Corythoraptor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Corythoraptor'' () is a
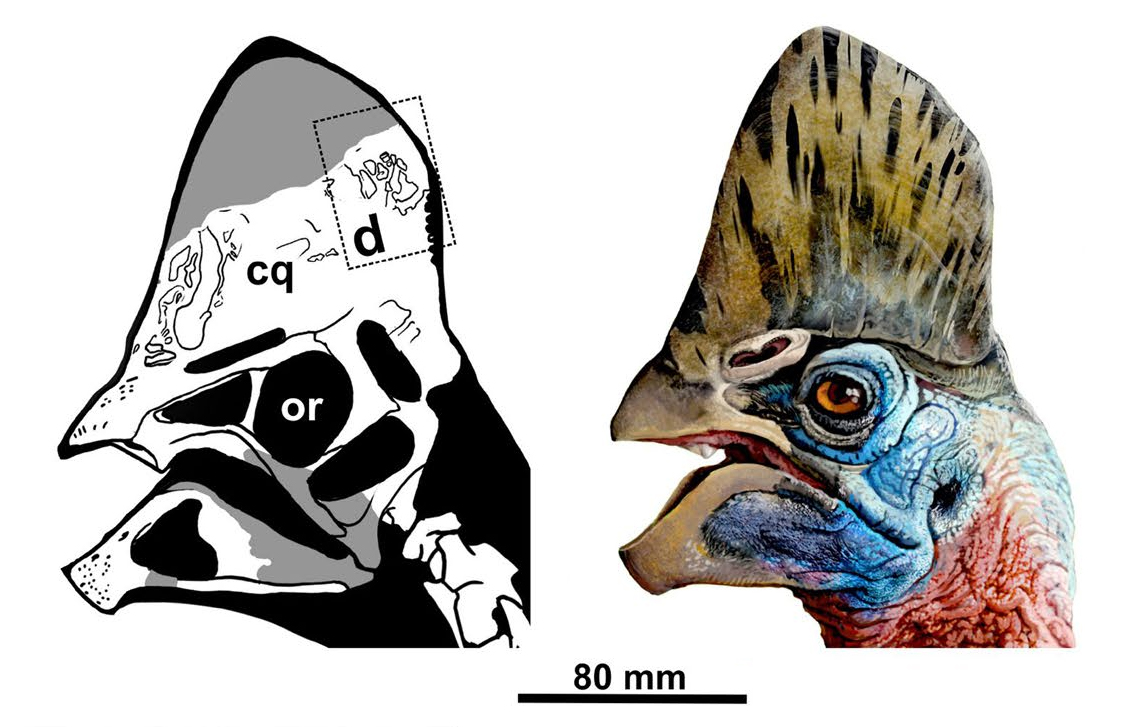 ''Corythoraptor'' bore a tall crest on its head similar to that of the modern
''Corythoraptor'' bore a tall crest on its head similar to that of the modern
 The left
The left
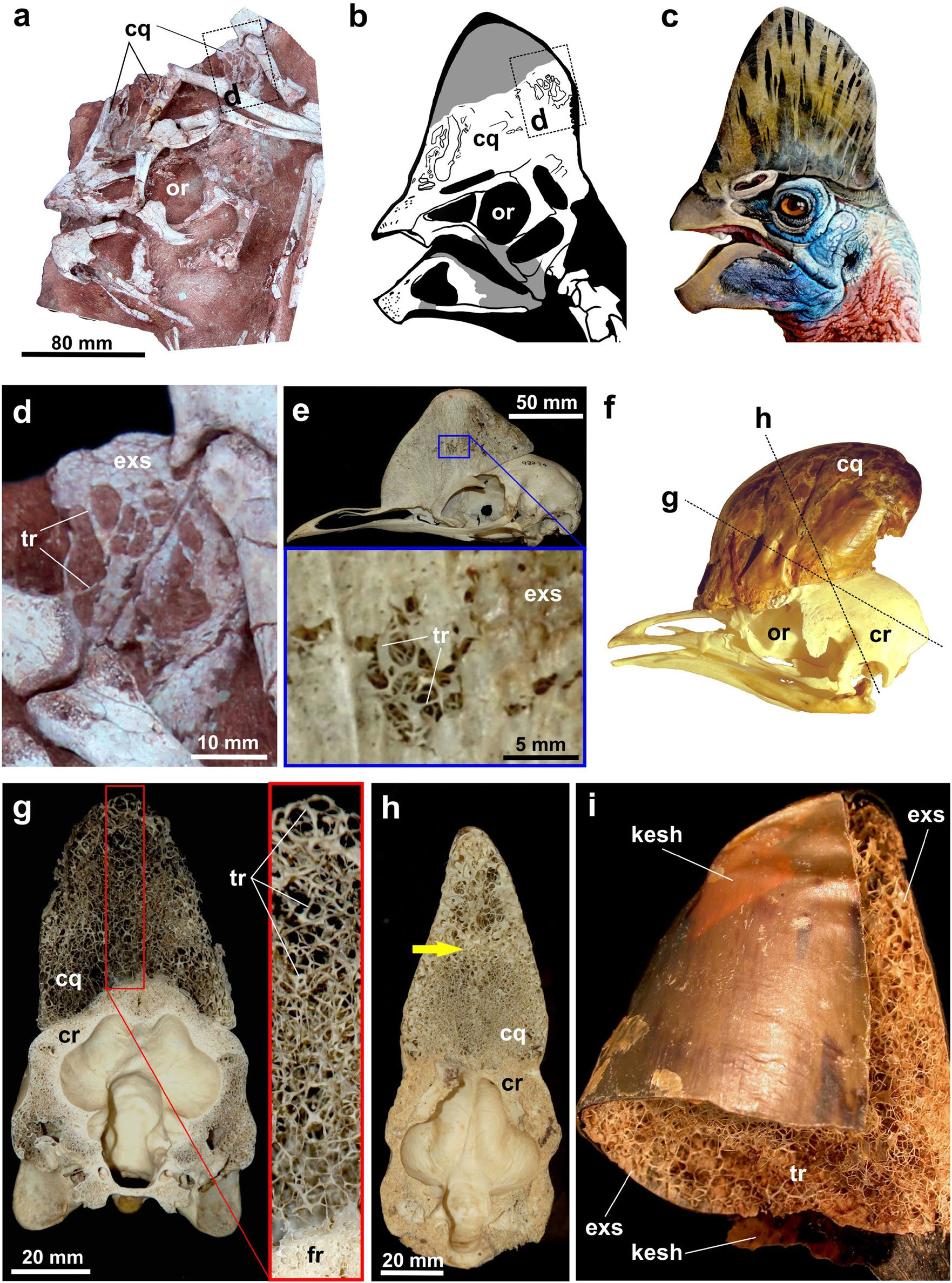 Based on
Based on
 Ganzhou is well renowned for its oviraptorid diversity, yielding oviraptorid egg clutches, skeletons, and six other genera: '' Banji'', '' Jiangxisaurus'', ''Nankangia'', '' Ganzhousaurus'', ''
Ganzhou is well renowned for its oviraptorid diversity, yielding oviraptorid egg clutches, skeletons, and six other genera: '' Banji'', '' Jiangxisaurus'', ''Nankangia'', '' Ganzhousaurus'', ''
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial n ...
of oviraptorid
Oviraptoridae is a group of bird-like, herbivorous and omnivorous maniraptoran dinosaurs. Oviraptorids are characterized by their toothless, parrot-like beaks and, in some cases, elaborate crests. They were generally small, measuring between on ...
dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
from the late Maastrichtian Nanxiong Formation of South China. It contains one species, ''C. jacobsi'', known from a single well-preserved skeleton, and named after paleontologist Louis L. Jacobs
Louis Leo Jacobs (born August 27, 1948) is an American vertebrate paleontologist who discovered ''Malawisaurus'' while on an expedition in Malawi. Much of his research concerns the interrelationships of Biotic component, biotic and abiotic events ...
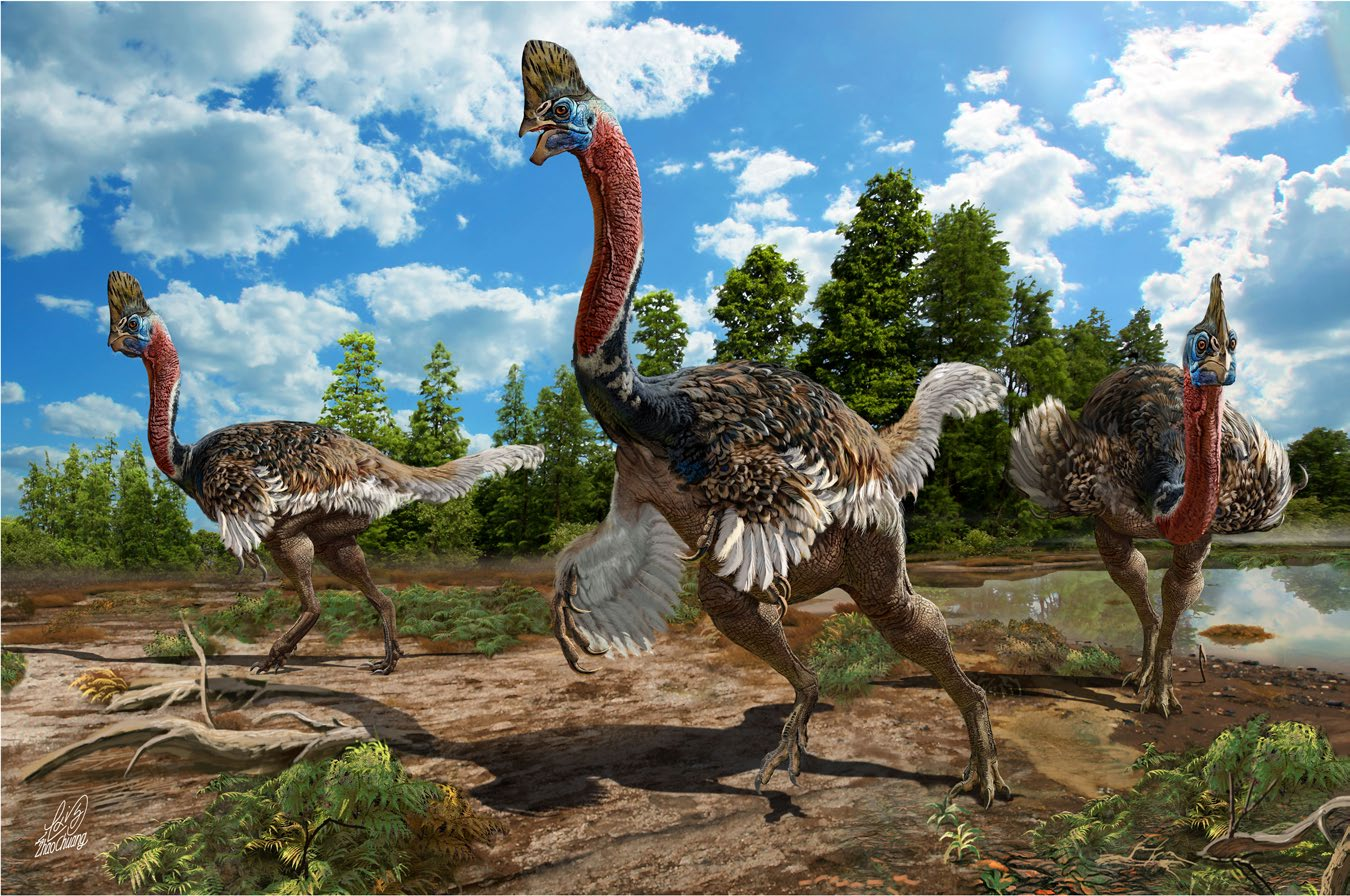
. It bears a tall crest similar to that of the modern cassowary
Cassowaries ( tpi, muruk, id, kasuari) are flightless birds of the genus ''Casuarius'' in the order Casuariiformes. They are classified as ratites (flightless birds without a keel on their sternum bones) and are native to the tropical ...
, and possibly had a similar functionality of display
Display may refer to:
Technology
* Display device, output device for presenting information, including:
** Cathode ray tube, video display that provides a quality picture, but can be very heavy and deep
** Electronic visual display, output dev ...
and resonance to detect lower-frequency sounds.
Like other oviraptorids, the bones of ''Corythoraptor'' were heavily pneumatized with many air pockets. Microanalysis of the bones indicates seasonal growth spurts, and the type specimen
In biology, a type is a particular specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the ...
probably died at the age of 6 or 7, meaning growth continued into at least the 8th year of development. The type specimen reached in length. Oviraptorids may have predominantly inhabited arid environments and ate xerophytic
A xerophyte (from Greek ξηρός ''xeros'' 'dry' + φυτόν ''phuton'' 'plant') is a species of plant that has adaptations to survive in an environment with little liquid water, such as a desert such as the Sahara or places in the Alps or th ...
(drought-resistant) plants, nuts, and seeds. However, ''Corythoraptor'' coexisted with six other oviraptorid genera, and they may have all eaten different foods (niche partitioning
In ecology, niche differentiation (also known as niche segregation, niche separation and niche partitioning) refers to the process by which competing species use the environment differently in a way that helps them to coexist. The competitive exclu ...
).
Discovery
''Corythoraptor'' was described by Chinese paleontologist Lü Junchang and colleagues in 2017. Theholotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of seve ...
, JPM-2015-001, is a nearly complete skeleton of an individual at least seven or eight years old, lacking distal caudal vertebrae but including the skull and lower jaw (JPM-2015-001). It is one of better preserved oviraptorosaurian specimens known so far. It was discovered in the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', ...
Nanxiong Formation near the Ganzhou Railway Station in Ganzhou
Ganzhou (), alternately romanized as Kanchow, is a prefecture-level city in the south of Jiangxi province, China, bordering Fujian to the east, Guangdong to the south, and Hunan to the west. Its administrative seat is at Zhanggong District.
Hist ...
, Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in the east of the People's Republic of China. Its major cities include Nanchang and Jiujiang. Spanning from the banks of the Yangtze river in the north into h ...
, in South China. The specimen is now kept at the Jinzhou Paleontological Museum in Jinzhou
Jinzhou (, ), formerly Chinchow, is a coastal prefecture-level city in central-west Liaoning province, China. It is a geographically strategic city located in the Liaoxi Corridor, which connects most of the land transports between North Chi ...
, Liaoning Province
Liaoning () is a coastal province in Northeast China that is the smallest, southernmost, and most populous province in the region. With its capital at Shenyang, it is located on the northern shore of the Yellow Sea, and is the northernmost ...
. It was not in a typical death pose
Non-avian dinosaur and bird fossils are frequently found in a characteristic posture consisting of head thrown back, tail extended, and mouth wide open. The cause of this posture—often called a "death pose"—has been a matter of scientific deba ...
, and the neck was in a circular curl much like the type specimen
In biology, a type is a particular specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the ...
for the contemporary oviraptorid '' Heyuannia''. What caused this is unclear.
The name ''Corythoraptor'' is in reference to the distinct crest on its head. The species name ''jacobsi'' honors American vertebrate paleontologist Louis L. Jacobs
Louis Leo Jacobs (born August 27, 1948) is an American vertebrate paleontologist who discovered ''Malawisaurus'' while on an expedition in Malawi. Much of his research concerns the interrelationships of Biotic component, biotic and abiotic events ...
who mentored three of the authors while they were getting their PhD's at Southern Methodist University
, mottoeng = " The truth will make you free"
, established =
, type = Private research university
, accreditation = SACS
, academic_affiliations =
, religious_affiliation = United Methodist Church
, president = R. Gerald Turner
, pr ...
, Dallas, Texas.
Description
Skull
 ''Corythoraptor'' bore a tall crest on its head similar to that of the modern
''Corythoraptor'' bore a tall crest on its head similar to that of the modern cassowary
Cassowaries ( tpi, muruk, id, kasuari) are flightless birds of the genus ''Casuarius'' in the order Casuariiformes. They are classified as ratites (flightless birds without a keel on their sternum bones) and are native to the tropical ...
, with a thick perhaps keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ...
ous bony shell casing. The crest is pneumatized and features several chambers separated by thin bony walls, though the crest of ''Corythoraptor'' is more pneumatized than that of the cassowary. This may have made the crest quite pliable, incapable of withstanding concussive force such as during head butting.
''Corythoraptor'' had a relatively large eyesocket
In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is , of ...
. The nasal bone
The nasal bones are two small oblong bones, varying in size and form in different individuals; they are placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face and by their junction, form the bridge of the upper one third of the nose.
Ea ...
s seem to be highly pneumatized. The lower part of the premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has ...
e (at the tip of the snout) features several irregularly distributed pits, which probably represent foramina
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (;Entry "foramen"
in
which allowed in
blood vessel
Blood vessels are the structures of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from ...
s to flow, indicating a keratinous sheath ( rhamphotheca) over a beak
The beak, bill, or rostrum is an external anatomical structure found mostly in birds, but also in turtles, non-avian dinosaurs and a few mammals. A beak is used for eating, preening, manipulating objects, killing prey, fighting, probing for fo ...
similar to ornithomimid
Ornithomimidae (meaning " bird-mimics") is a family of theropod dinosaurs which bore a superficial resemblance to modern ostriches. Ornithomimids were fast, omnivorous or herbivorous dinosaurs known mainly from the Late Cretaceous Period of ...
s. The ventral side (underside) of the premaxillae is highly broken up, which could indicate the bone was lightweight, perhaps being pneumatized. ''Corythoraptor'' was toothless.
Postcranial skeleton
''Corythoraptor'' has 12 neck vertebrae. The 6th and 11th vertebrae are the longest. There is a pleurocoel (an air pocket) on the 5th through 12th vertebrae located on the middle of each vertebra. The pleurocoel is nearly circular on the 5th vertebra, diameter , and ovular on the 6th, length . The articular surface (where a vertebra contacts another vertebra) on the anterior (headward) side is strongly concave, and the posterior (tailward) articular surface is moderately convex. The anterior articular surfaces are almost square and are wider than the posterior articular surfaces. Therib
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs ( la, costae) are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the chest, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the ch ...
s are fused to the vertebrae. The neural arches (which project outwards from the vertebrae) are densely pneumatized with several small air chambers.
It is unclear how many dorsal vertebrae ''Corythoraptor'' had because the specimen only preserves the first 6 vertebrae. The dorsal vertebrae are shorter than the neck vertebrae, but the 2nd and 3rd dorsal vertebrae have larger pleurocoels. The anterior articular surface is slightly concave, and the posterior articular surface nearly flat. Only the last 2 sacral vertebrae are preserved, and each are smooth, round, and bear a small pleurocoel. The rib of the last sacral vertebra is stout and touches the postacetabular process on the ilium
Ilium or Ileum may refer to:
Places and jurisdictions
* Ilion (Asia Minor), former name of Troy
* Ilium (Epirus), an ancient city in Epirus, Greece
* Ilium, ancient name of Cestria (Epirus), an ancient city in Epirus, Greece
* Ilium Building, a ...
of the pelvis. The first 5 tail vertebrae are preserved, of which the first 3 are complete. Both articular surfaces are flat. The pleurocoels are small and long on the first 2 vertebrae, and somewhat larger on the remaining. Like '' Nankangia'', there are 3 fossae (depressions) on the vertebrae except for the first one: the infraprezygapophyseal fossa on the anterior side near the junction of the prezygapophysis
The articular processes or zygapophyses ( Greek ζυγον = " yoke" (because it links two vertebrae) + απο = "away" + φυσις = " process") of a vertebra are projections of the vertebra that serve the purpose of fitting with an adjacent ver ...
(which locks two vertebrae together) and the transverse process (which juts out diagonally from the vertebra); the infradiapophyseal fossa at the base of the transverse process; and the pleurocoel. The neural arches are similar to those of ''Nankangia''.
 The left
The left humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a roun ...
is almost completely preserved, and makes up about 27% of the entire length of the arm, and 48% excluding the hand. Like other oviraptorids, the humerus is weakly twisted. The deltopectoral crest near the shoulder is short and runs across 31% of the humerus. The distal end (handward) is expanded and bears a well developed condyle (which forms the elbow joint). The ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of t ...
is slightly shorter than the humerus and makes up 26% of the entire arm length including the hand, and features a poorly developed olecranon
The olecranon (, ), is a large, thick, curved bony eminence of the ulna, a long bone in the forearm that projects behind the elbow. It forms the most pointed portion of the elbow and is opposite to the cubital fossa or elbow pit. The olecranon ...
(which also forms the elbow joint). The radius
In classical geometry, a radius ( : radii) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The name comes from the latin ''radius'', meaning ray but also the ...
is slightly shorter and narrower than the ulna, and is curved cranially which causes a gap between the radius and the ulna much like in ''Heyuannia''. The proximal end of the metacarpal
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus form the intermediate part of the skeletal hand located between the phalanges of the fingers and the carpal bones of the wrist, which forms the connection to the forearm. The metacarpal bones ...
s (at the wrist) are closely squeezed together. The first metacarpal bone (the thumb) is the shortest and is slightly concave on the underside. The second metacarpal bone is 41% longer than the first, and is moderately robust
Robustness is the property of being strong and healthy in constitution. When it is transposed into a system, it refers to the ability of tolerating perturbations that might affect the system’s functional body. In the same line ''robustness'' ca ...
with the shaft diameter being 13% of the total length. The third metacarpal bone is the same length as the second but 68% narrower. The phalanges
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones ...
(finger bones) are long and robust, the longest being the first phalanx about 72% longer than the second metacarpal, and the third phalanx is the smallest. The ungual
An ungual (from Latin ''unguis'', i.e. ''nail'') is a highly modified distal toe bone which ends in a hoof, claw, or nail. Elephants and ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammal ...
s (claws) are weakly curved, and decrease in size and curvature from first to third finger.
''Corythoraptor'', being a saurischia
Saurischia ( , meaning "reptile-hipped" from the Greek ' () meaning 'lizard' and ' () meaning 'hip joint') is one of the two basic divisions of dinosaurs (the other being Ornithischia), classified by their hip structure. Saurischia and Ornithi ...
n, had a saurischian hip. Like other late oviraptorids (except '' Nomingia''), the pubis bone
In vertebrates, the pubic region ( la, pubis) is the most forward-facing (ventral and anterior) of the three main regions making up the coxal bone. The left and right pubic regions are each made up of three sections, a superior ramus, inferior ra ...
is concave cranially. Like other oviraptorids, the obturator process is midway on the shaft of the ischium
The ischium () form ...
and is triangular. The femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates wit ...
is longer than the ilium and makes up 30% of the total leg length including the foot. The greater trochanter
The greater trochanter of the femur is a large, irregular, quadrilateral eminence and a part of the skeletal system.
It is directed lateral and medially and slightly posterior. In the adult it is about 2–4 cm lower than the femoral head.Stan ...
on the head of the femur is massive, and the lesser trochanter may have fused with it. There is a rough muscular scar where the fourth trochanter is expected to be, similar to '' Citipati'' and '' Khaan''. The tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects ...
is 19% longer than the femur, and features a pronounced cnemial crest The cnemial crest is a crestlike prominence located at the front side of the head of the tibiotarsus or tibia in the legs of many mammals and reptiles (including birds and other dinosaurs). The main extensor muscle of the thigh
In human ana ...
running along half of its length. The foot is 29% the length of the leg. Like other theropod
Theropoda (; ), whose members are known as theropods, is a dinosaur clade that is characterized by hollow bones and three toes and claws on each limb. Theropods are generally classed as a group of saurischian dinosaurs. They were ancestrally ...
s, the phalangeal formula
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones ...
(the number of phalanges per digit) is 2-3-4-5. The 3rd digit is the longest, and the 4th is slightly longer than the 2nd. The toe claws are moderately curved.
Classification
''Corythoraptor'' is anoviraptorid
Oviraptoridae is a group of bird-like, herbivorous and omnivorous maniraptoran dinosaurs. Oviraptorids are characterized by their toothless, parrot-like beaks and, in some cases, elaborate crests. They were generally small, measuring between on ...
, and phylogenetic analysis
In biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that pro ...
recovers it in a clade with ''Huanansaurus
''Huanansaurus'' is an extinct genus of oviraptorid dinosaur that lived approximately 72 million years ago, between the Campanian and Maastrichtian, during the latter part of the Cretaceous period in what is now China, in the Nanxiong Formation.
...
'', and closely related to '' Citipati'', the Zamyn Khondt oviraptorid
This list of informally named dinosaurs is a listing of dinosaurs (excluding Aves; birds and their extinct relatives) that have never been given formally published scientific names. This list only includes names that were not properly published ...
, ''Rinchenia
''Rinchenia'' (named after Byambyn Rinchen) is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous epoch in what is now Mongolia, Nemegt Formation, around 70 million years ago. The type and only known species, ''Rinch ...
'', and ''Oviraptor
''Oviraptor'' (; ) is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period. The first remains were collected from the Djadokhta Formation of Mongolia in 1923 during a paleontological expedition led by Roy Chapma ...
''. There was a high oviraptorid diversity in the Late Cretaceous of South China, with representatives of three different oviraptorid clades. Below is a family tree of Oviraptoridae based on Lü ''et al.'', 2017 (bolded species inhabited South China):
Paleobiology
Diet
The jaw structure of oviraptorids is similar to those of herbivorousdicynodonts
Dicynodontia is an extinct clade of anomodonts, an extinct type of non-mammalian therapsid. Dicynodonts were herbivorous animals with a pair of tusks, hence their name, which means 'two dog tooth'. Members of the group possessed a horny, typica ...
, parrot
Parrots, also known as psittacines (), are birds of the roughly 398 species in 92 genera comprising the order Psittaciformes (), found mostly in tropical and subtropical regions. The order is subdivided into three superfamilies: the Psittaco ...
s, and tortoise
Tortoises () are reptiles of the family Testudinidae of the order Testudines (Latin: ''tortoise''). Like other turtles, tortoises have a shell to protect from predation and other threats. The shell in tortoises is generally hard, and like ot ...
s; oviraptorids are usually quite abundant which is typical of an herbivore; and ''Caudipteryx
''Caudipteryx'' (which means "tail feather") is a genus of peacock-sized theropod dinosaurs that lived in the Barremian age of the early Cretaceous (about 124.6 million years ago). They were feathered and extremely birdlike in their overall app ...
'' was found with gastroliths
A gastrolith, also called a stomach stone or gizzard stone, is a rock held inside a gastrointestinal tract. Gastroliths in some species are retained in the muscular gizzard and used to grind food in animals lacking suitable grinding teeth. In othe ...
(stomach stones) which some herbivores use to aid in digesting tough plant matter, which all may indicate oviraptorids were herbivorous. It is unclear what plants they ate because the paleofloral assemblages of Late Cretaceous China is poorly known, which suggestions for xerophytic
A xerophyte (from Greek ξηρός ''xeros'' 'dry' + φυτόν ''phuton'' 'plant') is a species of plant that has adaptations to survive in an environment with little liquid water, such as a desert such as the Sahara or places in the Alps or th ...
(drought-resistant) plants as oviraptorids are typically found in arid environments, as well as nuts and seeds. It has also been proposed they ate shellfish
Shellfish is a colloquial and fisheries term for exoskeleton-bearing aquatic invertebrates used as food, including various species of molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish are harvested from saltwater env ...
, but the jaws do not appear to have been well-equipped to crush shells, and the arid environment probably did not sustain a high enough shellfish population.
Because six different oviraptorid species are known from Ganzhou, they may have exhibited niche partitioning
In ecology, niche differentiation (also known as niche segregation, niche separation and niche partitioning) refers to the process by which competing species use the environment differently in a way that helps them to coexist. The competitive exclu ...
, with different species targeting different foods.
Ontogeny
 Based on
Based on histological
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures vis ...
analysis on a portion of the fibula
The fibula or calf bone is a human leg, leg bone on the Lateral (anatomy), lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long ...
and radius, the growth marks indicate the holotype was older than 6 or 7 years when it died. A portion of the radius bears 3 distinct dark bands which indicate periods of arrested growth, which points to seasonal growth spurts. Because growth restarted near the edge of the bone, the specimen probably died at the beginning of a new growing season and therefore was still a young adult which had not yet reached its maximum size. If the crest did serve as a mating display, this would suggest ''Corythoraptor'' was sexually active before it finished growing, and that growth continued for more than 8 years. At this point in its development, ''Corythoraptor'' reached about in length, which is medium-sized for an oviraptorid.
Function of crest
The crest of ''Corythoraptor'' is apparently quite similar to the casque of the moderncassowary
Cassowaries ( tpi, muruk, id, kasuari) are flightless birds of the genus ''Casuarius'' in the order Casuariiformes. They are classified as ratites (flightless birds without a keel on their sternum bones) and are native to the tropical ...
. The cassowary uses its casque to dissipate heat from the brain cavity, and as an resonator to aid in the detection or gauge the point of origin of low frequency signals across a greater distance. In ''Corythoraptor'', the latter may have been used to hear predators or prey items, or possibly to pick up low frequency mating calls as modern cassowaries do. However, it is unclear if ''Corythoraptor'' was capable of producing low frequencies since these are produced in the throat. It is also possible the crests were used for display
Display may refer to:
Technology
* Display device, output device for presenting information, including:
** Cathode ray tube, video display that provides a quality picture, but can be very heavy and deep
** Electronic visual display, output dev ...
, with larger and more ornamented casques equating to higher ranking in the group hierarchy or better fitness during mating season, but cassowary casques do not vary very much between individuals. The cassowary-like crest, neck, and sharp claw may indicate ''Corythoraptor'' had a cassowary-like lifestyle.
Paleoenvironment
 Ganzhou is well renowned for its oviraptorid diversity, yielding oviraptorid egg clutches, skeletons, and six other genera: '' Banji'', '' Jiangxisaurus'', ''Nankangia'', '' Ganzhousaurus'', ''
Ganzhou is well renowned for its oviraptorid diversity, yielding oviraptorid egg clutches, skeletons, and six other genera: '' Banji'', '' Jiangxisaurus'', ''Nankangia'', '' Ganzhousaurus'', ''Huanansaurus
''Huanansaurus'' is an extinct genus of oviraptorid dinosaur that lived approximately 72 million years ago, between the Campanian and Maastrichtian, during the latter part of the Cretaceous period in what is now China, in the Nanxiong Formation.
...
'', and '' Tongtianlong''. The assemblage forms a distinct province, the "Ganzhou Dinosaurian Fauna". Other dinosaurs include the therizinosaurid
Therizinosauridae (meaning 'scythe lizards')Translated paper
is a family of derived (advanc ...
'' Nanshiungosaurus'', the tyrannosaurid '' Qianzhousaurus'', the is a family of derived (advanc ...
sauropod
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their ...
''Gannansaurus
''Gannansaurus'' (meaning " Gannan lizard") is an extinct genus of somphospondylan sauropod dinosaur known from the late Late Cretaceous Nanxiong Formation of Ganzhou Basin, Jiangxi Province of southern China. It is known from specimen GMNH F10 ...
'', and the hadrosaurid
Hadrosaurids (), or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod family, which incl ...
'' Microhadrosaurus''. Hadrosaurids are conspicuously rare. However, fossil trackway
A fossil track or ichnite (Greek "''ιχνιον''" (''ichnion'') – a track, trace or footstep) is a fossilized footprint. This is a type of trace fossil. A fossil trackway is a sequence of fossil tracks left by a single organism. Over the yea ...
s from the nearby Yangmeikeng area indicate an assemblage of predominantly ornithopod
Ornithopoda () is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs, called ornithopods (), that started out as small, bipedal running grazers and grew in size and numbers until they became one of the most successful groups of herbivores in the Cretaceous worl ...
s (hadrosaurids), but also nodosaurid
Nodosauridae is a family of ankylosaurian dinosaurs, from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous period in what is now North America, South America, Europe, and Asia.
Description
Nodosaurids, like their close relatives the ankylosaurids, w ...
s, therizinosaurids, tyrannosaurids, oviraptorids, coelurosauria
Coelurosauria (; from Greek, meaning "hollow tailed lizards") is the clade containing all theropod dinosaurs more closely related to birds than to carnosaurs.
Coelurosauria is a subgroup of theropod dinosaurs that includes compsognathids, ty ...
ns, deinonychosaurians, the bird '' Wupus'', sauropods (perhaps ''Gannansaurus
''Gannansaurus'' (meaning " Gannan lizard") is an extinct genus of somphospondylan sauropod dinosaur known from the late Late Cretaceous Nanxiong Formation of Ganzhou Basin, Jiangxi Province of southern China. It is known from specimen GMNH F10 ...
''), pterosaur
Pterosaurs (; from Greek ''pteron'' and ''sauros'', meaning "wing lizard") is an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the Order (biology), order, Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cre ...
s ('' Pteraichnus''), and turtle
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked ...
s (perhaps '' Jiangxichelys''). The area was probably a lakeside environment.
See also
*Timeline of oviraptorosaur research
This timeline of oviraptorosaur research is a chronological listing of events in the history of paleontology focused on the oviraptorosaurs, a group of beaked, bird-like theropod dinosaurs. The early history of oviraptorosaur paleontology is cha ...
*2017 in archosaur paleontology
The year 2017 in archosaur paleontology was eventful. Archosaurs include the only living dinosaur group — birds — and the reptile crocodilians, plus all extinct dinosaurs, extinct crocodilian relatives, and pterosaurs. Archosaur palaeontology ...
References
{{Portal bar, Dinosaurs, Cretaceous, China Late Cretaceous dinosaurs of Asia Oviraptorids Fossil taxa described in 2017 Paleontology in Jiangxi