|
Orbit Portrait
In mathematics, an orbit portrait is a combinatorial tool used in complex dynamics for understanding the behavior of one-complex dimensional quadratic maps. In simple words one can say that it is : * a list of external angles for which rays land on points of that orbit * graph showing above list Definition Given a quadratic map :f_c : z \to z^2 + c. from the complex plane to itself :f_c : \mathbb \to \mathbb and a repelling or parabolic periodic orbit = \ of f, so that f(z_j) = z_ (where subscripts are taken 1 + modulo n), let A_j be the set of angles whose corresponding external rays land at z_j. Then the set = () = \ is called the orbit portrait of the periodic orbit . All of the sets A_j must have the same number of elements, which is called the valence of the portrait. Examples Parabolic or repelling orbit portrait valence 2 = \left \{\left( \frac{1}{3},\frac{2}{3} \right) \right \rbrace {\mathcal P} = \left \{ \left( \frac{3}{7} , \frac{4}{7} \righ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julia Set With 3 External Rays
Julia is usually a feminine given name. It is a Latinate feminine form of the name Julio and Julius. (For further details on etymology, see the Wiktionary entry "Julius".) The given name ''Julia'' had been in use throughout Late Antiquity (e.g. Julia of Corsica) but became rare during the Middle Ages, and was revived only with the Italian Renaissance. It became common in the English-speaking world only in the 18th century. Today, it is frequently used throughout the world. Statistics Julia was the 10th most popular name for girls born in the United States in 2007 and the 88th most popular name for women in the 1990 census there. It has been among the top 150 names given to girls in the United States for the past 100 years. It was the 89th most popular name for girls born in England and Wales in 2007; the 94th most popular name for girls born in Scotland in 2007; the 13th most popular name for girls born in Spain in 2006; the 5th most popular name for girls born in Sweden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
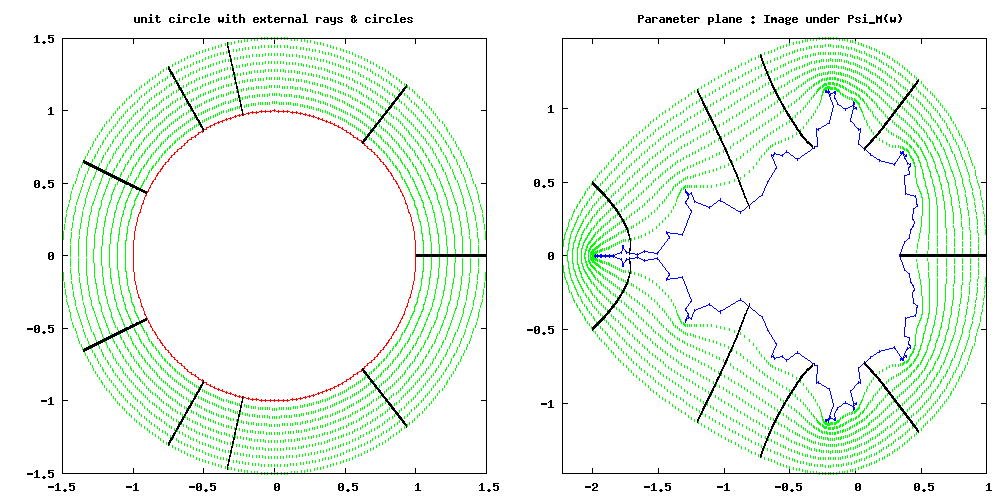
Mandelbrot Set
The Mandelbrot set () is the set of complex numbers c for which the function f_c(z)=z^2+c does not diverge to infinity when iterated from z=0, i.e., for which the sequence f_c(0), f_c(f_c(0)), etc., remains bounded in absolute value. This set was first defined and drawn by Robert W. Brooks and Peter Matelski in 1978, as part of a study of Kleinian groups. Afterwards, in 1980, Benoit Mandelbrot obtained high-quality visualizations of the set while working at IBM's Thomas J. Watson Research Center in Yorktown Heights, New York. Images of the Mandelbrot set exhibit an elaborate and infinitely complicated boundary that reveals progressively ever-finer recursive detail at increasing magnifications; mathematically, one would say that the boundary of the Mandelbrot set is a ''fractal curve''. The "style" of this recursive detail depends on the region of the set boundary being examined. Mandelbrot set images may be created by sampling the complex numbers and testing, for each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Ray
An external ray is a curve that runs from infinity toward a Julia or Mandelbrot set. Although this curve is only rarely a half-line (ray) it is called a ray because it is an image of a ray. External rays are used in complex analysis, particularly in complex dynamics and geometric function theory. History External rays were introduced in Douady and Hubbard's study of the Mandelbrot set Types Criteria for classification : * plane : parameter or dynamic * map * bifurcation of dynamic rays * Stretching * landing plane External rays of (connected) Julia sets on dynamical plane are often called dynamic rays. External rays of the Mandelbrot set (and similar one-dimensional connectedness loci) on parameter plane are called parameter rays. bifurcation Dynamic ray can be: * bifurcated = branched = broken * smooth = unbranched = unbroken When the filled Julia set is connected, there are no branching external rays. When the Julia set is not connected then some external r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julia Set
In the context of complex dynamics, a branch of mathematics, the Julia set and the Fatou set are two complementary sets (Julia "laces" and Fatou "dusts") defined from a function. Informally, the Fatou set of the function consists of values with the property that all nearby values behave similarly under repeated iteration of the function, and the Julia set consists of values such that an arbitrarily small perturbation can cause drastic changes in the sequence of iterated function values. Thus the behavior of the function on the Fatou set is "regular", while on the Julia set its behavior is "chaotic". The Julia set of a function is commonly denoted \operatorname(f), and the Fatou set is denoted \operatorname(f). These sets are named after the French mathematicians Gaston Julia and Pierre Fatou whose work began the study of complex dynamics during the early 20th century. Formal definition Let f(z) be a non-constant holomorphic function from the Riemann sphere on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Milnor
John Willard Milnor (born February 20, 1931) is an American mathematician known for his work in differential topology, algebraic K-theory and low-dimensional holomorphic dynamical systems. Milnor is a distinguished professor at Stony Brook University and one of the five mathematicians to have won the Fields Medal, the Wolf Prize, and the Abel Prize (the others being Serre, Thompson, Deligne, and Margulis.) Early life and career Milnor was born on February 20, 1931, in Orange, New Jersey. His father was J. Willard Milnor and his mother was Emily Cox Milnor. As an undergraduate at Princeton University he was named a Putnam Fellow in 1949 and 1950 and also proved the Fáry–Milnor theorem when he was only 19 years old. Milnor graduated with an A.B. in mathematics in 1951 after completing a senior thesis, titled "Link groups", under the supervision of Robert H. Fox. He remained at Princeton to pursue graduate studies and received his Ph.D. in mathematics in 1954 after completi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doubling Map
The dyadic transformation (also known as the dyadic map, bit shift map, 2''x'' mod 1 map, Bernoulli map, doubling map or sawtooth map) is the mapping (i.e., recurrence relation) : T: , 1) \to [0, 1)^\infty : x \mapsto (x_0, x_1, x_2, \ldots) (where [0, 1)^\infty is the set of sequences from [0, 1)) produced by the rule : x_0 = x : \text n \ge 0,\ x_ = (2 x_n) \bmod 1. Equivalently, the dyadic transformation can also be defined as the iterated function map of the piecewise linear function : T(x)=\begin2x & 0 \le x < \frac \\2x-1 & \frac \le x < 1. \end The name ''bit shift map'' arises because, if the value of an iterate is written in notation, the next iterate is obtained by shifting the binary point one bit to the right, and if the bit to the left of the new binary point is a "one", replacing it with a zero. The dyadic transform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Quadratic Polynomial
A complex quadratic polynomial is a quadratic polynomial whose coefficients and variable are complex numbers. Properties Quadratic polynomials have the following properties, regardless of the form: *It is a unicritical polynomial, i.e. it has one finite critical point in the complex plane, Dynamical plane consist of maximally 2 basins: basin of infinity and basin of finite critical point ( if finite critical point do not escapes) *It can be postcritically finite, i.e. the orbit of the critical point can be finite, because the critical point is periodic or preperiodic. * It is a unimodal function, * It is a rational function, * It is an entire function. Forms When the quadratic polynomial has only one variable (univariate), one can distinguish its four main forms: * The general form: f(x) = a_2 x^2 + a_1 x + a_0 where a_2 \ne 0 * The factored form used for the logistic map: f_r(x) = r x (1-x) * f_(x) = x^2 +\lambda x which has an indifferent fixed point with multiplier \ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parabolic Julia Set C = -1
Parabolic usually refers to something in a shape of a parabola, but may also refer to a parable. Parabolic may refer to: *In mathematics: **In elementary mathematics, especially elementary geometry: ** Parabolic coordinates **Parabolic cylindrical coordinates ** parabolic Möbius transformation **Parabolic geometry (other) ** Parabolic spiral **Parabolic line **In advanced mathematics: ***Parabolic cylinder function ***Parabolic induction ***Parabolic Lie algebra ***Parabolic partial differential equation *In physics: **Parabolic trajectory *In technology: **Parabolic antenna **Parabolic microphone **Parabolic reflector **Parabolic trough - a type of solar thermal energy collector **Parabolic flight - a way of achieving weightlessness ** Parabolic action, or parabolic bending curve - a term often used to refer to a progressive bending curve in fishing rods. *In commodities and stock markets: **Parabolic SAR - a chart pattern in which prices rise or fall with an increasingly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Analytic Dynamics
Complex commonly refers to: * Complexity, the behaviour of a system whose components interact in multiple ways so possible interactions are difficult to describe ** Complex system, a system composed of many components which may interact with each other * Complex (psychology), a core pattern of emotions etc. in the personal unconscious organized around a common theme such as power or status Complex may also refer to: Arts, entertainment and media * Complex (English band), formed in 1968, and their 1971 album ''Complex'' * Complex (band), a Japanese rock band * ''Complex'' (album), by Montaigne, 2019, and its title track * ''Complex'' (EP), by Rifle Sport, 1985 * "Complex" (song), by Gary Numan, 1979 * Complex Networks, publisher of magazine ''Complex'', now online Biology * Protein–ligand complex, a complex of a protein bound with a ligand * Exosome complex, a multi-protein intracellular complex * Protein complex, a group of two or more associated polypeptide chains * Spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Ray
An external ray is a curve that runs from infinity toward a Julia or Mandelbrot set. Although this curve is only rarely a half-line (ray) it is called a ray because it is an image of a ray. External rays are used in complex analysis, particularly in complex dynamics and geometric function theory. History External rays were introduced in Douady and Hubbard's study of the Mandelbrot set Types Criteria for classification : * plane : parameter or dynamic * map * bifurcation of dynamic rays * Stretching * landing plane External rays of (connected) Julia sets on dynamical plane are often called dynamic rays. External rays of the Mandelbrot set (and similar one-dimensional connectedness loci) on parameter plane are called parameter rays. bifurcation Dynamic ray can be: * bifurcated = branched = broken * smooth = unbranched = unbroken When the filled Julia set is connected, there are no branching external rays. When the Julia set is not connected then some external r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |