago. It is mainly known from the Ukhaa Tolgod locality at the Djadokhta Formation, where the first remains were collected during the 1990s. The genus and type species ''Citipati osmolskae'' were named and described in 2001. A second species from the adjacent Zamyn Khondt locality may also exist. ''Citipati'' is one of the best-known oviraptorids thanks to a number of well-preserved specimens, including individuals found in brooding positions atop nests of eggs, though most of them were initially referred to the related ''Oviraptor''. These nesting specimens have helped to solidify the link between non-avian dinosaurs and birds. ''Citipati'' was among the largest oviraptorids; it is estimated to have been around in length and to have weighed . Its skull was highly pneumatized, short, and had a characteristic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
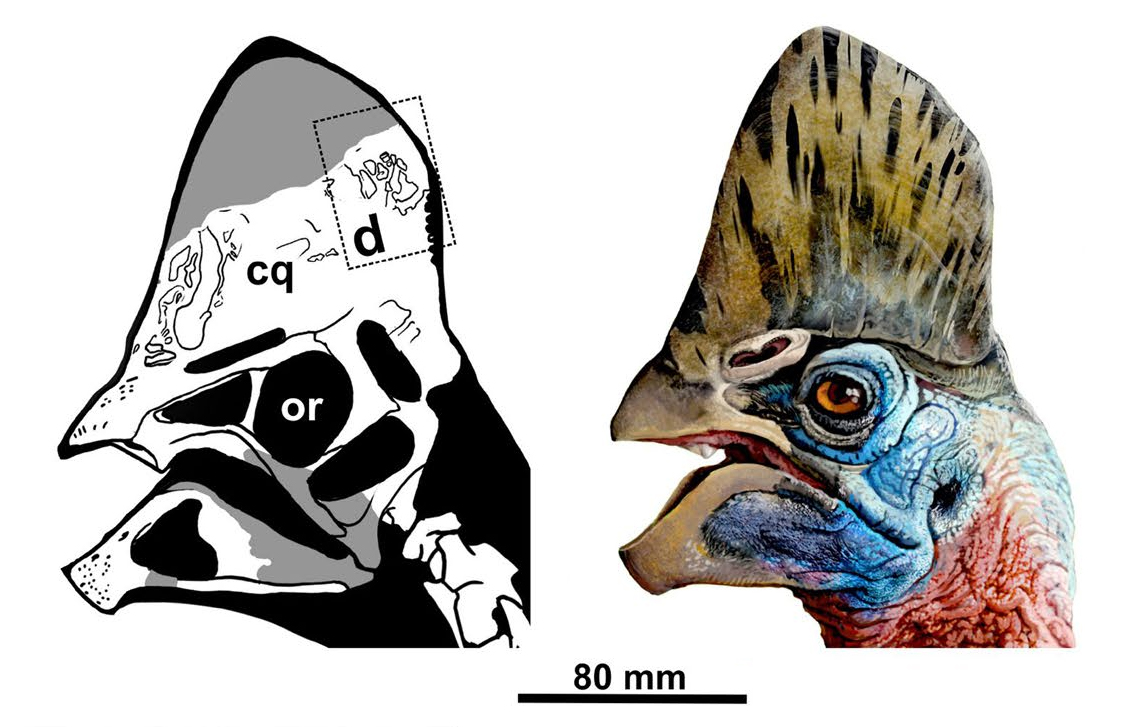
Corythoraptor
''Corythoraptor'' () is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaur from the late Maastrichtian Nanxiong Formation of South China. It contains one species, ''C. jacobsi'', known from a single well-preserved skeleton, and named after paleontologist Louis L. Jacobs. It bears a tall crest similar to that of the modern cassowary, and possibly had a similar functionality of display and resonance to detect lower-frequency sounds. Like other oviraptorids, the bones of ''Corythoraptor'' were heavily pneumatized with many air pockets. Microanalysis of the bones indicates seasonal growth spurts, and the type specimen probably died at the age of 6 or 7, meaning growth continued into at least the 8th year of development. The type specimen reached in length. Oviraptorids may have predominantly inhabited arid environments and ate xerophytic (drought-resistant) plants, nuts, and seeds. However, ''Corythoraptor'' coexisted with six other oviraptorid genera, and they may have all eaten different foods (n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tongtianlong
''Tongtianlong'' (meaning "Tongtianyan dragon") is a genus of oviraptorid theropod dinosaurs that lived in the late Maastrichtian epoch of the late Cretaceous period. It contains one species, ''T. limosus''. Description ''Tongtianlong'' was a sheep-sized member of the oviraptorids, a group of omnivorous, feathered, bird-like theropods. The describers of ''Tongtianlong'' recognized that it possessed a set of distinctive characteristics that differentiated it both from other oviraptorosaurs. In particular, unlike other oviraptorids, the crest of ''Tongtianlong'' was shaped like a dome, with its highest point just behind the eye socket; and the front edge of the toothless premaxilla, which would have supported its beak, was very rounded. Additionally, there is a distinct ridge on the front margin of the parietal bone, wedged between the frontal bones; the shaft of the lacrimal bone, which is located in front of the eye socket, is wide, flattened, and plate-like seen from the si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yulong Mini
''Yulong'' is an extinct genus of derived oviraptorid theropod dinosaur known from the Late Cretaceous Qiupa Formation of Henan Province, central China. It contains a single species, ''Yulong mini''. It is known from many juvenile specimens that represent some of the smallest known oviraptorids and also a single subadult specimen. Discovery and naming Specimens of ''Yulong'' were collected near Qiupa Town in Luanchuan County, Henan Province, from the Qiupa Formation. The exact geological age of the Qiupa Formation is unknown, but it probably dates to the Late Cretaceous based on the presence of oviraptorids (''Yulong''), dromaeosaurids ('' Luanchuanraptor''), ornithomimids (''Qiupalong''), alvarezsaurs ('' Qiupanykus'') and other, undescribed, derived dinosaur specimens. ''Yulong'' was first described and named by Junchang Lü, Philip J. Currie, Li Xu, Xingliao Zhang, Hanyong Pu and Songhai Jia in 2013 and the type species is ''Yulong mini''. The generic name is derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conchoraptor
