|
Oded Beja
Oded Béjà is a professor in the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, in the field of marine microbiology and metagenomics. Academic work Oded Béjà is best known for discovering the first bacterial rhodopsin naming it proteorhodopsin, during his postdoctoral fellowship in the laboratory of Edward DeLong. Oded Béjà's laboratory focuses currently on the role and diversity of photosynthetic viruses infecting cyanobacteria in the oceans, and the use of functional metagenomics for the discovery of new light sensing proteins. In 2018, the team of Oded Beja discovered a new family of rhodopsins with an inverted membrane topology, which can be found in bacteria, algae, algal viruses and archaea. Members of the new family were named heliorhodopsins. Early life and education Oded Béjà graduated with a B.Sc. degree from the Robert H. Smith Faculty of Agriculture, Food and Environment - Hebrew University of Jerusalem. He earned his M.Sc. and Ph.D. from the Weizmann Inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metagenomics
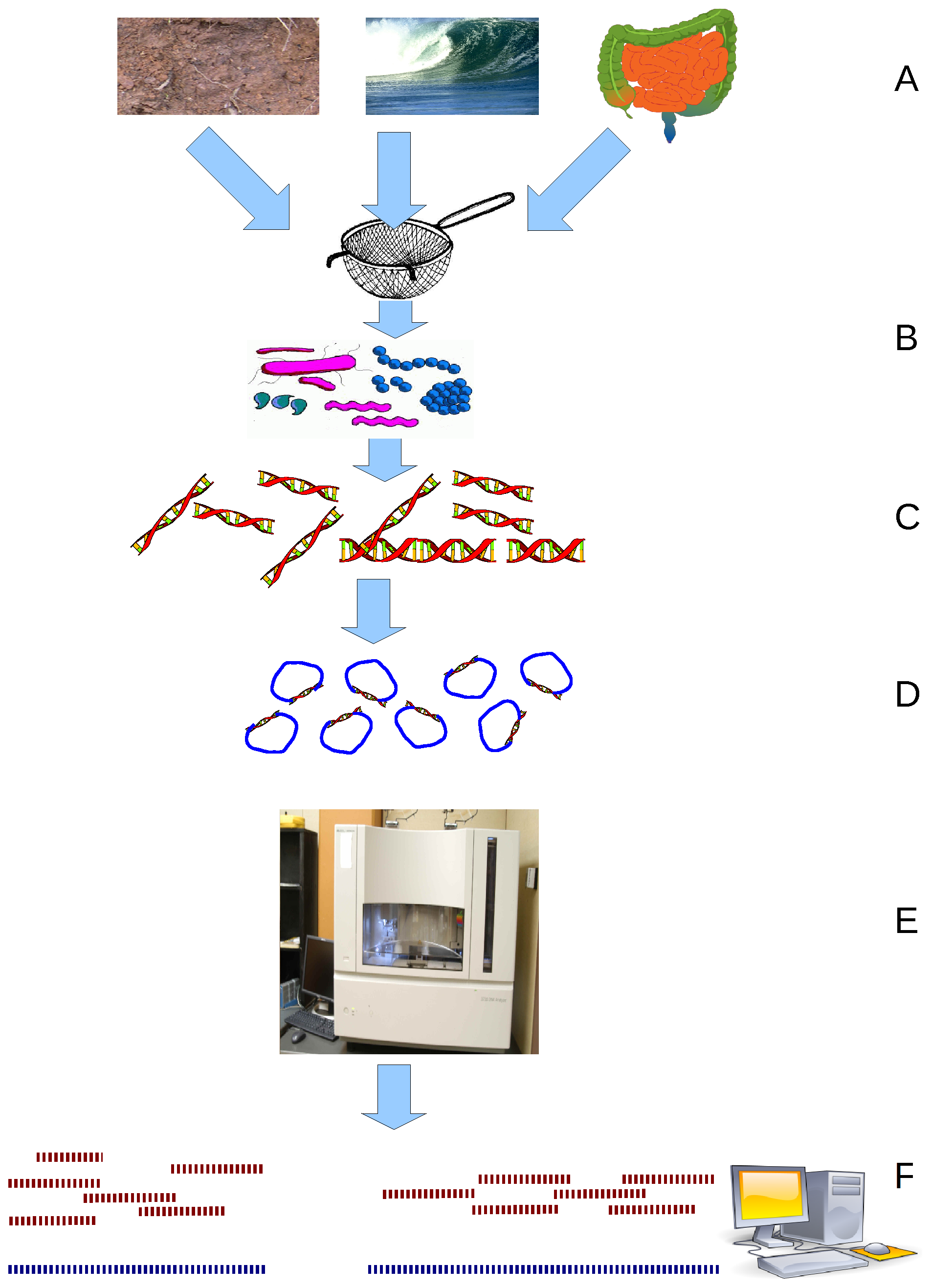
Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental or clinical samples by a method called sequencing. The broad field may also be referred to as environmental genomics, ecogenomics, community genomics or microbiomics. While traditional microbiology and microbial genome sequencing and genomics rely upon cultivated clonal cultures, early environmental gene sequencing cloned specific genes (often the 16S rRNA gene) to produce a profile of diversity in a natural sample. Such work revealed that the vast majority of microbial biodiversity had been missed by cultivation-based methods. Because of its ability to reveal the previously hidden diversity of microscopic life, metagenomics offers a powerful lens for viewing the microbial world that has the potential to revolutionize understanding of the entire living world. As the price of DNA sequencing continues to fall, metagenomics now allows microbial ecology to be investigated at a much greater sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteorhodopsin
Proteorhodopsin (also known as pRhodopsin) is a family of transmembrane proteins that use retinal as a chromophore for light-mediated functionality, in this case, a proton pump. pRhodopsin is found in marine planktonic bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes ( protae), but was first discovered in bacteria. Its name is derived from proteobacteria (now called Pseudomonadota) that were named after Ancient Greek Πρωτεύς (Proteus), an early sea god mentioned by Homer as "Old Man of the Sea", Ῥόδος (rhódon) for "rose", due to its pinkish color, and ὄψις ( opsis) for "sight". Some members of the family, Homologous rhodopsin-like pigments, i.e. bacteriorhodopsin (of which there are more than 800 types) have Sensory Functions like opsins, integral for visual phototransduction. Many of these sensory functions are unknown – for example, the function of Neuropsin in the human retina. Members are known to have different absorption spectra including green and blue visible l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israeli Microbiologists
Israeli may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to the State of Israel * Israelis, citizens or permanent residents of the State of Israel * Modern Hebrew, a language * ''Israeli'' (newspaper), published from 2006 to 2008 * Guni Israeli (born 1984), Israeli basketball player See also * Israelites The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan. The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ..., the ancient people of the Land of Israel * List of Israelis {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Molecular Biology Organization
The European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO) is a professional, non-profit organization of more than 1,800 life scientists. Its goal is to promote research in life science and enable international exchange between scientists. It co-funds courses, workshops and conferences, publishes five scientific journals and supports individual scientists. The organization was founded in 1964 and is a founding member of the Initiative for Science in Europe. the Director of EMBO is Fiona Watt, a stem cell researcher, professor at King's College London and a group leader at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory. Conferences and journals EMBO funds or co-funds over 90 meetings involving more than 11,000 participants every year. EMBO publishes five peer-reviewed scientific journals: '' The EMBO Journal'', '' EMBO Reports'', '' Molecular Systems Biology'', '' EMBO Molecular Medicine'', and ''Life Science Alliance'', History The European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO) was lau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Society For Microbial Ecology
The International Society for Microbial Ecology (ISME) is the principal scientific society for the burgeoning field of microbial ecology and its related disciplines. ISME is a non-profit association and is owner of the International Symposia on Microbial Ecology and also owner of The ISME Journal which is published by Springer Nature (impact factor 2016 9.6 - Reuters Thomson). The ISME Office is based at the Netherlands Institute of Ecology ( NIOO-KNAW) in Wageningen, The Netherlands. Goals ISME fosters the exchange of scientific information by organizing international symposia as well as specific workshops, sponsoring publications, and promoting education and research. ISME provides services to the scientific as well as the wider community. The society enjoys close collaborations with other key scientific organizations, and has established effective scientific interactions in all geographical regions through a network of scientific leaders who serve as ISME National Ambassadors. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew University Of Jerusalem
The Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HUJI; he, הַאוּנִיבֶרְסִיטָה הַעִבְרִית בִּירוּשָׁלַיִם) is a public research university based in Jerusalem, Israel. Co-founded by Albert Einstein and Dr. Chaim Weizmann in July 1918, the public university officially opened in April 1925. It is the second-oldest Israeli university, having been founded 30 years before the establishment of the State of Israel but six years after the older Technion university. The HUJI has three campuses in Jerusalem and one in Rehovot. The world's largest library for Jewish studies—the National Library of Israel—is located on its Edmond J. Safra campus in the Givat Ram neighbourhood of Jerusalem. The university has five affiliated teaching hospitals (including the Hadassah Medical Center), seven faculties, more than 100 research centers, and 315 academic departments. , one-third of all the doctoral candidates in Israel were studying at the HUJI. Among its fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliorhodopsin
Heliorhodopsin is a family of rhodopsins discovered in 2018 by Alina Pushkarev in the laboratory of Professor Oded Beja. The new family of heliorhodopsins has a distinct protein sequence from known Type 1 (microbial) and Type 2 (animal) rhodopsins. Heliorhodopsins also exhibit the reverse orientation in the membrane compared with the other rhodopsins, with the N-terminus facing the inside of the cell and the C-terminus outside the cell. Heliorhodopsins use ''all-trans'' retinal as a chromophore, and do not have any ion pumping activity across the membrane. Heliorhodopsins are distributed globally and exist in eukaryotes, prokaryotes and even some viruses. Despite the wide distribution, Heliorhodopsins are never present in true diderms, where there is a proper double membrane around the microorganism. It has been suggested that the function of Heliorhodopsin requires a direct interaction with the environment. Crystal structures of Heliorhodopsins suggest they form a homodim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blue-green algae, although they are not usually scientifically classified as algae. They appear to have originated in a freshwater or terrestrial environment. Sericytochromatia, the proposed name of the paraphyletic and most basal group, is the ancestor of both the non-photosynthetic group Melainabacteria and the photosynthetic cyanobacteria, also called Oxyphotobacteria. Cyanobacteria use photosynthetic pigments, such as carotenoids, phycobilins, and various forms of chlorophyll, which absorb energy from light. Unlike heterotrophic prokaryotes, cyanobacteria have internal membranes. These are flattened sacs called thylakoids where photosynthesis is performed. Phototrophic eukaryotes such as green plants perform photosynthesis in pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward DeLong
Edward Francis DeLong (born 1958), is a marine microbiologist and professor in the Department of Oceanography at the University of Hawaii, Manoa, and is considered a pioneer in the field of metagenomics. He is best known for his discovery of the bacterial use of the rhodopsin protein in converting sunlight to biochemical energy in marine microbial communities. Early life and education DeLong was born in Sonoma, California. He studied biology at Santa Rosa Junior College and obtained an A.S. degree in 1980. While continuing his education at the University of California, Davis, DeLong had originally planned on becoming a medical technologist, but after a meeting and working as an undergraduate researcher with bacteriologist Paul Baumann, he found a new interest in marine microbiology. He graduated with a B.S. degree in bacteriology at UCD in 1982 and moved to the Scripps Institution of Oceanography, where he received a Ph.D. in marine biology after finishing doctoral work wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Rhodopsins
Microbial rhodopsins, also known as bacterial rhodopsins are retinal-binding proteins that provide light-dependent ion transport and sensory functions in halophilic and other bacteria. They are integral membrane proteins with seven transmembrane helices, the last of which contains the attachment point (a conserved lysine) for retinal. This protein family includes light-driven proton pumps, ion pumps and ion channels, as well as light sensors. For example, the proteins from halobacteria include bacteriorhodopsin and archaerhodopsin, which are light-driven proton pumps; halorhodopsin, a light-driven chloride pump; and sensory rhodopsin, which mediates both photoattractant (in the red) and photophobic (in the ultra-violet) responses. Proteins from other bacteria include proteorhodopsin. Contrary to their name, microbial rhodopsins are found not only in Archaea and Bacteria, but also in Eukaryota (such as algae) and viruses; although they are rare in complex multicellular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbiology
Microbiology () is the scientific study of microorganisms, those being unicellular (single cell), multicellular (cell colony), or acellular (lacking cells). Microbiology encompasses numerous sub-disciplines including virology, bacteriology, protistology, mycology, immunology, and parasitology. Eukaryotic microorganisms possess membrane-bound organelles and include fungi and protists, whereas prokaryotic organisms—all of which are microorganisms—are conventionally classified as lacking membrane-bound organelles and include Bacteria and Archaea. Microbiologists traditionally relied on culture, staining, and microscopy. However, less than 1% of the microorganisms present in common environments can be cultured in isolation using current means. Microbiologists often rely on molecular biology tools such as DNA sequence based identification, for example the 16S rRNA gene sequence used for bacteria identification. Viruses have been variably classified as organisms, as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metagenomics
Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental or clinical samples by a method called sequencing. The broad field may also be referred to as environmental genomics, ecogenomics, community genomics or microbiomics. While traditional microbiology and microbial genome sequencing and genomics rely upon cultivated clonal cultures, early environmental gene sequencing cloned specific genes (often the 16S rRNA gene) to produce a profile of diversity in a natural sample. Such work revealed that the vast majority of microbial biodiversity had been missed by cultivation-based methods. Because of its ability to reveal the previously hidden diversity of microscopic life, metagenomics offers a powerful lens for viewing the microbial world that has the potential to revolutionize understanding of the entire living world. As the price of DNA sequencing continues to fall, metagenomics now allows microbial ecology to be investigated at a much greater sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

