|
Otho F
Marcus Otho (; born Marcus Salvius Otho; 28 April 32 – 16 April 69) was the seventh Roman emperor, ruling for three months from 15 January to 16 April 69. He was the second emperor of the Year of the Four Emperors. A member of a noble Etruscan family, Otho was initially a friend and courtier of the young emperor Nero until he was effectively banished to the governorship of the remote province of Lusitania in 58 following his wife Poppaea Sabina's affair with Nero. After a period of moderate rule in the province, he allied himself with Galba, the governor of neighbouring Hispania Tarraconensis, during the revolts of 68. He accompanied Galba on his march to Rome, but revolted and murdered Galba at the start of the next year. Inheriting the problem of the rebellion of Vitellius, commander of the army in Germania Inferior, Otho led a sizeable force which met Vitellius' army at the Battle of Bedriacum. After initial fighting resulted in 40,000 casualties, and a retreat of his fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusus and Antonia Minor at Lugdunum in Roman Gaul, where his father was stationed as a military legate. He was the first Roman emperor to be born outside Italia (Roman Empire), Italy. Nonetheless, Claudius was an Italian of Sabine origins. As he had a limp and slight deafness due to sickness at a young age, he was ostracized by his family and was excluded from public office until his Roman consul, consulship (which was shared with his nephew, Caligula, in 37). Claudius's infirmity probably saved him from the fate of many other nobles during the purges throughout the reigns of Tiberius and Caligula, as potential enemies did not see him as a serious threat. His survival led to him being declared emperor by the Praetorian Guard after Caligula's a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aulus Marius Celsus
Aulus Marius Celsus was a Roman senator who held several offices in the emperor's service during the first century AD, as well as playing a role in the Year of Four Emperors. He was suffect consul of the ''nundinium'' of July to August 69 as the colleague of Gnaeus Arrius Antoninus. Life Ronald Syme suggests that Marius Celsus was a native of Nemausus in Gallia Narbonensis (modern Nîmes), based on the existence of Gaius Marius Celsus, a magistrate of that city and husband of Pompeia the daughter of Toutodivix. His career began under Nero. Celsus' earliest known appointment was ''legatus legionis'' or commander of the Legio XV Apollinaris, first in Pannonia, then in Asia Minor. Nero designated Celsus suffect consul for a designated ''nundinium'' in 69 before his death. After the suicide of Nero, Galba made him part of his inner circle; Celsus was present, along with Aulus Ducenius Geminus, Urban prefect, when Galba announced Piso Licinianus as his choice for his heir. Then Cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
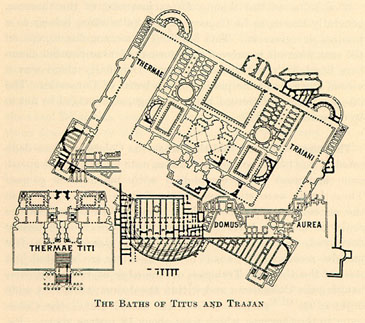
Domus Aurea
The Domus Aurea (Latin, "Golden House") was a vast landscaped complex built by the Emperor Nero largely on the Oppian Hill in the heart of ancient Rome after the great fire in 64 AD had destroyed a large part of the city.Roth (1993) It replaced and extended his Domus Transitoria that he had built as his first palace complex on the site. History The Domus Aurea was probably never completed. Otho and possibly Titus allotted money to finish at least the structure on the Oppian Hill; this continued to be inhabited, notably by emperor Vitellius in 69 but only after falling ill, until it was destroyed in a fire under Trajan in 104. A symbol of decadence that caused severe embarrassment to Nero's successors, the Domus Aurea was stripped of its marble, jewels, and ivory within a decade. Although the Oppian villa continued to be inhabited for some years, soon after Nero's death other parts of the palace and grounds, encompassing 2.6 km2 (c. 1 mi2), were filled with earth a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporus
Sporus was a young slave boy whom the Roman Emperor Nero favored, had castrated, and married.Champlin, 2005, p.145Smith, 1849, p.897 Life Little is known about Sporus' background except that he was a youth to whom Nero took a liking. He may have been a ''puer delicatus'', who were sometimes castrated to preserve their youthful qualities. The ''puer delicatus'' generally was a child-slave chosen by his master for his beauty and sexual attractiveness. Cassius Dio identifies Sporus as the child of a freedman. Marriage to Nero Nero's wife, Poppaea Sabina, died in 65 AD. This was supposedly in childbirth, although it was later rumored Nero kicked her to death. At the beginning of 66, Nero married Statilia Messalina. Later that year or in 67, he married Sporus, who was said to bear a remarkable resemblance to Poppaea. Nero had Sporus castrated, and during their marriage, Nero had Sporus appear in public as his wife wearing the regalia that was customary for Roman empresses. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effeminacy
Effeminacy is the embodiment of traits and/or expressions in those who are not of the female sex (e.g. boys and men) that are often associated with what is generally perceived to be feminine behaviours, mannerisms, styles, or gender roles, rather than with traditionally masculine behaviours, mannerisms, styles or roles. Effeminacy and other gender expressions are independent of a person's sexuality or sexual identity and are displayed by people of all sexualities and none. However, effeminacy is seen in some societies as something embodied by some in the homosexual male community. The embodiment of effeminacy by people in some societies has resulted in prejudice, discrimination, antagonism and insults towards those who display it. History Terminology ''Effeminate'' comes from Latin '' effeminātus'', from the factitive prefix ''ex-'' (from ''ex'' 'out') and ''femina'' 'woman'; it means 'made feminine, emasculated, weakened'. Another Latin term is ''mollities'', meaning 'soft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognomen
A ''cognomen'' (; plural ''cognomina''; from ''con-'' "together with" and ''(g)nomen'' "name") was the third name of a citizen of ancient Rome, under Roman naming conventions. Initially, it was a nickname, but lost that purpose when it became hereditary. Hereditary ''cognomina'' were used to augment the second name, the ''nomen gentilicium'' (the family name, or clan name), in order to identify a particular branch within a family or family within a clan. The term has also taken on other contemporary meanings. Roman names Because of the limited nature of the Latin '' praenomen'', the ''cognomen'' developed to distinguish branches of the family from one another, and occasionally, to highlight an individual's achievement, typically in warfare. One example of this is Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus, whose cognomen ''Magnus'' was earned after his military victories under Sulla's dictatorship. The ''cognomen'' was a form of distinguishing people who accomplished important feats, and those who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Calpurnius Piso Licinianus
Lucius Calpurnius Piso Frugi Licinianus (38 – 15 January 69) was a Roman nobleman who lived in the 1st century. He was adopted by the Roman Emperor Galba as his heir to the throne, only to be killed during the Year of Four Emperors on the same day as Galba. Life Licinianus was a nobleman of the highest ancient birth. Licinianus was one among the sons of Marcus Licinius Crassus Frugi (consul 27) and Scribonia. By birth and adoption through his father, Licinianus was of the ''gens Licinia''. From his name, it appears he was likely adopted into the '' gens Calpurnia'', but by whom is uncertain. Licinianus’ maternal grandparents were both direct descendants of Pompeia, the daughter of triumvir Pompey from third marriage to Mucia Tertia. His paternal grandfather was consul and governor Marcus Licinius Crassus, (consul 14 BC). Crassus was the adoptive son of consul and general Marcus Licinius Crassus (consul 30 BC), the grandson of triumvir Marcus Licinius Crassus. He was the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aulus Vitellius
The gens Vitellia was a family of ancient Rome, which rose from obscurity in imperial times, and briefly held the Empire itself in AD 69. The first of this gens to obtain the consulship was Aulus Vitellius, uncle of the emperor Vitellius, in AD 32.''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology'', vol. III, p. 1272 ("Vitellii"). Origin Suetonius relates two conflicting accounts of the Vitellii, which he ascribes to the emperor's flatterers and his detractors, respectively. According to the first account, the family was descended from Faunus, King of the Aborigines, and Vitellia, who ruled over Latium in the distant past, and were later regarded as two of the indigenous deities. The Vitellii were Sabines, who migrated to Rome under the monarchy, and were enrolled among the patricians. One family of the Vitellii settled at Nuceria Apulorum in the time of the Samnite Wars, and it was from this family that the emperor Vitellius was sprung.Suetonius, "The Life of Vitelliu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
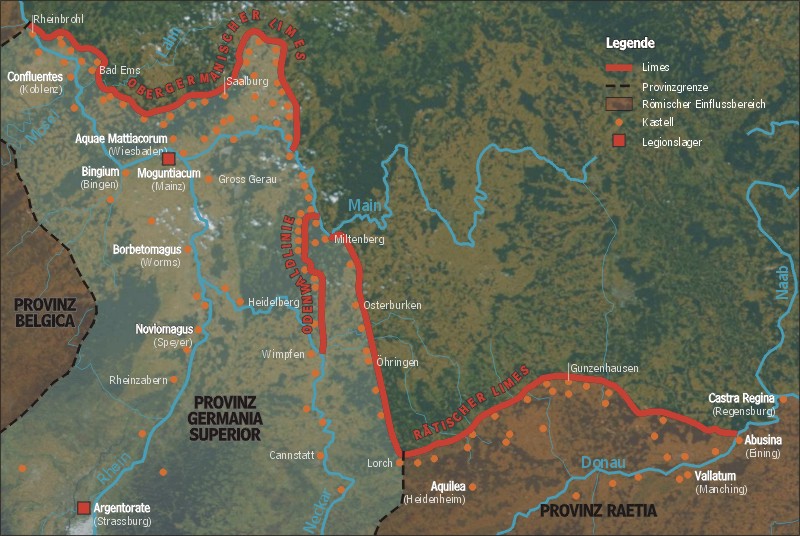
Lower Germany
Germania Inferior ("Lower Germania") was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed Germania Secunda in the fourth century, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Agrippinensis (modern-day Cologne). Geography According to Ptolemy (2.9), Germania Inferior included the Rhine from its mouth up to the mouth of the ''Obringa'', a river identified with either the Aar or the Moselle. The territory included modern-day Luxembourg, the southern Netherlands, part of Belgium, and part of North Rhine-Westphalia in Germany, west of the Rhine. The principal settlements of the province were Castra Vetera and Colonia Ulpia Traiana (both near Xanten), Coriovallum (Heerlen), Albaniana ( Alphen aan den Rijn), Lugdunum Batavorum (Katwijk), Forum Hadriani (Voorburg), Ulpia Noviomagus Batavorum ( Nijmegen), Traiectum (Utrecht), Atuatuca Tungrorum (Tongeren), Bona (Bonn), and Colonia Agrippinensis (Cologne), the capital of Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Germany
Germania Superior ("Upper Germania") was an imperial province of the Roman Empire. It comprised an area of today's western Switzerland, the French Jura and Alsace regions, and southwestern Germany. Important cities were Besançon ('' Vesontio''), Strasbourg (''Argentoratum''), Wiesbaden ('' Aquae Mattiacae''), and Germania Superior's capital, Mainz (''Mogontiacum''). It comprised the Middle Rhine, bordering on the ''Limes Germanicus'', and on the Alpine province of Raetia to the south-east. Although it had been occupied militarily since the reign of Augustus, Germania Superior (along with Germania Inferior) was not made into an official province until c. 85 AD. Origin Initial Roman involvement The terms, "Upper Germania" and "Lower Germania" do not appear in the ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'' of Julius Caesar, yet he writes about reports that the people who lived in those regions were referred to as "Germani" locally, a term used for a tribe that the Romans called the Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titus Vinius
Titus Vinius (12 – 69) was a Roman general and one of the most powerful men in Rome during the reign of the Emperor Galba. Stories Plutarch has a number of stories of Vinius' early life, all to his discredit. He says that when, as a young man, he was serving in his first campaign, he brought his commander's wife into the camp by night disguised as a soldier, and had sex with her in the general's quarters. He was imprisoned for this by Caligula, but on that emperor's death was released. Later on, again according to Plutarch and Tacitus, when he was invited to supper by the emperor Claudius he stole a gold drinking cup. Claudius was told of this, and invited him to supper again the following evening. When Vinius came, Claudius made his point by having his attendants set earthenware plates before him instead of silver. Nevertheless, Tacitus, who elsewhere describes him as "the most worthless of mankind", says that as proconsul of Gallia Narbonensis he administered the province ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |