|
Operation Donnerkeil
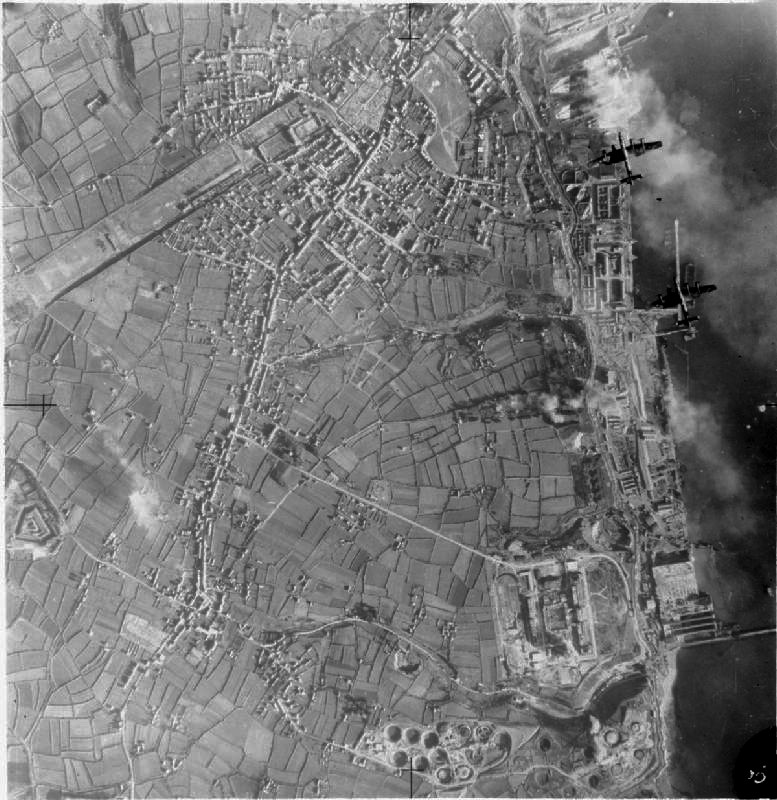
Unternehmen Donnerkeil (Operation Thunderbolt) was the codename for a German military operation of the Second World War. ''Donnerkeil'' was an air superiority operation to support the ''Kriegsmarine'' (German Navy) Operation Cerberus, also known as the Channel Dash. In 1941 ''Kriegsmarine'' surface vessels had carried out commerce raiding sorties in support of the German U-boats in the Battle of the Atlantic. In January 1941 Operation Berlin was launched followed by Operation Rheinübung in May 1941. The dominance of the Royal Navy's surface fleet prevented the German units returning to ports in the Baltic Sea or Germany. The surviving ships, the battleships ''Scharnhorst'' and '' Gneisenau'' and the cruiser '' Prinz Eugen'', docked in the port of Brest, France. Throughout 1941 RAF Bomber Command attacked the ships in dock. The proximity of the ports to Royal Air Force (RAF) airfields allowed a large number of sorties to be flown against the targets in quick succession. The ''Ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Front (World War II)
The Western Front was a European theatre of World War II, military theatre of World War II encompassing Denmark, Norway, Luxembourg, Belgium, Netherlands, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, France, and Germany. The Italian campaign (World War II), Italian front is considered a separate but related theater. The Western Front's 1944-1945 phase was officially deemed the European Theater of Operations, United States Army, European Theater by the United States, whereas Italy fell under the Mediterranean Theater of Operations, United States Army, Mediterranean Theater along with North Africa. The Western Front was marked by two phases of large-scale combat operations. The first phase saw the capitulation of Luxembourg, Netherlands, Belgium, and France during May and June 1940 after their defeat in the Low Countries and the northern half of France, and continued into an air war between Germany and Britain that climaxed with the Battle of Britain. The second phase consisted of large- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation (military)
A military operation is the coordinated military actions of a state, or a non-state actor, in response to a developing situation. These actions are designed as a military plan to resolve the situation in the state or actor's favor. Operations may be of a combat or non-combat nature and may be referred to by a code name for the purpose of national security. Military operations are often known for their more generally accepted common usage names than their actual operational objectives. Types of military operations Military operations can be classified by the scale and scope of force employment, and their impact on the wider conflict. The scope of military operations can be: * Theater: this describes an operation over a large, often continental, area of operation and represents a strategic national commitment to the conflict, such as Operation Barbarossa, with general goals that encompass areas of consideration outside the military, such as the economic and political impact of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
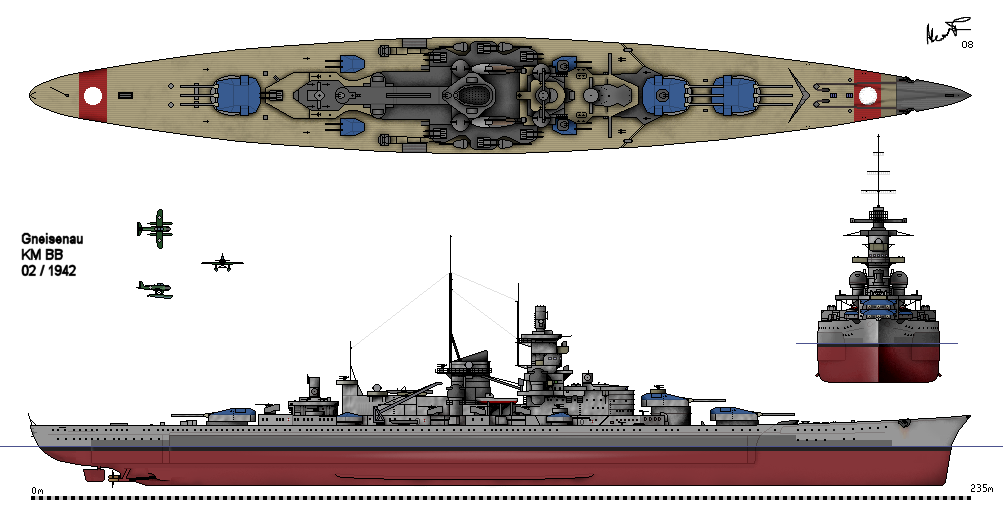
German Battleship Gneisenau
''Gneisenau'' () was a German capital ship, alternatively described as a battleship and battlecruiser, of Nazi Germany's ''Kriegsmarine''. She was the second vessel of her class, which included her sister ship, . The ship was built at the '' Deutsche Werke'' dockyard in Kiel; she was laid down on 6 May 1935 and launched on 8 December 1936. Completed in May 1938, the ship was armed with a main battery of nine 28 cm (11 in) C/34 guns in three triple turrets. Plans were approved, once construction had started, to replace these weapons with six 38 cm (15 in) SK C/34 guns in twin turrets, but as this would involve a lot of redesign, construction continued with the lower calibre guns. The intent was to make the upgrade in the winter of 1940–41, but the outbreak of World War II stopped this. ''Gneisenau'' and ''Scharnhorst'' operated together for much of the early portion of World War II, including sorties into the Atlantic to raid British merchant shipping ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
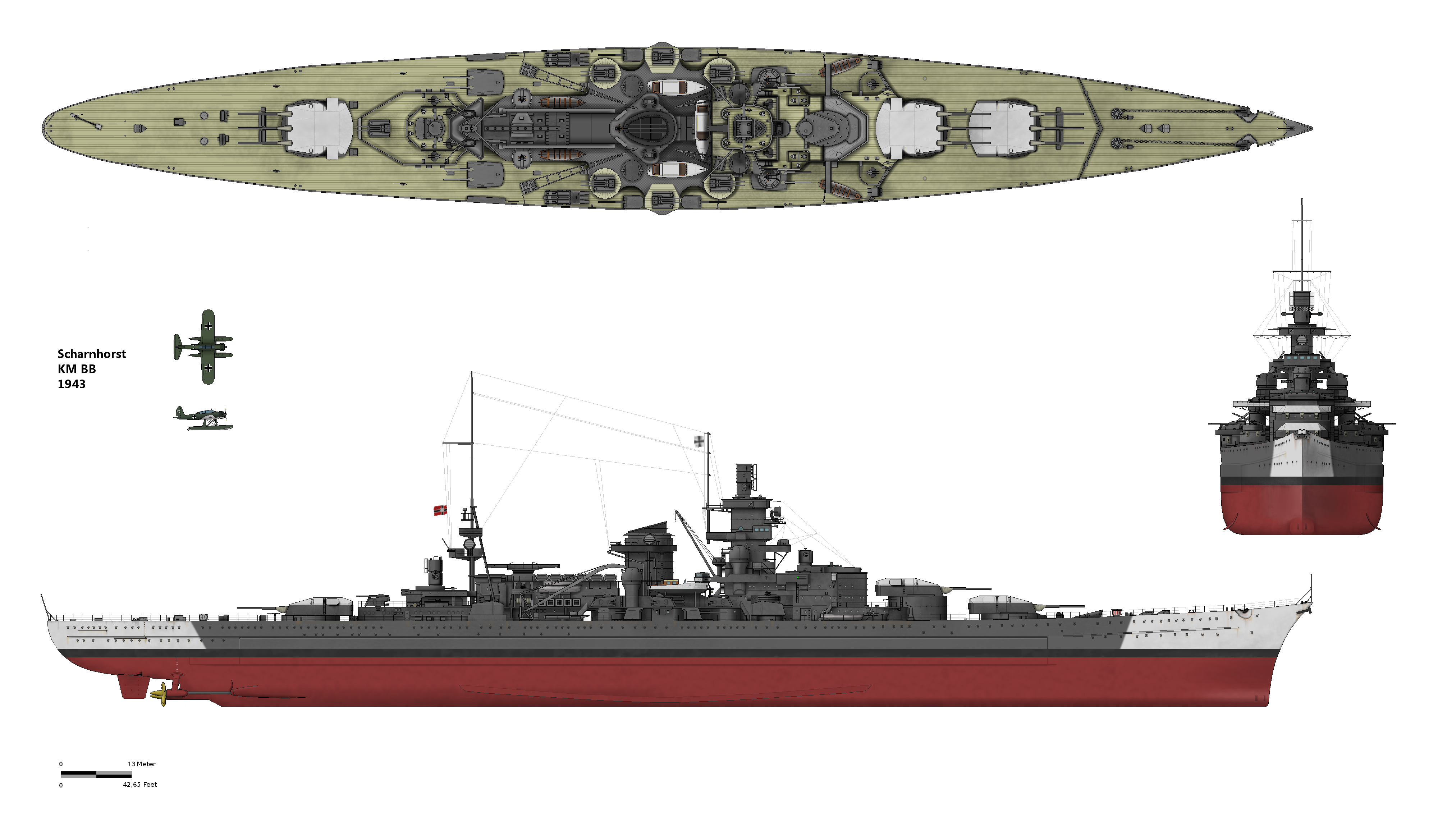
German Battleship Scharnhorst
''Scharnhorst'' was a German capital ship, alternatively described as a battleship or battlecruiser, of Nazi Germany's ''Kriegsmarine''. She was the lead ship of her class, which included her sister ship . The ship was built at the ''Kriegsmarinewerft'' dockyard in Wilhelmshaven; she was laid down on 15 June 1935 and launched a year and four months later on 3 October 1936. Completed in January 1939, the ship was armed with a main battery of nine 28 cm (11 in) C/34 guns in three triple turrets. Plans to replace these weapons with six 38 cm (15 in) SK C/34 guns in twin turrets were never carried out. ''Scharnhorst'' and ''Gneisenau'' operated together for much of the early portion of World War II, including sorties into the Atlantic to raid British merchant shipping. During her first operation, ''Scharnhorst'' sank the armed merchant in a short engagement (November 1939). ''Scharnhorst'' and ''Gneisenau'' participated in Operation Weserübung (April–Jun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain. The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 10°E to 30°E longitude. A marginal sea of the Atlantic, with limited water exchange between the two water bodies, the Baltic Sea drains through the Danish Straits into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, Great Belt and Little Belt. It includes the Gulf of Bothnia, the Bay of Bothnia, the Gulf of Finland, the Gulf of Riga and the Bay of Gdańsk. The "Baltic Proper" is bordered on its northern edge, at latitude 60°N, by Åland and the Gulf of Bothnia, on its northeastern edge by the Gulf of Finland, on its eastern edge by the Gulf of Riga, and in the west by the Swedish part of the southern Scandinavian Peninsula. The Baltic Sea is connected by artificial waterways to the White Sea via the White Sea–Baltic Canal and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Kingdom of France, France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the British Armed Forces, UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the World War II, Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Rheinübung
Operation Rheinübung ("Exercise Rhine") was the sortie into the Atlantic by the new German battleship and heavy cruiser on 18–27 May 1941, during World War II. This operation to block Allied shipping to the United Kingdom culminated with the sinking of ''Bismarck''. Background During both World Wars, the island of Britain was dependent upon huge numbers of merchant ships to bring in food and essential raw materials, and protecting this lifeline was one of the highest priorities for British forces. If this lifeline could be severed, the British Empire in Europe would have to either sue for peace; negotiate an armistice; or abandon the British Isles as a base of operations to blockade the sea approaches to Western Europe; giving Germany in effect, complete mastery of Western Europe, with no tactical base in Europe to oppose that control. Germany's naval leadership (under Admiral Erich Johann Albert Raeder) at the time firmly believed that defeat by blockade was achievabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Berlin (Atlantic)
Operation Berlin was a raid conducted by the two German ''Scharnhorst''-class battleships against Allied shipping in the North Atlantic between 22 January and 22 March 1941. It formed part of the Battle of the Atlantic during World War II. The and sailed from Germany, operated across the North Atlantic, sank or captured 22 Allied merchant vessels, and finished their mission by docking in occupied France. The British military sought to locate and attack the German battleships, but failed to damage them. The operation was one of several made by German warships during late 1940 and early 1941. Its main goal was for the battleships to overwhelm the escort of one of the convoys transporting supplies to the United Kingdom and then sink large numbers of merchant ships. The British were expecting this given previous attacks, and assigned battleships of their own to escort convoys. This proved successful, with the German force having to abandon attacks against convoys on 8 February a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Atlantic
The Battle of the Atlantic, the longest continuous military campaign in World War II, ran from 1939 to the defeat of Nazi Germany in 1945, covering a major part of the naval history of World War II. At its core was the Allied naval blockade of Germany, announced the day after the declaration of war, and Germany's subsequent counter-blockade. The campaign peaked from mid-1940 through to the end of 1943. The Battle of the Atlantic pitted U-boats and other warships of the German '' Kriegsmarine'' (Navy) and aircraft of the ''Luftwaffe'' (Air Force) against the Royal Navy, Royal Canadian Navy, United States Navy, and Allied merchant shipping. Convoys, coming mainly from North America and predominantly going to the United Kingdom and the Soviet Union, were protected for the most part by the British and Canadian navies and air forces. These forces were aided by ships and aircraft of the United States beginning September 13, 1941. Carney, Robert B., Admiral, USN. "Comment and D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U-boat
U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic warfare role (commerce raiding) and enforcing a naval blockade against enemy shipping. The primary targets of the U-boat campaigns in both wars were the merchant convoys bringing supplies from Canada and other parts of the British Empire, and from the United States, to the United Kingdom and (during the Second World War) to the Soviet Union and the Allied territories in the Mediterranean. German submarines also destroyed Brazilian merchant ships during World War II, causing Brazil to declare war on both Germany and Italy on 22 August 1942. The term is an anglicised version of the German word ''U-Boot'' , a shortening of ''Unterseeboot'' ('under-sea-boat'), though the German term refers to any submarine. Austro-Hungarian Navy submarines were also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commerce Raiding
Commerce raiding (french: guerre de course, "war of the chase"; german: Handelskrieg, "trade war") is a form of naval warfare used to destroy or disrupt logistics of the enemy on the open sea by attacking its merchant shipping, rather than engaging its combatants or enforcing a blockade against them. Privateering The first sort of commerce raiding was for nations to commission privateers. Early instances of this type of warfare were by the English and Dutch against the Spanish treasure fleets of the 16th century, which resulted in financial gain for both captain and crew upon capture of enemy vessels (" prizes"). 17th and 18th centuries Privateers formed a large part of the total military force at sea during the 17th and 18th centuries. In the First Anglo-Dutch War, English privateers attacked the trade on which the United Provinces entirely depended, capturing over 1,000 Dutch merchant ships. During the subsequent war with Spain, Spanish and Flemish privateers in the ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Cerberus
The Channel Dash (german: Unternehmen Zerberus, Operation Cerberus) was a German naval operation during the Second World War. (Cerberus), a three-headed dog of Greek mythology who guards the gate to Hades. A (German Navy) squadron comprising the two s, the heavy cruiser and their escorts was evacuated from Brest in Brittany to German ports. ''Scharnhorst'' and ''Gneisenau'' had arrived in Brest on 22 March 1941 after the success of Operation Berlin in the Atlantic. More raids were planned and the ships were refitted at Brest. The ships were a threat to Allied trans-Atlantic convoys and RAF Bomber Command attacked them from 30 March 1941. ''Gneisenau'' was hit on 6 April 1941 and ''Scharnhorst'' on 24 July 1941, after dispersal to La Pallice. In late 1941, Adolf Hitler ordered the (OKM; German Navy High Command) to plan an operation to return the ships to German bases against a British invasion of Norway. The short route up the English Channel was preferred to a detour arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |