|
Nurgan
The Nurgan Regional Military Commission () was a Chinese administrative seat established in Manchuria during the Ming dynasty, located on the banks of the Amur River, about 100 km from the sea, at Nurgan city (modern Tyr, Russia). Nurgan ( ) in the Jurchen language means “painting”. History The seat was nominally established in 1409, but was abandoned in 1435. Nurgan was the site of Yongning Temple (永寧寺), a Buddhist temple dedicated to Guanyin, that was founded by Yishiha (Išiqa) in 1413. The founding of Yongning Temple is recorded in the Yongning Temple Stele with inscriptions in Chinese, Mongolian and Jurchen scripts. The commission was an important institution during the Ming rule of Manchuria, obtaining at least the nominal allegiance of the lower Amur's tribes to the Ming government.L. Carrington Godrich, Chaoying Fang (editors), "Dictionary of Ming Biography, 1368–1644". Volume I (A-L). Columbia University Press, 1976. By 1409, the Yongle Emperor's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchuria Under Ming Rule
Manchuria under Ming rule refers to the domination of the Ming dynasty over Manchuria, including today's Northeast China and Outer Manchuria. The Ming rule of Manchuria began with its conquest of Manchuria in the late 1380s after the fall of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty, and reached its peak in the early 15th century with the establishment of the Nurgan Regional Military Commission, but the Ming power waned considerably in Manchuria after that. Starting in the 1580s, the Jianzhou Jurchen chieftain Nurhaci (chieftain who was nominally a Ming vassal) began to take control of most of Manchuria over the next several decades, and in 1616 he established the Later Jin. The Qing dynasty established by his son Hong Taiji would eventually conquer the Ming and take control of Southern China. From the late 14th century to early 17th century, the Ming dynasty ruled over Manchuria. Rebellions by Jurchen tribes were suppressed by the Ming government. The Nurgan Regional Military Commission was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuergan
The Nurgan Regional Military Commission () was a Chinese administrative seat established in Manchuria during the Ming dynasty, located on the banks of the Amur River, about 100 km from the sea, at Nurgan city (modern Tyr, Russia). Nurgan ( ) in the Jurchen language means “painting”. History The seat was nominally established in 1409, but was abandoned in 1435. Nurgan was the site of Yongning Temple (永寧寺), a Buddhist temple dedicated to Guanyin, that was founded by Yishiha (Išiqa) in 1413. The founding of Yongning Temple is recorded in the Yongning Temple Stele with inscriptions in Chinese, Mongolian and Jurchen scripts. The commission was an important institution during the Ming rule of Manchuria, obtaining at least the nominal allegiance of the lower Amur's tribes to the Ming government.L. Carrington Godrich, Chaoying Fang (editors), "Dictionary of Ming Biography, 1368–1644". Volume I (A-L). Columbia University Press, 1976. By 1409, the Yongle Emperor's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yishiha
Yishiha (; also Išiqa or Isiha; Jurchen: ) ( fl. 1409–1451) was a Jurchen eunuch of the Ming dynasty of China. He served the Ming emperors who commissioned several expeditions down the Songhua and Amur Rivers during the period of Ming rule of Manchuria, and is credited with the construction of the only two Ming dynasty Buddhist temples ever built on the territory of present-day Russia. Early life It is believed that Yishiha was a Haixi Jurchen by origin, and was captured by the Ming forces in the late 14th century. He worked under two important eunuchs, Wang Zhen and Cao Jixiang. It is speculated by modern historians that he rose to prominence by participating in imperial court politics and serving the Yongle Emperor's concubines of Manchu (Jurchen) origin. Amur expeditions Yishiha's Amur expeditions belong to the same period of the Yongle Emperor's reign (1402–1424) which saw another eunuch admiral, Zheng He, sail across the Indian Ocean, and Chinese ambassador Che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yongning Temple Stele
The Yongning Temple Stele () is a stele erected by the Chinese Ming dynasty in 1413 with a trilingual inscription to commemorate the founding of the Yongning Temple (永寧寺) in the Nurgan outpost, near the mouth of the Amur River, by the eunuch Yishiha. The location of the temple is the village of Tyr near Nikolayevsk-on-Amur in Russia. This stele is renowned both as the latest known example of a monumental inscription in the Jurchen script, and also for the inscription of the Buddhist ''mantra'' Om mani padme hum in four different scripts on its sides. A stele with a monolingual Chinese inscription, commemorating the repair of the temple by Yishiha, was erected in 1433. Both monuments are now held at the Arsenyev Museum in Vladivostok. Background The Ming government under the Yongle Emperor (reigned 1402–1424) attempted to expand its influence in the far north and defend itself against the Mongols by setting up a system of guards and posts in the territory of the Haixi J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer Manchuria). Its meaning may vary depending on the context: * Historical polities and geographical regions usually referred to as Manchuria: ** The Later Jin (1616–1636), the Manchu-led dynasty which renamed itself from "Jin" to "Qing", and the ethnicity from "Jurchen" to "Manchu" in 1636 ** the subsequent duration of the Qing dynasty prior to its conquest of China proper (1644) ** the northeastern region of Qing dynasty China, the homeland of Manchus, known as "Guandong" or "Guanwai" during the Qing dynasty ** The region of Northeast Asia that served as the historical homeland of the Jurchens and later their descendants Manchus ***Qing control of Dauria (the region north of the Amur River, but in its watershed) was contested in 1643 when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jianzhou Jurchens
The Jianzhou Jurchens () were one of the three major groups of Jurchens as identified by the Ming dynasty. Although the geographic location of the Jianzhou Jurchens changed throughout history, during the 14th century they were located south of the Wild Jurchens and the Haixi Jurchens, and inhabited modern-day Liaoning and Jilin provinces in China. The Jianzhou Jurchens were known to possess an abundant supply of natural resources. They also possessed industrial secrets, particularly in processing ginseng and the dyeing of cloth. They were powerful due to their proximity to Ming trading towns such as Fushun, Kaiyuan, and Tieling in Liaodong, and to Manpojin camp near Korea. Origins According to Pamela Crossley, a historian specializing in Manchu history, the origin of the name Jianzhou is contested. Xu Zhongsha thought it was derived from the region of Parhae, from the Songari and Hun Rivers. Japanese scholars disagree and state that the name was created from the migrating Jur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
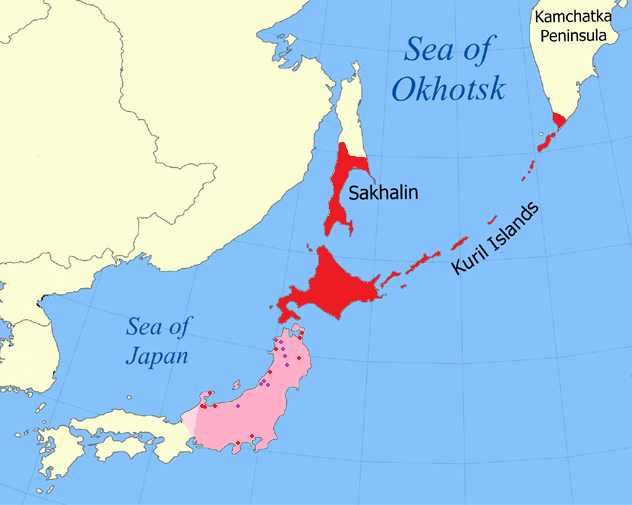
Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, r=Sakhalín, p=səxɐˈlʲin; ja, 樺太 ''Karafuto''; zh, c=, p=Kùyèdǎo, s=库页岛, t=庫頁島; Manchu: ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ, ''Sahaliyan''; Orok: Бугата на̄, ''Bugata nā''; Nivkh: Yh-mif) is the largest island of Russia. It is north of the Japanese archipelago, and is administered as part of the Sakhalin Oblast. Sakhalin is situated in the Pacific Ocean, sandwiched between the Sea of Okhotsk to the east and the Sea of Japan to the west. It is located just off Khabarovsk Krai, and is north of Hokkaido in Japan. The island has a population of roughly 500,000, the majority of which are Russians. The indigenous peoples of the island are the Ainu, Oroks, and Nivkhs, who are now present in very small numbers. The Island's name is derived from the Manchu word ''Sahaliyan'' (ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ). Sakhalin was once part of China during the Qing dynasty, although Chinese control was relaxed at times. Sakhalin was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nivkh People
The Nivkh, or Gilyak (also Nivkhs or Nivkhi, or Gilyaks; ethnonym: Нивхгу, ''Nʼivxgu'' (Amur) or Ниғвңгун, ''Nʼiɣvŋgun'' (E. Sakhalin) "the people"), are an indigenous ethnic group inhabiting the northern half of Sakhalin Island and the lower Amur River and coast on the adjacent Russian mainland and historically possibly parts of Manchuria. Nivkh were traditionally fishermen, hunters, and dog breeders. They were semi-nomadic, living near the coasts in the summer and wintering inland along streams and rivers to catch salmon. The land the Nivkh inhabit is characterized as taiga forest with cold snow-laden winters and mild summers with sparse tree cover. The Nivkh are believed to be the original inhabitants of the region, and to derive from a proposed Neolithic people that migrated from the Transbaikal region during the Late Pleistocene.Fitzhugh, William, and Durbreui pp.39, 40 The Nivkh had long maintained trade and cultural relations with neighboring China and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ming Dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han Chinese, Han people, the majority ethnic group in China. Although the primary capital of Beijing fell in 1644 to a rebellion led by Li Zicheng (who established the short-lived Shun dynasty), numerous rump state, rump regimes ruled by remnants of the House of Zhu, Ming imperial family—collectively called the Southern Ming—survived until 1662. The Ming dynasty's founder, the Hongwu Emperor (r. 1368–1398), attempted to create a society of self-sufficient rural communities ordered in a rigid, immobile system that would guarantee and support a permanent class of soldiers for his dynasty: the empire's standing army exceeded one million troops and the naval history of China, navy's dockyards in Nanjin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ainu People
The Ainu are the indigenous people of the lands surrounding the Sea of Okhotsk, including Hokkaido Island, Northeast Honshu Island, Sakhalin Island, the Kuril Islands, the Kamchatka Peninsula and Khabarovsk Krai, before the arrival of the Yamato Japanese and Russians. These regions are referred to as in historical Japanese texts. Official estimates place the total Ainu population of Japan at 25,000. Unofficial estimates place the total population at 200,000 or higher, as the near-total assimilation of the Ainu into Japanese society has resulted in many individuals of Ainu descent having no knowledge of their ancestry. As of 2000, the number of "pure" Ainu was estimated at about 300 people. In 1966, there were about 300 native Ainu speakers; in 2008, however, there were about 100. Names This people's most widely known ethnonym, "Ainu" ( ain, ; ja, アイヌ; russian: Айны) means "human" in the Ainu language, particularly as opposed to , divine beings. Ainu also i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanai People
The Nanai people are a Tungusic people of East Asia who have traditionally lived along Heilongjiang (Amur), Songhuajiang (Sunggari) and Wusuli River on the Middle Amur Basin. The ancestors of the Nanai were the Jurchens of northernmost Manchuria (Outer Manchuria). The Nanai/Hezhe language belongs to the Manchu-Tungusic languages. According to the 2010 census there were 12,003 Nanai in Russia. Name Common names for these people include нанай/Nanai (meaning 'natives, locals, people of the land/earth'); self-designation Hezhen (means 'people of the Orient'); russian: нанайцы ; ; . There are also terms formerly in use: Goldi, Golds, Goldes, Heje, and Samagir. Own names are ( and ) and (). means 'land, earth, ground, country' or, in this context, 'native, local' and , , means 'people' in different dialects. The Russian linguist L. I. Sem gives the self-name in the Cyrillic form, ''хэǯэ най'' (''Hezhe nai'') or ''хэǯэны'' (''Hezheni''), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military History Of The Ming Dynasty
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_family.jpg)