''Conchoraptor'' (meaning "conch plunderer") is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous epoch, about 70 million years ago. It is known from the Barun Goyot and Nemegt formations of Mongolia. Discovery When first discovered in the Red Beds of Hermiin Tsav of the Early Maastrichtian Nemegt Formation by a Polish-Mongolian expedition in 1971, scientists believed that ''Conchoraptor'' was a juvenile ''Oviraptor'' and that the animal's missing crest would have begun to grow when the animal reached sexual maturity. Further study of multiple skeletons showed that ''Conchoraptor'' belonged in a new genus. The hands of ''Conchoraptor'' were a major reason that scientists decided to split it off from ''Oviraptor''. Anatomically the hands seemed to be an evolutionary intermediate between those of '' Ajancingenia'' and ''Oviraptor'', making it obvious that this animal was not a member of a known species. The type species of this new genus, ''Conchorap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiangxisaurus
''Jiangxisaurus'' is an extinct genus of oviraptorid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Nanxiong Formation of southern China. It was similar to '' Heyuannia'', but with more strongly curved anterior claws and a thinner, frailer mandible. This find is paleontologically significant because it contributes to current knowledge about the paleogeographical distribution of oviraptorids in southern China. It was most likely a herbivorous animal along with its close relatives '' Nankangia'' and '' Ganzhousaurus''. Etymology The genus name ''Jiangxisaurus'', refers to the Jiangxi Province of southern China. The specific name ''ganzhouensis'', is derived from Ganzhou, the locality where the specimen was discovered. ''Jiangxisaurus'' was described and named by Wei Xuefang, Pu Hanyong, Xu Li, Liu Di, and Lü Junchang in 2013 and the type species is ''Jiangxisaurus ganzhouensis''. Description The holotype specimen HGM41-HIII0421 consists of an incomplete skull, a lower jaw, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heyuannia
''Heyuannia'' ("from Heyuan") is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous epoch, in what is now China and Mongolia. It was the first oviraptorid found in China; most others were found in neighbouring Mongolia. Two species are known: ''H. huangi'', named by Lü Junchang in 2002 from the Dalangshan Formation; and ''H. yanshini'', originally named as a separate genus ''Ingenia'' from the Barun Goyot Formation by Rinchen Barsbold in 1981, and later renamed to ''Ajancingenia'' in 2013 due to the preoccupation of ''Ingenia''. The latter name was eventually discarded due to various ethical issues surrounding the author. Discovery and naming ''H. huangi'' The type species, ''Heyuannia huangi'', was named and described by Lü Junchang in 2002. The generic name refers to the city of Heyuan. The specific name honours Huang Dong, the director of the Heyuan Museum. The holotype, HYMV1-1, was discovered in Guangdong near Huangsha in layers of the D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khaan
''Khaan'' (; from Mongol 'lord') was an oviraptorid dinosaur that was found in the Djadochta Formation of Mongolia and lived in the Late Cretaceous Period (Campanian), 75-71 million years ago. Description ''Khaan'' did not differ much from other oviraptorids. At first, its remains were assigned to "Ingenia", but the ''Khaan'' manual structure, lacking the expansion of the upper third metacarpal, was considered to differ sufficiently from that of "Ingenia" for it to be assigned to its own genus. The oviraptorid diet is disputed, with plants and molluscs having been suggested. Like other oviraptorids, ''Khaan'' was probably at least partially a meat eater, feeding on small vertebrates like mammals, lizards and possibly other small dinosaurs. It was also probably feathered. Discovery The type species ''Khaan mckennai'' was in 2001 named by James M. Clark e.a. The genus name is derived from Mongol ''khaan'', "lord" or "ruler". The specific name honours the paleontologist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nankangia
''Nankangia'' is an extinct genus of caenagnathoid oviraptorosaurian dinosaur known from the Upper Cretaceous The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', ... Nanxiong Formation of Nankang, Jiangxi, Nankang County, Ganzhou City of Jiangxi Province, southeastern China. It contains a single species, ''Nankangia jiangxiensis''. ''N. jiangxiensis'' coexisted with at least four other caenagnathoids, including but not limited to ''Corythoraptor'', ''Banji long'', ''Ganzhousaurus nankangensis'' and ''Jiangxisaurus ganzhouensis''. The relatively short dentary and non-downturned mandibular symphysis of ''Nankangia'' suggest that it may have been more herbivorous than carnivorous. Its diet consisted of leaves and seeds. Discovery ''Nankangia'' was first described and named by Lü Juncha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |