|
NZR X Class
The New Zealand X class was a pioneering class of eighteen 4-8-2 steam locomotives built for New Zealand Railways Department (NZR) and designed by A. L. Beattie that operated on the national rail network of New Zealand. In 1908, a heavy and powerful locomotive was required to haul traffic on the newly completed mountainous central section of the North Island Main Trunk Railway, and as a logical progression of the 4-6-2 Q class design, the 4-8-2 wheel arrangement was created for the X class. Overview When the first X was completed in 1908 at NZR's Addington Workshops in Christchurch, it was the very first 4-8-2 tender locomotive built in the world. The 4-8-2 design went on to be popular in the United States and was nicknamed the "Mountain" type; one theory suggests this name stems from the mountainous terrain that inspired the X's design, while another suggests the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway first coined the name in reference to its 4-8-2s of 1911 that were built to oper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petone Workshops
The Petone Workshops were a government-owned railways maintenance and repair facility located in Petone, in Lower Hutt in the Wellington region of New Zealand's North Island. It took over construction and maintenance of rolling stock in the Wellington region from the Pipitea Point facility, starting in 1876, and became the only such facility in the region from 1878 until the opening of the replacement Hutt Workshops facility in 1929. History Predecessor The first railway workshops in the Wellington region were near Wellington's first railway station at Pipitea Point. These workshops started out as a set of storage sheds for rolling stock when the first section of the Wairarapa The Wairarapa (; ), a geographical region of New Zealand, lies in the south-eastern corner of the North Island, east of metropolitan Wellington and south-west of the Hawke's Bay Region. It is lightly populated, having several rural service ... Line was being constructed from 1872 to 1874 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
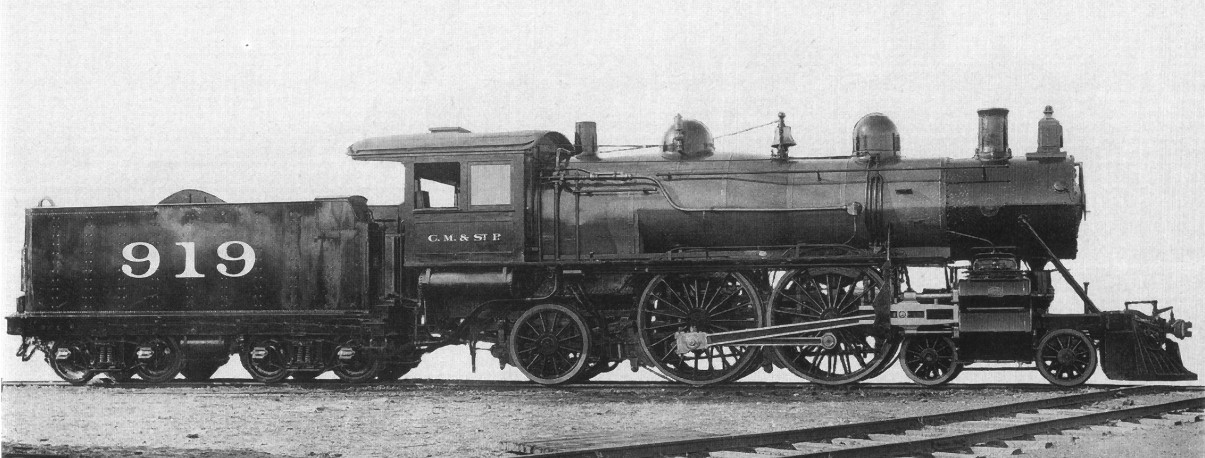
NZR A Class (1906)
The NZR A class were a class of steam locomotives built in 1906 with a 4-6-2 wheel arrangement for the New Zealand Railways Department (NZR). The class should not be confused with the older and more obscure A class of 1873. They were designed by the NZR's Chief Mechanical Engineer, A. L. Beattie and his Chief Draughtsman, G. A. Pearson to replace less powerful locomotives struggling with increasing loads on the South Island Main Trunk Railway, and in anticipation of the traffic volumes that would be created upon the completion of the North Island Main Trunk railway. Origin and design The Baldwin Q had established the Pacific as the way forward for Express passenger locomotives, but the C.M.E decided that greater efficiency was needed. The new locomotives were therefore designed as compounds. The Vauclain system had proved ineffective in New Zealand so the type attributed to Frenchman Alfred de Glehn was adopted. The first four had Stephenson valve gear inside and Walschaerts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3 Ft 6 In Gauge Locomotives Of New Zealand
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious or cultural significance in many societies. Evolution of the Arabic digit The use of three lines to denote the number 3 occurred in many writing systems, including some (like Roman and Chinese numerals) that are still in use. That was also the original representation of 3 in the Brahmic (Indian) numerical notation, its earliest forms aligned vertically. However, during the Gupta Empire the sign was modified by the addition of a curve on each line. The Nāgarī script rotated the lines clockwise, so they appeared horizontally, and ended each line with a short downward stroke on the right. In cursive script, the three strokes were eventually connected to form a glyph resembling a with an additional stroke at the bottom: ३. The Indian digits spread to the Caliphate in the 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound Locomotives
A compound locomotive is a steam locomotive which is powered by a compound engine, a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages. The locomotive was only one application of compounding. Two and three stages were used in ships, for example. Compounding became popular for railway locomotives from the early 1880s and by the 1890s were becoming common. Large numbers were constructed, mostly two- and four-cylinder compounds, in France, Germany, Austria, Hungary, and the United States. It declined in popularity due to maintenance issues and because superheating provided similar efficiencies at lower cost. Nonetheless, compound Mallets were built by the Norfolk and Western Railway right up to 1952. Introduction In the usual arrangement for a compound engine the steam is first expanded in one or two high-pressure ''(HP)'' cylinders, then having given up some heat and lost some pressure, it exhausts into a larger-volume low-pressure ''(LP)'' cylinder, (or two, - or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Locomotives Of New Zealand
Steam is a substance containing water in the gas phase, and sometimes also an aerosol of liquid water droplets, or air. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporization. Steam that is saturated or superheated is invisible; however, "steam" often refers to wet steam, the visible mist or aerosol of water droplets formed as water vapor condenses. Water increases in volume by 1,700 times at standard temperature and pressure; this change in volume can be converted into mechanical work by steam engines such as reciprocating piston type engines and steam turbines, which are a sub-group of steam engines. Piston type steam engines played a central role in the Industrial Revolution and modern steam turbines are used to generate more than 80% of the world's electricity. If liquid water comes in contact with a very hot surface or depressurizes quickly below its vapor pressure, it can create a steam explosion. Types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainline Steam
The Mainline Steam Heritage Trust is a New Zealand charitable trust devoted to the restoration and operation of historic New Zealand Railways and overseas mainline steam locomotives. Regular day excursions and multi-day tours are operated over rail lines throughout New Zealand. Excursions are operated by the Auckland, Wellington and Christchurch branches. About The Trust began in 1988 after the Ferrymead 125 events in Christchurch. Based around the collection of steam locomotives that were privately owned by Ian Welch, the first of which had begun operating on the mainline with J 1211 with an excursion to Timaru and Arthurs Pass double-heading with the Glenbrook Vintage Railway's JA 1250. Depots operated by the Trust included Parnell, (Auckland) Middleton and later Plimmerton. The Auckland depot used to be based in the former Parnell diesel depot. It was in the past the organisation's primary restoration base and most of Mainline Steam's currently active locomotives were r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feilding And District Steam Rail Society
The Feilding and District Steam Rail Society, also known as Feilding Steam Rail, is a railway preservation society located in Feilding in the Manawatu region of New Zealand. The society has restored or is restoring a number of locomotives and wagons once used on New Zealand's national rail network, with its star attraction being a WAB class tank locomotive, WAB 794. The society also has X 442 and F 163. Although nine members of the F class are preserved, this is the only one in mainline running condition. The society also possesses two small diesel shunters, DSA 227 and TR 13, along with a large mainline diesel locomotive, DA 1401, and a varied collection of rolling stock including both passenger and freight wagons. The society's depot includes the turntable from Palmerston, a town in north Otago in the South Island, as well as the Taonui station building that used to be located near Feilding on the North Island Main Trunk railway at the junction with the short-lived Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferrymead Railway
The Ferrymead Railway is a New Zealand heritage railway built upon the track formation of New Zealand's first public railway, from Ferrymead to Christchurch, which opened on 1 December 1863. On the opening of the line to Lyttelton on 9 December 1867, the Ferrymead Railway became the Ferrymead Branch and was closed shortly thereafter. In 1964, rail enthusiasts began relaying track on the historic formation and the new narrow gauge. Ferrymead Railway officially reopened in 1977. It now operates steam, diesel and electric trains regularly and is recognised as one of the most significant rail preservation sites in New Zealand. Early history The original line was built with the same gauge as the Canterbury Provincial Railways to suit rolling stock imported from the Melbourne and Essendon Railway Company in the Australian state of Victoria. It serviced ships which docked at the Ferrymead wharf. Construction of the tunnel to the port of Lyttelton was in progress: when this was finishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Railway And Locomotive Society
The New Zealand Railway and Locomotive Society Inc is a society of railway enthusiasts, based in Wellington. It was incorporated in 1958. The society archives are in the ''Thomas McGavin Building'' on Ava railway station's former goods yard in the Hutt Valley. At one time an old railway carriage held at the Ngaio railway station was used. Publications The society publishes a magazine, the ''New Zealand Railway Observer'' (), that was first published by the New Zealand Railway Correspondence Society on a Gestetner The Gestetner is a type of duplicating machine named after its inventor, David Gestetner (18541939). During the 20th century, the term ''Gestetner'' was used as a verb—as in ''Gestetnering''. The Gestetner company established its base in London ... in 1944, and a newsletter ''Turntable''. The society publishes books on railway subjects. There are currently about 25 books available, as listed on the website. Most are about New Zealand railways, but there is a book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wairio Branch
The Ohai Line, formerly known as the Ohai Industrial Line and previously the Wairio Branch and the Ohai Railway Board's line, is a 54.5 km branch line railway in Southland, New Zealand. It opened in 1882 and is one of two remaining branch lines in Southland, and one of only a few in the country. A number of smaller privately owned railways fanned out from Wairio; one of these lines, to Ohai, was originally built by the Ohai Railway Board and was worked by New Zealand Railways from 1990 and incorporated into the national network in 1992. Construction Wairio Branch Built at about the same time as the Riverton section of the Tuatapere Branch, what became the Wairio Branch left the Tuatapere Branch at Thornbury, where the junction originally faced Riverton rather than Invercargill, implying that the developers might have thought Riverton was going to be the region's major port. The line was built to open up new land to settlement and agricultural use and to access coal de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohai Railway Board
The Ohai Railway Board (ORB) was a short railway in Southland, New Zealand. The railway line itself still exists as the Ohai branch line, but the ORB was dissolved in 1990, and in 1992 the Southland District Council sold the board's assets to New Zealand Rail Limited. History Construction In the 1870s, coal was discovered in Ohai. Mines opened in the area, mostly with own 2 ft gauge railways to carry coal. Coal production boomed in the area in 1882 when a private spur railway line was built by the Nightcaps Coal Company from the terminus of the New Zealand Government Railways Wairio Branch at Wairio to Nightcaps to provide more efficient transport of coal. In 1916 a proposal was made to build another line to coal interests around Ohai. The construction of this line was fiercely opposed by the Nightcaps Coal Company, fearing a loss of business. The Ohai Railway Board (ORB) was formed under the District Railways Act 1877. Much like the Port Chalmers Railway Company Limi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |