|
Operation Gearbox II
Operation Gearbox II (17 September 1942 – 7 September 1943) was a Norwegian and British operation during the Second World War on the Arctic island of Spitsbergen in the Svalbard Archipelago. Operation Fritham, the first attempt to establish a base had been defeated when the two ships carrying the force were sunk by bombers on 14 May. In Operation Gearbox (30 June – 17 September 1942), 57 Norwegian reinforcements with of supplies had arrived by cruiser on 2 July. The reinforcements consolidated the defences of the former settlement at Barentsburg and made preparations for Gearbox II, another reinforcement of the Norwegians and part of the plan for Convoy PQ 18, to prevent a repeat of Convoy PQ 17 (27 June – 10 July 1942) in which 24 of the 35 freighters in the convoy had been sunk. Force P (the Spitsbergen Fuelling Force) comprising the fleet oilers and and four destroyer escorts, sailed from Scapa Flow on 3 September and anchored in Lowe Sound (Van Mijenfjorden) se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic Naval Operations Of World War II
The Arctic Circle defining the "midnight sun" encompasses the Atlantic Ocean from the northern edge of Iceland to the Bering Strait in the Pacific Ocean. Military activity in this area between 1939 and 1945 is often consideredRear Admiral Samuel Eliot Morison's definitive ''History of United States Naval Operations in World War II'' includes operations from the north pole southward in the first volume entitled ''The Battle of the Atlantic''. Eligibility for the United States European–African–Middle Eastern Campaign Medal was defined by Executive Order 9265 to include military service aboard a ship operating in the north polar region eastward from the 75th meridian west longitude to the 60th meridian east longitude. part of the Battle of the Atlantic or of the European Theatre of World War II. Pre-war navigation focused on fishing and the international ore-trade from Narvik and Petsamo. Soviet settlements along the coast and rivers of the Barents Sea and Kara Sea relied upo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isfjorden (Svalbard)
Isfjorden is the second longest fjord in the Norwegian archipelago of Svalbard. It lies on the west side of Spitsbergen, an island in the Arctic Ocean about midway between Norway and the North Pole, and the largest in the archipelago. The mountain of Alkhornet stands on the northern side of the entrance to the fjord, as does the coastal plain of Daudmannsøyra. A portion of Isfjorden is included in the national parks of Norway as Nordre Isfjorden Land National Park. Around the fjord lie many of the largest settlements in Svalbard: Barentsburg, Longyearbyen (on the Adventfjorden) and Pyramiden. History A Basque whaling ship from San Sebastian, under the command of Juan de Erauso and piloted by the Englishman Nicholas Woodcock, was the first to establish a temporary whaling station here in 1612. In 1613 French, Basque, and Dutch whaling ships resorted to Safehaven (Trygghamna) on the north side of Isford or in Green Harbour on the south side of the fjord. All were either dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
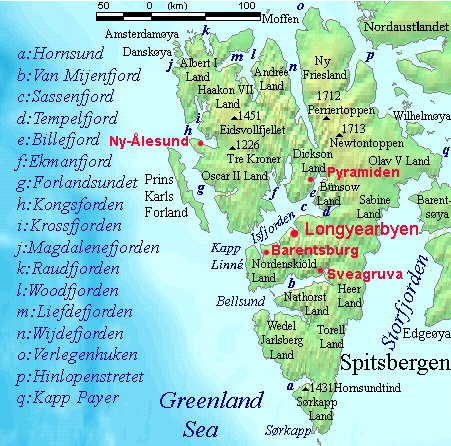
Topographic Map Of Svalbard
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps. Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary science and is concerned with local detail in general, including not only relief, but also natural, artificial, and cultural features such as roads, land boundaries, and buildings. In the United States, topography often means specifically ''relief'', even though the USGS topographic maps record not just elevation contours, but also roads, populated places, structures, land boundaries, and so on. Topography in a narrow sense involves the recording of relief or terrain, the three-dimensional quality of the surface, and the identification of specific landforms; this is also known as geomorphometry. In modern usage, this involves generation of elevation data in digital form (DEM). It is often considered to include the graphic representation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Naval Intelligence Service
The German Naval Intelligence Service (German: ''Marinenachrichtendienst'' (MND)) was the naval intelligence department of the Germany Navy and had a long history, going back to the naval aspirations of German emperor Wilhelm II in 1899. The department had various names throughout its existence. Between 1901 and 1919, the service was called the Nachrichten-Abteilung also known as N (English: Military intelligence department) and was the naval intelligence service of the Imperial German Navy. It focused its efforts on France, the United States and above all the United Kingdom, whose Royal Navy was Germany's principal rival for naval supremacy. Its activities had little practical impact on the course of the First World War and it was dissolved in 1919 after Germany's defeat in the war. After the war, saw the establishment of the observation service (B-Dienst) in 1918–1919. In spring 1925, the Naval Intelligence Division was disbanded and did not reform until October 1934 under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kriegsmarine
The (, ) was the navy of Germany from 1935 to 1945. It superseded the Imperial German Navy of the German Empire (1871–1918) and the inter-war (1919–1935) of the Weimar Republic. The was one of three official branches, along with the and the , of the , the German armed forces from 1935 to 1945. In violation of the Treaty of Versailles, the grew rapidly during German naval rearmament in the 1930s. The 1919 treaty had limited the size of the German navy and prohibited the building of submarines. ships were deployed to the waters around Spain during the Spanish Civil War (1936–1939) under the guise of enforcing non-intervention, but in reality supported the Nationalists against the Spanish Republicans. In January 1939, Plan Z, a massive shipbuilding program, was ordered, calling for surface naval parity with the British Royal Navy by 1944. When World War II broke out in September 1939, Plan Z was shelved in favour of a crash building program for submarines (U-boat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-Dienst
The ''B-Dienst'' (german: Beobachtungsdienst, observation service), also called x''B-Dienst'', X-''B-Dienst'' and χ''B-Dienst'', was a Department of the German Naval Intelligence Service (german: Marinenachrichtendienst, MND III) of the OKM, that dealt with the interception and recording, decoding and analysis of the enemy, in particular British radio communications before and during World War II. B-Dienst worked on cryptanalysis and deciphering (decrypting) of enemy and neutral states' message traffic and security control of ''Kriegsmarine'' key processes and machinery. :"The ultimate goal of all evaluation was recognizing the opponent's goal by pro-active identification of data." B-Dienst was instrumental in moulding Wehrmacht operations during the Battles of Norway and France in spring 1940, primarily due to the cryptanalysis successes it had achieved against early and less secure British Naval cyphers. B-Dienst broke British Naval Combined Cypher No. 3 in October 1941, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wireless Telegraphy
Wireless telegraphy or radiotelegraphy is transmission of text messages by radio waves, analogous to electrical telegraphy using cables. Before about 1910, the term ''wireless telegraphy'' was also used for other experimental technologies for transmitting telegraph signals without wires. In radiotelegraphy, information is transmitted by pulses of radio waves of two different lengths called "dots" and "dashes", which spell out text messages, usually in Morse code. In a manual system, the sending operator taps on a switch called a telegraph key which turns the transmitter on and off, producing the pulses of radio waves. At the receiver the pulses are audible in the receiver's speaker as beeps, which are translated back to text by an operator who knows Morse code. Radiotelegraphy was the first means of radio communication. The first practical radio transmitters and receivers invented in 1894–1895 by Guglielmo Marconi used radiotelegraphy. It continued to be the only type of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Y-stations
The "Y" service was a network of British signals intelligence collection sites, the Y-stations. The service was established during the First World War and used again during the Second World War. The sites were operated by a range of agencies including the Army, Navy and RAF plus the Foreign Office (MI6 and MI5), General Post Office and Marconi Company receiving stations ashore and afloat. There were more than 600 receiving sets in use at Y-stations during the Second World War. Background The "Y" stations tended to be of two types, for intercepting of the signals and for identifying where they were coming from. Sometimes both functions were operated at the same site, with the direction finding (D/F) hut being a few hundred metres from the main interception building, because of the need to minimise interference. The sites collected radio traffic which was then either analysed locally or if encrypted, passed for processing initially to the Admiralty Room 40 in London and during Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traffic Analysis
Traffic analysis is the process of intercepting and examining messages in order to deduce information from patterns in communication, it can be performed even when the messages are encrypted. In general, the greater the number of messages observed, the greater information be inferred. Traffic analysis can be performed in the context of military intelligence, counter-intelligence, or pattern-of-life analysis, and is also a concern in computer security. Traffic analysis tasks may be supported by dedicated computer software programs. Advanced traffic analysis techniques which may include various forms of social network analysis. Traffic analysis has historically been a vital technique in cryptanalysis, especially when the attempted crack depends on successfully seeding a known-plaintext attack, which often requires an inspired guess based on how specific the operational context might likely influence what an adversary communicates, which may be sufficient to establish a short crib. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bletchley Park
Bletchley Park is an English country house and estate in Bletchley, Milton Keynes ( Buckinghamshire) that became the principal centre of Allied code-breaking during the Second World War. The mansion was constructed during the years following 1883 for the financier and politician Sir Herbert Leon in the Victorian Gothic, Tudor, and Dutch Baroque styles, on the site of older buildings of the same name. During World War II, the estate housed the Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS), which regularly penetrated the secret communications of the Axis Powersmost importantly the German Enigma and Lorenz ciphers. The GC&CS team of codebreakers included Alan Turing, Gordon Welchman, Hugh Alexander, Bill Tutte, and Stuart Milner-Barry. The nature of the work at Bletchley remained secret until many years after the war. According to the official historian of British Intelligence, the "Ultra" intelligence produced at Bletchley shortened the war by two to four years, and without it th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Communications Headquarters
Government Communications Headquarters, commonly known as GCHQ, is an intelligence and security organisation responsible for providing signals intelligence (SIGINT) and information assurance (IA) to the government and armed forces of the United Kingdom. Primarily based at "The Doughnut" in the suburbs of Cheltenham, GCHQ is the responsibility of the country's Secretary of State for Foreign and Commonwealth Affairs (Foreign Secretary), but it is not a part of the Foreign Office and its Director ranks as a Permanent Secretary. GCHQ was originally established after the First World War as the Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) and was known under that name until 1946. During the Second World War it was located at Bletchley Park, where it was responsible for breaking the German Enigma codes. There are two main components of the GCHQ, the Composite Signals Organisation (CSO), which is responsible for gathering information, and the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |