Wireless Telegraphy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Wireless telegraphy or radiotelegraphy is transmission of text messages by
Wireless telegraphy or radiotelegraphy is transmission of text messages by
 US inventors William Henry Ward (1871) and Mahlon Loomis (1872) developed electrical conduction systems based on the erroneous belief that there was an electrified atmospheric stratum accessible at low altitude. They thought atmosphere current, connected with a return path using "Earth currents" would allow for wireless telegraphy as well as supply power for the telegraph, doing away with artificial batteries. A more practical demonstration of wireless transmission via conduction came in Amos Dolbear's 1879 magneto electric telephone that used ground conduction to transmit over a distance of a quarter of a mile.Christopher Cooper, The Truth About Tesla: The Myth of the Lone Genius in the History of Innovation, Race Point Publishing, 2015, page 165
In the 1890s inventor
US inventors William Henry Ward (1871) and Mahlon Loomis (1872) developed electrical conduction systems based on the erroneous belief that there was an electrified atmospheric stratum accessible at low altitude. They thought atmosphere current, connected with a return path using "Earth currents" would allow for wireless telegraphy as well as supply power for the telegraph, doing away with artificial batteries. A more practical demonstration of wireless transmission via conduction came in Amos Dolbear's 1879 magneto electric telephone that used ground conduction to transmit over a distance of a quarter of a mile.Christopher Cooper, The Truth About Tesla: The Myth of the Lone Genius in the History of Innovation, Race Point Publishing, 2015, page 165
In the 1890s inventor
 Wireless telegraphy or radiotelegraphy is transmission of text messages by
Wireless telegraphy or radiotelegraphy is transmission of text messages by radio wave
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies of 300 gigahertz ( GHz) and below. At 300 GHz, the corresponding wavelength is 1 mm (sho ...
s, analogous to electrical telegraphy using cables. Before about 1910, the term ''wireless telegraphy'' was also used for other experimental technologies for transmitting telegraph signals without wires. In radiotelegraphy, information is transmitted by pulses of radio waves of two different lengths called "dots" and "dashes", which spell out text messages, usually in Morse code
Morse code is a method used in telecommunication to encode text characters as standardized sequences of two different signal durations, called ''dots'' and ''dashes'', or ''dits'' and ''dahs''. Morse code is named after Samuel Morse, one ...
. In a manual system, the sending operator taps on a switch called a telegraph key
A telegraph key is a specialized electrical switch used by a trained operator to transmit text messages in Morse code in a telegraphy system. Keys are used in all forms of electrical telegraph systems, including landline (also called wire) t ...
which turns the transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to ...
on and off, producing the pulses of radio waves. At the receiver the pulses are audible in the receiver's speaker as beeps, which are translated back to text by an operator who knows Morse code.
Radiotelegraphy was the first means of radio communication. The first practical radio transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to ...
s and receivers invented in 1894–1895 by Guglielmo Marconi
Guglielmo Giovanni Maria Marconi, 1st Marquis of Marconi (; 25 April 187420 July 1937) was an Italian inventor and electrical engineer, known for his creation of a practical radio wave-based wireless telegraph system. This led to Marconi b ...
used radiotelegraphy. It continued to be the only type of radio transmission during the first few decades of radio, called the "wireless telegraphy era" up until World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, when the development of amplitude modulation (AM) radiotelephony allowed sound ( audio) to be transmitted by radio. Beginning about 1908, powerful transoceanic radiotelegraphy stations transmitted commercial telegram
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas ...
traffic between countries at rates up to 200 words per minute.
Radiotelegraphy was used for long-distance person-to-person commercial, diplomatic, and military text communication throughout the first half of the 20th century. It became a strategically important capability during the two world war
A world war is an international conflict which involves all or most of the world's major powers. Conventionally, the term is reserved for two major international conflicts that occurred during the first half of the 20th century, World War I, Worl ...
s since a nation without long-distance radiotelegraph stations could be isolated from the rest of the world by an enemy cutting its submarine telegraph cables. Radiotelegraphy remains popular in amateur radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency communi ...
. It is also taught by the military for use in emergency communications. However, commercial radiotelegraphy is obsolete.
Overview
Wireless telegraphy or radiotelegraphy, commonly called CW ( continuous wave), ICW (interrupted continuous wave) transmission, or on-off keying, and designated by theInternational Telecommunication Union
The International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Unio ...
as emission type A1A or A2A, is a radio communication
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transm ...
method. It was transmitted by several different modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the '' carrier signal'', with a separate signal called the ''modulation signal'' that typically contains informat ...
methods during its history. The primitive spark-gap transmitters used until 1920 transmitted damped waves, which had very wide bandwidth and tended to interfere with other transmissions. This type of emission was banned by 1934, except for some legacy use on ships.Individual nations enforce this prohibition in their communication laws. In the United States, this is the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) regulations: The vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied.
The type kn ...
(valve) transmitters which came into use after 1920 transmitted code by pulses of unmodulated sinusoidal carrier wave called continuous wave (CW), which is still used today. To receive CW transmissions, the receiver requires a circuit called a beat frequency oscillator (BFO). The third type of modulation, frequency-shift keying (FSK) was used mainly by radioteletype networks (RTTY). Morse code radiotelegraphy was gradually replaced by radioteletype in most high volume applications by World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
.
In manual radiotelegraphy the sending operator manipulates a switch
In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can disconnect or connect the conducting path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the electric current or diverting it from one conductor to another. The most common type ...
called a telegraph key
A telegraph key is a specialized electrical switch used by a trained operator to transmit text messages in Morse code in a telegraphy system. Keys are used in all forms of electrical telegraph systems, including landline (also called wire) t ...
, which turns the radio transmitter on and off, producing pulses of unmodulated carrier wave of different lengths called "dots" and "dashes", which encode characters of text in Morse code
Morse code is a method used in telecommunication to encode text characters as standardized sequences of two different signal durations, called ''dots'' and ''dashes'', or ''dits'' and ''dahs''. Morse code is named after Samuel Morse, one ...
. At the receiving location, Morse code is audible in the receiver's earphone or speaker as a sequence of buzzes or beeps, which is translated back to text by an operator who knows Morse code. With automatic radiotelegraphy teleprinter
A teleprinter (teletypewriter, teletype or TTY) is an electromechanical device that can be used to send and receive typed messages through various communications channels, in both point-to-point (telecommunications), point-to-point and point- ...
s at both ends use a code such as the International Telegraph Alphabet No. 2
The Baudot code is an early character encoding for telegraphy invented by Émile Baudot in the 1870s. It was the predecessor to the International Telegraph Alphabet No. 2 (ITA2), the most common teleprinter code in use until the advent of ASCII. ...
and produced typed text.
Radiotelegraphy is obsolete in commercial radio communication, and its last civilian use, requiring maritime shipping radio operators to use Morse code for emergency communications, ended in 1999 when the International Maritime Organization switched to the satellite-based GMDSS
The Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS) is a worldwide system for automated emergency signal communication for ships at sea developed by the United Nations' International Maritime Organization (IMO) as part of the SOLAS Convent ...
system. However it is still used by amateur radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency communi ...
operators, and military services require signalmen to be trained in Morse code for emergency communication. A CW coastal station, KSM, still exists in California, run primarily as a museum by volunteers, and occasional contacts with ships are made. In a minor legacy use, VHF omnidirectional range (VOR) and NDB NDB may refer to:
* Do not let Belgrade drown (''Ne davimo Beograd''), a political party in Serbia
* ''Nachrichtendienst des Bundes'' ("Federal Intelligence Service"), one of the Swiss intelligence agencies
* National Defense Battalions (Iraq) (19 ...
radio beacons in the aviation radio navigation
Radio navigation or radionavigation is the application of radio frequencies to determine a position of an object on the Earth, either the vessel or an obstruction. Like radiolocation, it is a type of radiodetermination.
The basic principles ...
service still transmit their one to three letter identifiers
An identifier is a name that identifies (that is, labels the identity of) either a unique object or a unique ''class'' of objects, where the "object" or class may be an idea, physical countable object (or class thereof), or physical noncountable ...
in Morse code.
Radiotelegraphy is popular amongst radio amateurs world-wide, who commonly refer to it as continuous wave, or just CW. A 2021 analysis of over 700 million communications logged by the Club Log blog, and a similar review of data logged by the American Radio Relay League, both show that wireless telegraphy is the 2nd most popular mode of amateur radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency communi ...
communication, accounting for nearly 20% of contacts. This makes it more popular than voice communication, but not as popular as the FT8
FT8 or Franke & Taylor 8 is a frequency shift keying digital mode which was released on June 29, 2017, by the creators Joe Taylor, K1JT and Steve Franke, K9AN along with the software package WSJT.Burmester, Dale March 12, 2019. Amateur Radio Di ...
digital mode, which accounted for 60% of amateur radio contacts made in 2021. Since 2003, knowledge of Morse code and wireless telegraphy has no longer been required to obtain an amateur radio license in many countries, it is, however, still required in some countries to obtain a licence of a different class. As of 2021, licence Class A in Belarus and Estonia, or the General class in Monaco, or Class 1 in Ukraine require Morse proficiency to access the full amateur radio spectrum including the high frequency (HF) bands. Further, CEPT Class 1 licence in Ireland, and Class 1 in Russia, both of which require proficiency in wireless telegraphy, offer additional privileges: a shorter and more desirable call sign
In broadcasting and radio communications, a call sign (also known as a call name or call letters—and historically as a call signal—or abbreviated as a call) is a unique identifier for a transmitter station. A call sign can be formally assig ...
in both countries, and the right to use a higher transmit power in Russia.
Non-radio methods
Efforts to find a way to transmit telegraph signals without wires grew out of the success of electric telegraph networks, the first instant telecommunication systems. Developed beginning in the 1830s, a telegraph line was a person-to-person text message system consisting of multipletelegraph office
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas ...
s linked by an overhead wire supported on telegraph poles. To send a message, an operator at one office would tap on a switch
In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can disconnect or connect the conducting path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the electric current or diverting it from one conductor to another. The most common type ...
called a telegraph key
A telegraph key is a specialized electrical switch used by a trained operator to transmit text messages in Morse code in a telegraphy system. Keys are used in all forms of electrical telegraph systems, including landline (also called wire) t ...
, creating pulses of electric current which spelled out a message in Morse code
Morse code is a method used in telecommunication to encode text characters as standardized sequences of two different signal durations, called ''dots'' and ''dashes'', or ''dits'' and ''dahs''. Morse code is named after Samuel Morse, one ...
. When the key was pressed, it would connect a battery to the telegraph line, sending current down the wire. At the receiving office, the current pulses would operate a telegraph sounder, a device that would make a "click" sound when it received each pulse of current. The operator at the receiving station who knew Morse code would translate the clicking sounds to text and write down the message. The ground
Ground may refer to:
Geology
* Land, the surface of the Earth not covered by water
* Soil, a mixture of clay, sand and organic matter present on the surface of the Earth
Electricity
* Ground (electricity), the reference point in an electrical c ...
was used as the return path for current in the telegraph circuit, to avoid having to use a second overhead wire.
By the 1860s, the telegraph was the standard way to send most urgent commercial, diplomatic and military messages, and industrial nations had built continent-wide telegraph networks, with submarine telegraph cables allowing telegraph messages to bridge oceans. However installing and maintaining a telegraph line linking distant stations was very expensive, and wires could not reach some locations such as ships at sea. Inventors realized if a way could be found to send electrical impulses of Morse code between separate points without a connecting wire, it could revolutionize communications.
The successful solution to this problem was the discovery of radio wave
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies of 300 gigahertz ( GHz) and below. At 300 GHz, the corresponding wavelength is 1 mm (sho ...
s in 1887, and the development of practical radiotelegraphy transmitters and receivers by about 1899, described in the next section. However, this was preceded by a 50-year history of ingenious but ultimately unsuccessful experiments by inventors to achieve wireless telegraphy by other means.
Ground, water, and air conduction
Several wireless electrical signaling schemes based on the (sometimes erroneous) idea that electric currents could be conducted long-range through water, ground, and air were investigated for telegraphy before practical radio systems became available. The original telegraph lines used two wires between the two stations to form a completeelectrical circuit
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical components (e.g., batteries, resistors, inductors, capacitors, switches, transistors) or a model of such an interconnection, consisting of electrical elements (e.g., voltage sour ...
or "loop". In 1837, however, Carl August von Steinheil of Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and Ha ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
, found that by connecting one leg of the apparatus at each station to metal plates buried in the ground, he could eliminate one wire and use a single wire for telegraphic communication. This led to speculation that it might be possible to eliminate both wires and therefore transmit telegraph signals through the ground without any wires connecting the stations. Other attempts were made to send the electric current through bodies of water, to span rivers, for example. Prominent experimenters along these lines included Samuel F. B. Morse in the United States and James Bowman Lindsay
James Bowman Lindsay (8 September 1799 – 29 June 1862) was a Scottish inventor and author. He is credited with early developments in several fields, such as incandescent lighting and telegraphy.
Life and work
James Bowman Lindsay was bor ...
in Great Britain, who in August 1854, was able to demonstrate transmission across a mill dam at a distance of .
 US inventors William Henry Ward (1871) and Mahlon Loomis (1872) developed electrical conduction systems based on the erroneous belief that there was an electrified atmospheric stratum accessible at low altitude. They thought atmosphere current, connected with a return path using "Earth currents" would allow for wireless telegraphy as well as supply power for the telegraph, doing away with artificial batteries. A more practical demonstration of wireless transmission via conduction came in Amos Dolbear's 1879 magneto electric telephone that used ground conduction to transmit over a distance of a quarter of a mile.Christopher Cooper, The Truth About Tesla: The Myth of the Lone Genius in the History of Innovation, Race Point Publishing, 2015, page 165
In the 1890s inventor
US inventors William Henry Ward (1871) and Mahlon Loomis (1872) developed electrical conduction systems based on the erroneous belief that there was an electrified atmospheric stratum accessible at low altitude. They thought atmosphere current, connected with a return path using "Earth currents" would allow for wireless telegraphy as well as supply power for the telegraph, doing away with artificial batteries. A more practical demonstration of wireless transmission via conduction came in Amos Dolbear's 1879 magneto electric telephone that used ground conduction to transmit over a distance of a quarter of a mile.Christopher Cooper, The Truth About Tesla: The Myth of the Lone Genius in the History of Innovation, Race Point Publishing, 2015, page 165
In the 1890s inventor Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla ( ; ,"Tesla"
'' wireless electric power transmission system, similar to Loomis', which he planned to include wireless telegraphy. Tesla's experiments had led him to incorrectly conclude that he could use the entire globe of the Earth to conduct electrical energy and his 1901 large scale application of his ideas, a high-voltage wireless power station, now called Wardenclyffe Tower, lost funding and was abandoned after a few years. Telegraphic communication using earth conductivity was eventually found to be limited to impractically short distances, as was communication conducted through water, or between trenches during World War I.
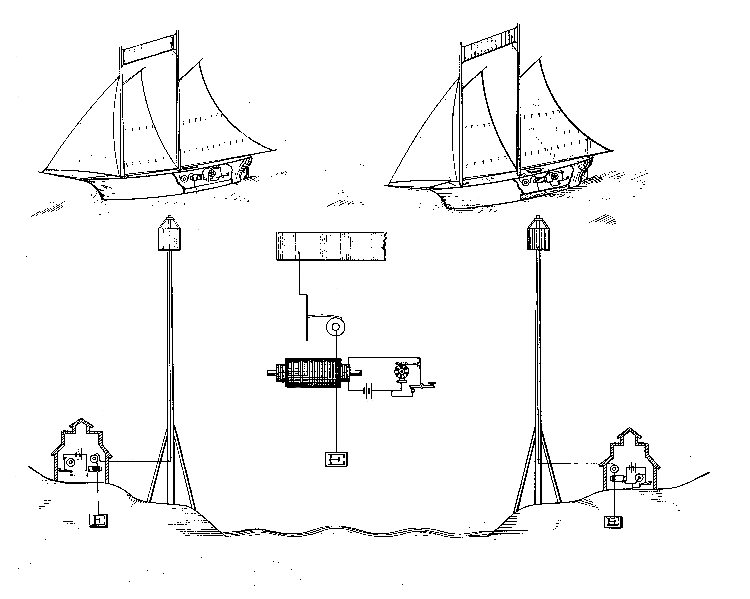 Both electrostatic and electromagnetic induction were used to develop wireless telegraph systems that saw limited commercial application. In the United States,
Both electrostatic and electromagnetic induction were used to develop wireless telegraph systems that saw limited commercial application. In the United States,
 Over several years starting in 1894, the Italian inventor
Over several years starting in 1894, the Italian inventor
TITLE 47—Telecommunication CHAPTER I—FEDERAL COMMUNICATIONS COMMISSION SUBCHAPTER A—GENERAL PART 13—COMMERCIAL RADIO OPERATORS
/ref>
File: Guglielmo Marconi 1901 wireless signal.jpg,
Wireless Telephony – By R. A. Fessenden (Illustrated.)
Transactions of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers
New York: American Institute of Electrical Engineers. ;Citations
History of wireless
Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Interscience. * Hugh G. J. Aitken, ''Syntony and Spark: The Origins of Radio'', . 1976. * Elliot N. Sivowitch, ''A Technological Survey of Broadcasting’s Pre-History,'' Journal of Broadcasting, 15:1–20 (Winter 1970–71). * Colby, F. M., Williams, T., & Wade, H. T. (1930).
Wireless Telegraphy
The New international encyclopaedia
New York: Dodd, Mead, and Co. *
Wireless telegraphy
The Encyclopædia Britannica
(1922). London: Encyclopædia Britannica. * Stanley, R. (1919)
Text-book on wireless telegraphy
London: Longmans, Green * Miessner, B. F. (1916)
Radiodynamics: The wireless control of torpedoes and other mechanisms
New York: D. Van Nostrand Co * Thompson, S. P. (1915)
Elementary lessons in electricity and magnetism
New York: Macmillan. * Stanley, R. (1914)
Textbook on wireless telegraphy
London: Longmans, Green. * Ashley, C. G., & Hayward, C. B. (1912)
Wireless telegraphy and wireless telephony
an understandable presentation of the science of wireless transmission of intelligence. Chicago: American School of Correspondence. * Massie, W. W., & Underhill, C. R. (1911)
Wireless telegraphy and telephony popularly explained
New York: D. Van Nostrand. * Captain S.S. Robison(1911)
Developments in Wireless Telegraphy
International marine engineering, Volume 16. Simmons-Boardman Pub. Co. * Bottone, S. R. (1910)
Wireless telegraphy and Hertzian waves
London: Whittaker & Co. * Erskine-Murray, J. (1909)
A handbook of wireless telegraphy: its theory and practice, for the use of electrical engineers, students, and operators
New York: Van Nostrand. * Twining, H. L. V., & Dubilier, W. (1909)
Wireless telegraphy and high-frequency electricity; a manual containing detailed information for the construction of transformers, wireless telegraph, and high-frequency apparatus, with chapters on their theory and operation
Los Angeles, Cal: The author.
''The New Physics and Its Evolution''. Chapter VII: A Chapter in the History of Science: Wireless telegraphy
by Lucien Poincaré, eBook #15207, released 2005. riginally, published: New York, D. Appleton, and Company. 1909 * Fleming, J. A. (1908)
The principles of electric wave telegraphy
London: New York and Co. * Simmons, H. H. (1908).
Wireless telegraphy
Outlines of electrical engineering
London: Cassell and Co. * Murray, J. E. (1907)
A handbook of wireless telegraphy
New York: D. Van Nostrand Co.; tc. * Mazzotto, D., & Bottone, S. R. (1906)
Wireless telegraphy and telephony
London: Whittaker & Co. * Collins, A. F. (1905)
Wireless telegraphy; its history, theory, and practice
New York: McGraw Pub. * Sewall, C. H. (1904)
Wireless telegraphy: its origins, development, inventions, and apparatus
New York: D. Van Nostrand. * Trevert, E. (1904)
The A.B.C. of wireless telegraphy; a plain treatise on Hertzian wave signaling; embracing theory, methods of operation, and how to build various pieces of the apparatus employed
Lynn, Mass: Bubier Pub. * Fahie, J. J. (1900)
A history of wireless telegraphy, 1838–1899: including some bare-wire proposals for subaqueous telegraphs
Edinburgh: W. Blackwood and Sons.
Telegraphing across space, Electric wave method
The Electrical engineer. (1884). London: Biggs & Co. * American Institute of Electrical Engineers. (1884)
Transactions of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers
New York: American Institute of Electrical Engineers. ed., Contains ''Radio Telephony'' – By E. B. Craft and E. H. Colpitts (Illustrated)
p. 305
''A History of Wireless Telegraphy, 1838–1899: including some bare-wire proposals for subaqueous telegraphs''
1899 (first edition). * John Joseph Fahie
''A History of Wireless Telegraphy: including some bare-wire proposals for subaqueous telegraphs''
1901 (second edition). * John Joseph Fahie
1901 (second edition, in HTML format). * Alfred Thomas Story, ''The Story of Wireless Telegraphy'', 190
James Bowman Lindsay
A short biography on his efforts on electric lamps and telegraphy.
Sparks Telegraph Key Review
''Principles of Radiotelegraphy'' (1919)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Wireless Telegraphy Radio Telegraphy Wireless communication systems
'' wireless electric power transmission system, similar to Loomis', which he planned to include wireless telegraphy. Tesla's experiments had led him to incorrectly conclude that he could use the entire globe of the Earth to conduct electrical energy and his 1901 large scale application of his ideas, a high-voltage wireless power station, now called Wardenclyffe Tower, lost funding and was abandoned after a few years. Telegraphic communication using earth conductivity was eventually found to be limited to impractically short distances, as was communication conducted through water, or between trenches during World War I.
Electrostatic and electromagnetic induction
 Both electrostatic and electromagnetic induction were used to develop wireless telegraph systems that saw limited commercial application. In the United States,
Both electrostatic and electromagnetic induction were used to develop wireless telegraph systems that saw limited commercial application. In the United States, Thomas Edison
Thomas Alva Edison (February 11, 1847October 18, 1931) was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices in fields such as electric power generation, mass communication, sound recording, and motion pictures. These invent ...
, in the mid-1880s, patented an electromagnetic induction system he called "grasshopper telegraphy", which allowed telegraphic signals to jump the short distance between a running train and telegraph wires running parallel to the tracks. This system was successful technically but not economically, as there turned out to be little interest by train travelers in the use of an on-board telegraph service. During the Great Blizzard of 1888, this system was used to send and receive wireless messages from trains buried in snowdrifts. The disabled trains were able to maintain communications via their Edison induction wireless telegraph systems, perhaps the first successful use of wireless telegraphy to send distress calls. Edison would also help to patent a ship-to-shore communication system based on electrostatic induction.
The most successful creator of an electromagnetic induction telegraph system was William Preece, chief engineer of Post Office Telegraphs of the General Post Office
The General Post Office (GPO) was the state mail, postal system and telecommunications carrier of the United Kingdom until 1969. Before the Acts of Union 1707, it was the postal system of the Kingdom of England, established by Charles II of En ...
(GPO) in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
. Preece first noticed the effect in 1884 when overhead telegraph wires in Grays Inn Road were accidentally carrying messages sent on buried cables. Tests in Newcastle succeeded in sending a quarter of a mile using parallel rectangles of wire.Kieve, Jeffrey L., ''The Electric Telegraph: A Social and Economic History'', David and Charles, 1973 . In tests across the Bristol Channel
The Bristol Channel ( cy, Môr Hafren, literal translation: "Severn Sea") is a major inlet in the island of Great Britain, separating South Wales from Devon and Somerset in South West England. It extends from the lower estuary of the River S ...
in 1892, Preece was able to telegraph across gaps of about . However, his induction system required extensive lengths of antenna wires, many kilometers long, at both the sending and receiving ends. The length of those sending and receiving wires needed to be about the same length as the width of the water or land to be spanned. For example, for Preece's station to span the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" ( Cotentinais) or (Jèrriais), ( Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kan ...
from Dover, England, to the coast of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
would require sending and receiving wires of about along the two coasts. These facts made the system impractical on ships, boats, and ordinary islands, which are much smaller than Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
or Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is ...
. Also, the relatively short distances that a practical Preece system could span meant that it had few advantages over underwater telegraph cables.
Radiotelegraphy
 Over several years starting in 1894, the Italian inventor
Over several years starting in 1894, the Italian inventor Guglielmo Marconi
Guglielmo Giovanni Maria Marconi, 1st Marquis of Marconi (; 25 April 187420 July 1937) was an Italian inventor and electrical engineer, known for his creation of a practical radio wave-based wireless telegraph system. This led to Marconi b ...
worked on adapting the newly discovered phenomenon of radio waves to communication, turning what was essentially a laboratory experiment up to that point into a useful communication system, building the first radiotelegraphy system using them. Preece and the GPO in Britain at first supported and gave financial backing to Marconi's experiments conducted on Salisbury Plain
Salisbury Plain is a chalk plateau in the south western part of central southern England covering . It is part of a system of chalk downlands throughout eastern and southern England formed by the rocks of the Chalk Group and largely lies w ...
from 1896. Preece had become convinced of the idea through his experiments with wireless induction. However, the backing was withdrawn when Marconi formed the Wireless Telegraph & Signal Company
The Marconi Company was a British telecommunications and engineering company that did business under that name from 1963 to 1987. Its roots were in the Wireless Telegraph & Signal Company founded by Italian inventor Guglielmo Marconi in 1897 ...
. GPO lawyers determined that the system was a telegraph under the meaning of the Telegraph Act
Telegraph Act is a stock short title which used to be used for legislation in the United Kingdom, relating to telegraphy.
The Bill for an Act with this short title may have been known as a Telegraph Bill during its passage through Parliament.
Tel ...
and thus fell under the Post Office monopoly. This did not seem to hold back Marconi. After Marconi sent wireless telegraphic signals across the Atlantic Ocean in 1901, the system began being used for regular communication including ship-to-shore and ship-to-ship communication.
With this development, wireless telegraphy came to mean ''radiotelegraphy'', Morse code
Morse code is a method used in telecommunication to encode text characters as standardized sequences of two different signal durations, called ''dots'' and ''dashes'', or ''dits'' and ''dahs''. Morse code is named after Samuel Morse, one ...
transmitted by radio waves. The first radio transmitters, primitive spark gap transmitters used until World War I, could not transmit voice ( audio signals). Instead, the operator would send the text message on a telegraph key
A telegraph key is a specialized electrical switch used by a trained operator to transmit text messages in Morse code in a telegraphy system. Keys are used in all forms of electrical telegraph systems, including landline (also called wire) t ...
, which turned the transmitter on and off, producing short ("dot") and long ("dash") pulses of radio waves, groups of which comprised the letters and other symbols of the Morse code. At the receiver, the signals could be heard as musical "beeps" in the earphones by the receiving operator, who would translate the code back into text. By 1910, communication by what had been called "Hertzian waves" was being universally referred to as "radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transm ...
", and the term wireless telegraphy has been largely replaced by the more modern term "radiotelegraphy".
Continuous wave (CW)
The primitive spark-gap transmitters used until 1920 transmitted by a modulation method called damped wave. As long as the telegraph key was pressed, the transmitter would produce a string of transient pulses of radio waves which repeated at an audio rate, usually between 50 and several thousandhertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that one her ...
. In a receiver's earphone, this sounded like a musical tone, rasp or buzz. Thus the Morse code "dots" and "dashes" sounded like beeps. Damped wave had a large frequency bandwidth, meaning that the radio signal was not a single frequency but occupied a wide band of frequencies. Damped wave transmitters had a limited range and interfered with the transmissions of other transmitters on adjacent frequencies.
After 1905 new types of radiotelegraph transmitters were invented which transmitted code using a new modulation method: continuous wave (CW) (designated by the International Telecommunication Union
The International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Unio ...
as emission type A1A). As long as the telegraph key was pressed, the transmitter produced a continuous sinusoidal wave of constant amplitude. Since all the radio wave's energy was concentrated at a single frequency, CW transmitters could transmit further with a given power, and also caused virtually no interference to transmissions on adjacent frequencies. The first transmitters able to produce continuous wave were the arc converter (Poulsen arc) transmitter, invented by Danish engineer Valdemar Poulsen in 1903, and the Alexanderson alternator, invented 1906-1912 by Reginald Fessenden
Reginald Aubrey Fessenden (October 6, 1866 – July 22, 1932) was a Canadian-born inventor, who did a majority of his work in the United States and also claimed U.S. citizenship through his American-born father. During his life he received hundre ...
and Ernst Alexanderson. These slowly replaced the spark transmitters in high power radiotelegraphy stations.
However, the radio receivers used for damped wave could not receive continuous wave. Because the CW signal produced while the key was pressed was just an unmodulated carrier wave, it made no sound in a receiver's earphones. To receive a CW signal, some way had to be found to make the Morse code carrier wave pulses audible in a receiver.
This problem was solved by Reginald Fessenden in 1901. In his "heterodyne" receiver, the incoming radiotelegraph signal is mixed in the receiver's detector crystal or vacuum tube with a constant sine wave generated by an electronic oscillator in the receiver called a beat frequency oscillator (BFO). The frequency of the oscillator is offset from the radio transmitter's frequency . In the detector the two frequencies subtract, and a beat frequency ( heterodyne) at the difference between the two frequencies is produced: . If the BFO frequency is near enough to the radio station's frequency, the beat frequency is in the audio frequency range and can be heard in the receiver's earphones. During the "dots" and "dashes" of the signal, the beat tone is produced, while between them there is no carrier so no tone is produced. Thus the Morse code is audible as musical "beeps" in the earphones.
The BFO was rare until the invention in 1913 of the first practical electronic oscillator, the vacuum tube feedback oscillator by Edwin Armstrong. After this time BFOs were a standard part of radiotelegraphy receivers. Each time the radio was tuned to a different station frequency, the BFO frequency had to be changed also, so the BFO oscillator had to be tunable. In later superheterodyne receivers from the 1930s on, the BFO signal was mixed with the constant intermediate frequency (IF) produced by the superheterodyne's detector. Therefore, the BFO could be a fixed frequency.
Continuous-wave vacuum tube transmitters replaced the other types of transmitter with the availability of power tubes after World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
because they were cheap. CW became the standard method of transmitting radiotelegraphy by the 20s, damped wave spark transmitters were banned by 1930 and CW continues to be used today. Even today most communications receivers produced for use in shortwave communication stations have BFOs.
The radiotelegraphy industry
The International Radiotelegraph Union was unofficially established at the first International Radiotelegraph Convention in 1906, and was merged into theInternational Telecommunication Union
The International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Unio ...
in 1932. When the United States entered World War I, private radiotelegraphy stations were prohibited, which put an end to several pioneers' work in this field. By the 1920s, there was a worldwide network of commercial and government radiotelegraphic stations, plus extensive use of radiotelegraphy by ships for both commercial purposes and passenger messages. The transmission of sound ( radiotelephony) began to displace radiotelegraphy by the 1920s for many applications, making possible radio broadcasting
Broadcasting is the distribution of audio or video content to a dispersed audience via any electronic mass communications medium, but typically one using the electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves), in a one-to-many model. Broadcasting began ...
. Wireless telegraphy continued to be used for private person-to-person business, governmental, and military communication, such as telegram
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas ...
s and diplomatic communications, and evolved into radioteletype networks. The ultimate implementation of wireless telegraphy was telex, using radio signals, which was developed in the 1930s and was for many years the only reliable form of communication between many distant countries. The most advanced standard, CCITT R.44, automated both routing and encoding of messages by short wave
Shortwave radio is radio transmission using shortwave (SW) radio frequencies. There is no official definition of the band, but the range always includes all of the High frequency, high frequency band (HF), which extends from 3 to 30 MHz (10 ...
transmissions.
Today, due to more modern text transmission methods, Morse code radiotelegraphy for commercial use has become obsolete. On shipboard, the computer and satellite-linked GMDSS
The Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS) is a worldwide system for automated emergency signal communication for ships at sea developed by the United Nations' International Maritime Organization (IMO) as part of the SOLAS Convent ...
system have largely replaced Morse as a means of communication.
Regulation of radiotelegraphy
Continuous wave (CW) radiotelegraphy is regulated by theInternational Telecommunication Union
The International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Unio ...
(ITU) as emission type A1A.
The US Federal Communications Commission
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government that regulates communications by radio, television, wire, satellite, and cable across the United States. The FCC maintains jurisd ...
issues a lifetime commercial Radiotelegraph Operator License. This requires passing a simple written test on regulations, a more complex written exam on technology, and demonstrating Morse reception at 20 words per minute plain language and 16 wpm code groups. (Credit is given for amateur extra class licenses earned under the old 20 wpm requirement.)/ref>
Gallery
Guglielmo Marconi
Guglielmo Giovanni Maria Marconi, 1st Marquis of Marconi (; 25 April 187420 July 1937) was an Italian inventor and electrical engineer, known for his creation of a practical radio wave-based wireless telegraph system. This led to Marconi b ...
, the father of radio-based wireless telegraphy, in 1901, with one of his first wireless transmitters ''(right)'' and receivers ''(left)''
File: German WW I field telegraph 001.jpg, German troops erecting a wireless field telegraph station during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
File: German WW I field telegraph 002.jpg, German officers and troops manning a wireless field telegraph station during World War I
File:Bildschirmfoto 2019-04-14 um 09.45.16.png, Mobile radio station in German South West Africa
German South West Africa (german: Deutsch-Südwestafrika) was a colony of the German Empire from 1884 until 1915, though Germany did not officially recognise its loss of this territory until the 1919 Treaty of Versailles. With a total area of ...
, using a hydrogen balloon to lift the antenna
See also
*AT&T Corporation
AT&T Corporation, originally the American Telephone and Telegraph Company, is the subsidiary of AT&T Inc. that provides voice, video, data, and Internet telecommunications and professional services to businesses, consumers, and government agen ...
originally American Telephone and Telegraph Company
* Electrical telegraph
Electrical telegraphs were point-to-point text messaging systems, primarily used from the 1840s until the late 20th century. It was the first electrical telecommunications system and the most widely used of a number of early messaging system ...
* Imperial Wireless Chain
References and notes
; General * American Institute of Electrical Engineers. (1908).Wireless Telephony – By R. A. Fessenden (Illustrated.)
Transactions of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers
New York: American Institute of Electrical Engineers. ;Citations
Further reading
Listed by date 'latest to earliest'' * Sarkar, T. K., & Baker, D. C. (2006)History of wireless
Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Interscience. * Hugh G. J. Aitken, ''Syntony and Spark: The Origins of Radio'', . 1976. * Elliot N. Sivowitch, ''A Technological Survey of Broadcasting’s Pre-History,'' Journal of Broadcasting, 15:1–20 (Winter 1970–71). * Colby, F. M., Williams, T., & Wade, H. T. (1930).
Wireless Telegraphy
The New international encyclopaedia
New York: Dodd, Mead, and Co. *
Wireless telegraphy
The Encyclopædia Britannica
(1922). London: Encyclopædia Britannica. * Stanley, R. (1919)
Text-book on wireless telegraphy
London: Longmans, Green * Miessner, B. F. (1916)
Radiodynamics: The wireless control of torpedoes and other mechanisms
New York: D. Van Nostrand Co * Thompson, S. P. (1915)
Elementary lessons in electricity and magnetism
New York: Macmillan. * Stanley, R. (1914)
Textbook on wireless telegraphy
London: Longmans, Green. * Ashley, C. G., & Hayward, C. B. (1912)
Wireless telegraphy and wireless telephony
an understandable presentation of the science of wireless transmission of intelligence. Chicago: American School of Correspondence. * Massie, W. W., & Underhill, C. R. (1911)
Wireless telegraphy and telephony popularly explained
New York: D. Van Nostrand. * Captain S.S. Robison(1911)
Developments in Wireless Telegraphy
International marine engineering, Volume 16. Simmons-Boardman Pub. Co. * Bottone, S. R. (1910)
Wireless telegraphy and Hertzian waves
London: Whittaker & Co. * Erskine-Murray, J. (1909)
A handbook of wireless telegraphy: its theory and practice, for the use of electrical engineers, students, and operators
New York: Van Nostrand. * Twining, H. L. V., & Dubilier, W. (1909)
Wireless telegraphy and high-frequency electricity; a manual containing detailed information for the construction of transformers, wireless telegraph, and high-frequency apparatus, with chapters on their theory and operation
Los Angeles, Cal: The author.
''The New Physics and Its Evolution''. Chapter VII: A Chapter in the History of Science: Wireless telegraphy
by Lucien Poincaré, eBook #15207, released 2005. riginally, published: New York, D. Appleton, and Company. 1909 * Fleming, J. A. (1908)
The principles of electric wave telegraphy
London: New York and Co. * Simmons, H. H. (1908).
Wireless telegraphy
Outlines of electrical engineering
London: Cassell and Co. * Murray, J. E. (1907)
A handbook of wireless telegraphy
New York: D. Van Nostrand Co.; tc. * Mazzotto, D., & Bottone, S. R. (1906)
Wireless telegraphy and telephony
London: Whittaker & Co. * Collins, A. F. (1905)
Wireless telegraphy; its history, theory, and practice
New York: McGraw Pub. * Sewall, C. H. (1904)
Wireless telegraphy: its origins, development, inventions, and apparatus
New York: D. Van Nostrand. * Trevert, E. (1904)
The A.B.C. of wireless telegraphy; a plain treatise on Hertzian wave signaling; embracing theory, methods of operation, and how to build various pieces of the apparatus employed
Lynn, Mass: Bubier Pub. * Fahie, J. J. (1900)
A history of wireless telegraphy, 1838–1899: including some bare-wire proposals for subaqueous telegraphs
Edinburgh: W. Blackwood and Sons.
Telegraphing across space, Electric wave method
The Electrical engineer. (1884). London: Biggs & Co. * American Institute of Electrical Engineers. (1884)
Transactions of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers
New York: American Institute of Electrical Engineers. ed., Contains ''Radio Telephony'' – By E. B. Craft and E. H. Colpitts (Illustrated)
p. 305
External links
* John Joseph Fahie''A History of Wireless Telegraphy, 1838–1899: including some bare-wire proposals for subaqueous telegraphs''
1899 (first edition). * John Joseph Fahie
''A History of Wireless Telegraphy: including some bare-wire proposals for subaqueous telegraphs''
1901 (second edition). * John Joseph Fahie
1901 (second edition, in HTML format). * Alfred Thomas Story, ''The Story of Wireless Telegraphy'', 190
James Bowman Lindsay
A short biography on his efforts on electric lamps and telegraphy.
Sparks Telegraph Key Review
''Principles of Radiotelegraphy'' (1919)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Wireless Telegraphy Radio Telegraphy Wireless communication systems