Manchuria on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym "
 Manchuria is now most often associated with the three Chinese provinces of Heilongjiang, Jilin, and
Manchuria is now most often associated with the three Chinese provinces of Heilongjiang, Jilin, and
File:EB1911 Manchuria.png , Map of the three provinces of Northeast China (1911)
File:Manchukuo Railmap en.png , Map of
 "Manchuria"variations of which arrived in European languages through Dutchis a
"Manchuria"variations of which arrived in European languages through Dutchis a
.
. According to Mark C. Elliott, the term ''Manshū'' first appeared as a place name in Katsuragawa Hoshū's 1794 work ''Hokusa Bunryaku'' in two maps, "Ashia zenzu" and "Chikyū hankyū sōzu", which were also created by Katsuragawa. ''Manshū'' then began to appear as a place name in more maps created by Japanese like Kondi Jūzō, Takahashi Kageyasu, Baba Sadayoshi and Yamada Ren, and these maps were brought to Europe by the Dutch Philipp von Siebold. According to Nakami Tatsuo, Philip Franz von Siebold was the one who brought the usage of the term ''Manchuria'' to Europeans after borrowing it from the Japanese, who were the first to use it in a geographic manner in the 18th century.ed. Wolff & Steinberg 2007
, p. 514. According to Bill Sewell, it was Europeans who first started using the name Manchuria to refer to the location and it is "not a genuine geographic term". The historian Gavan McCormack agreed with Robert H. G. Lee's statement that "The term Manchuria or Man-chou is a modern creation used mainly by westerners and Japanese", with McCormack writing that the term Manchuria is imperialistic in nature and has no "precise meaning" since the Japanese deliberately promoted the use of "Manchuria" as a geographic name to promote its separation from China at the time they were setting up their puppet state of Manchukuo. The Japanese had their own motive for deliberately spreading the usage of the term Manchuria. The historian Norman Smith wrote that "The term 'Manchuria' is controversial". Professor Mariko Asano Tamanoi said that she "should use the term in quotation marks" when referring to Manchuria. In 18th-century Europe, the region later known as "Manchuria", was most commonly referred to as " hinese Tartary". However, the term Manchuria (''Mantchourie'', in French) started appearing by the end of the century; French missionaries used it as early as 1800. The French-based geographers Conrad Malte-Brun and
, p. 7. since 1683 when Jilin and Heilongjiang were separated even though it was not until 1907 that they were turned into actual provinces. The administrators of the three areas were the General of Heilongjiang (Sahaliyan Ula i Jiyanggiyūn), General of Jilin (Girin i Jiyanggiyūn), and General of Shengjing (Mukden i Jiyanggiyūn). The area of Manchuria was then converted into three provinces by the late
 Manchuria consists mainly of the northern side of the funnel-shaped North China Craton, a large area of tilled and overlaid
Manchuria consists mainly of the northern side of the funnel-shaped North China Craton, a large area of tilled and overlaid  No part of Manchuria was glaciated during the
No part of Manchuria was glaciated during the

 Manchuria was the homeland of several ethnic groups, including
Manchuria was the homeland of several ethnic groups, including 
 In the early 12th century the
In the early 12th century the  Chinese cultural and religious influence such as Chinese New Year, the " Chinese god", motifs such as the dragon, spirals, and scrolls, agriculture, husbandry, methods of heating, and material goods such as iron cooking-pots, silk, and cotton spread among the Amur natives including the
Chinese cultural and religious influence such as Chinese New Year, the " Chinese god", motifs such as the dragon, spirals, and scrolls, agriculture, husbandry, methods of heating, and material goods such as iron cooking-pots, silk, and cotton spread among the Amur natives including the  After conquering the Ming, the Qing often identified their state as "China" (中國, ''Zhongguo''; "Middle Kingdom"), and referred to it as ''Dulimbai Gurun'' ("Middle Kingdom") in Manchu. In the ''
After conquering the Ming, the Qing often identified their state as "China" (中國, ''Zhongguo''; "Middle Kingdom"), and referred to it as ''Dulimbai Gurun'' ("Middle Kingdom") in Manchu. In the '' The Russian conquest of Siberia was met with indigenous resistance to colonization, but
The Russian conquest of Siberia was met with indigenous resistance to colonization, but
 Inner Manchuria also came under strong Russian influence with the building of the
Inner Manchuria also came under strong Russian influence with the building of the  Around the time of
Around the time of
Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East ( Outer Manchuria). Its meaning may vary depending on the context:
* Historical polities and geographical regions usually referred to as Manchuria:
** The Later Jin (1616–1636), the Manchu-led dynasty which renamed itself from "Jin" to "Qing", and the ethnicity from "Jurchen" to "Manchu" in 1636
** the subsequent duration of the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
prior to its conquest of China proper (1644)
** the northeastern region of Qing dynasty China, the homeland of Manchus, known as "Guandong" or "Guanwai" during the Qing dynasty
** The region of Northeast Asia that served as the historical homeland of the Jurchens and later their descendants Manchus
***Qing control of Dauria
Transbaikal, Trans-Baikal, Transbaikalia ( rus, Забайка́лье, r=Zabaykalye, p=zəbɐjˈkalʲjɪ), or Dauria (, ''Dauriya'') is a mountainous region to the east of or "beyond" (trans-) Lake Baikal in Far Eastern Russia.
The steppe an ...
(the region north of the Amur River, but in its watershed) was contested in 1643 when Russians entered; the ensuing Sino-Russian border conflicts ended when Russia agreed to withdraw in the 1689 Treaty of Nerchinsk
***controlled in whole by Qing Dynasty China until the Amur Annexation of Outer Manchuria by Russia in 1858-1860
***controlled as a whole by the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended th ...
after the Russian invasion of Manchuria in 1900 until the Russo-Japanese War and the Treaty of Portsmouth in 1905, which required Russian withdrawal.
***controlled by Qing China again, and reorganised in 1907 under the Viceroy of the Three Northeast Provinces (東三省; the area had previously not been considered "provinces")
***controlled by the Republic of China (1912–1949) after the 1911 revolution
***controlled by the Fengtian clique lead by Zhang Zuolin from 1917–1928 (during the Warlord Era), until the military Northern Expedition and the Northeast Flag Replacement brought it under control the Republic of China (1912–1949) again (specifically, the Nationalist government of the Second Republic of China, 1925-1948, then allied with the Chinese Communist Party
The Chinese Communist Party (CCP), officially the Communist Party of China (CPC), is the founding and sole ruling party of the People's Republic of China (PRC). Under the leadership of Mao Zedong, the CCP emerged victorious in the Chinese Ci ...
)
***controlled by Imperial Japan as the puppet state of Manchukuo
Manchukuo, officially the State of Manchuria prior to 1934 and the Empire of (Great) Manchuria after 1934, was a puppet state of the Empire of Japan in Northeast China, Manchuria from 1932 until 1945. It was founded as a republic in 1932 afte ...
, often translated as "Manchuria", (1932–1945). Formed after the Japanese invasion of Manchuria
The Empire of Japan's Kwantung Army invaded Manchuria on 18 September 1931, immediately following the Mukden Incident. At the war's end in February 1932, the Japanese established the puppet state of Manchukuo. Their occupation lasted until t ...
, it included the entire Northeast China, the northern fringes of present-day Hebei Province, and the eastern part of Inner Mongolia.
***briefly entirely controlled by the USSR after the Soviet invasion of Manchuria in 1945, but then divided with China
** Modern Northeast China (also known as "Inner Manchuria"), specifically the three provinces of Heilongjiang, Jilin, and Liaoning
Liaoning () is a coastal province in Northeast China that is the smallest, southernmost, and most populous province in the region. With its capital at Shenyang, it is located on the northern shore of the Yellow Sea, and is the northernmos ...
, but broadly also including the eastern Inner Mongolian prefectures of Hulunbuir
Hulunbuir or Hulun Buir ( mn, , ''Kölün buyir'', Mongolian Cyrillic: Хөлөнбуйр, ''Khölönbuir''; zh, s=呼伦贝尔, ''Hūlúnbèi'ěr'') is a region that is governed as a prefecture-level city in northeastern Inner Mongolia, China. ...
, Hinggan, Tongliao, and Chifeng
Chifeng ( zh, s=赤峰市), also known as Ulanhad ( mn, (Улаанхад хот), ''Ulaɣanqada qota'', , "red cliff"), is a prefecture-level city in Southeastern Inner Mongolia, People's Republic of China. It borders Xilin Gol League to t ...
, and sometimes Xilin Gol
**Areas of the modern Russian Federation
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia
North Asia or Northern Asia, also referred to as Siberia, is the northern region of Asia, which is defined in geographic ...
also known as "Outer Northeast China" or " Outer Manchuria". The two areas involved are Priamurye between the Amur River and the Stanovoy Range to the north, and Primorye which runs down the coast from the Amur mouth to the Korean border, including the island of Sakhalin
First used in the 19th century by the Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the no ...
ese, the term is deprecated among people of the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, sli ...
(PRC) due to its association with pro Japanese imperialism, the historical puppet state of Manchukuo
Manchukuo, officially the State of Manchuria prior to 1934 and the Empire of (Great) Manchuria after 1934, was a puppet state of the Empire of Japan in Northeast China, Manchuria from 1932 until 1945. It was founded as a republic in 1932 afte ...
of the Empire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent for ...
, and its origination of alleged contemporary "Manchurian nationalism
Manchurian nationalism or Manchu nationalism () refers to the ethnic nationalism of the Manchu people or the territorial nationalism of the inhabitants of Manchuria, regardless of ethnic origin.
Overview
While ruling China proper, the Manchu- ...
". Official state documents use the term Northeast Region (东北; Dōngběi) to describe the region. Northeast China is predominantly occupied by Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive v ...
due to internal Chinese migrations and Sinicization of the Manchus
The Sinicization of the Manchus is the process in which the Manchu people became assimilated into the Han-dominated Chinese society. It had occurred most prominently during the Qing dynasty when attempts were made by the new Manchu rulers of Ch ...
especially during the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
. It is considered the homeland of several minority groups besides the Manchus, including the Yemaek the Xianbei, the Shiwei Shiwei may refer to:
*Shiwei people, a historic Mongolic people
*Shiwei, Inner Mongolia, a township in Ergun City, Inner Mongolia
Given names
*Che Shiwei (born 1996), Chinese footballer
*Chen Shiwei, Chinese track and field athlete
*Pan Shiwei (bo ...
, and the Khitans. The area is also home to many Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
and Hui.
Manchuria is often referred to as the "Chinese rust belt", due to the shrinking cities that used to be the center of China's heavy industry and natural resource mining, but today face increasing economic decline.
Boundaries
 Manchuria is now most often associated with the three Chinese provinces of Heilongjiang, Jilin, and
Manchuria is now most often associated with the three Chinese provinces of Heilongjiang, Jilin, and Liaoning
Liaoning () is a coastal province in Northeast China that is the smallest, southernmost, and most populous province in the region. With its capital at Shenyang, it is located on the northern shore of the Yellow Sea, and is the northernmos ...
. The former Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo further included the prefectures of Chengde
Chengde, formerly known as Jehol and Rehe, is a prefecture-level city in Hebei province, situated about 225 km northeast of Beijing. It is best known as the site of the Mountain Resort, a vast imperial garden and palace formerly used by t ...
(now in Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and ...
), and Hulunbuir
Hulunbuir or Hulun Buir ( mn, , ''Kölün buyir'', Mongolian Cyrillic: Хөлөнбуйр, ''Khölönbuir''; zh, s=呼伦贝尔, ''Hūlúnbèi'ěr'') is a region that is governed as a prefecture-level city in northeastern Inner Mongolia, China. ...
, Hinggan, Tongliao, and Chifeng
Chifeng ( zh, s=赤峰市), also known as Ulanhad ( mn, (Улаанхад хот), ''Ulaɣanqada qota'', , "red cliff"), is a prefecture-level city in Southeastern Inner Mongolia, People's Republic of China. It borders Xilin Gol League to t ...
(now in Inner Mongolia). The region of the Qing dynasty referenced as Manchuria originally further included Primorskiy Kray
Primorsky Krai (russian: Приморский край, r=Primorsky kray, p=prʲɪˈmorskʲɪj kraj), informally known as Primorye (, ), is a federal subject (a krai) of Russia, located in the Far East region of the country and is a part of the ...
, the Jewish Autonomous Oblast, the southern parts of Amur Oblast and Khabarovskiy Kray
Khabarovsk Krai ( rus, Хабаровский край, r=Khabarovsky kray, p=xɐˈbarəfskʲɪj kraj) is a federal subject (a krai) of Russia. It is geographically located in the Russian Far East and is a part of the Far Eastern Federal District ...
, and a corner of Zabaykalʼskiy Kray. These districts were acknowledged as Qing territory by the 1689 Treaty of Nerchinsk but ceded to the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended th ...
due to the Amur Annexation in the unequal 1858 Treaty of Aigun and 1860 Convention of Beijing. (The People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, sli ...
indirectly questioned the legitimacy of these treaties in the 1960s but has more recently signed agreements such as the 2001 Sino-Russian Treaty of Friendship, which affirm the current status quo; a minor exchange nonetheless occurred in 2004 at the confluence of the Amur and Ussuri rivers.) Various senses of Greater Manchuria sometimes further include Sakhalin Island
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, r=Sakhalín, p=səxɐˈlʲin; ja, 樺太 ''Karafuto''; zh, c=, p=Kùyèdǎo, s=库页岛, t=庫頁島; Manchu: ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ, ''Sahaliyan''; Orok: Бугата на̄, ''Bugata nā''; Nivkh: ...
, which despite its lack of mention in treaties was shown as Qing territory on period Chinese, Japanese, Russian, and French maps of the area.
Manchukuo
Manchukuo, officially the State of Manchuria prior to 1934 and the Empire of (Great) Manchuria after 1934, was a puppet state of the Empire of Japan in Northeast China, Manchuria from 1932 until 1945. It was founded as a republic in 1932 afte ...
and its rail network, c.1945
File:Amurrivermap.png , Drainage basin of the Amur River, also showing the island of Sakhalin in the east
Etymology and names
 "Manchuria"variations of which arrived in European languages through Dutchis a
"Manchuria"variations of which arrived in European languages through Dutchis a Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
ate calque
In linguistics, a calque () or loan translation is a word or phrase borrowed from another language by literal word-for-word or root-for-root translation. When used as a verb, "to calque" means to borrow a word or phrase from another language ...
of the Japanese place name ''Manshū'' "Region of the Manchus"), which dates from the 19th century. The name ''Manju'' was invented and given to the Jurchen people by Hong Taiji
Hong Taiji (28 November 1592 – 21 September 1643), also rendered as Huang Taiji and sometimes referred to as Abahai in Western literature, also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizong of Qing, was the second khan of the Later Jin ...
in 1635 as a new name for their ethnic group; however, the name "Manchuria" was never used by the Manchus or the Qing dynasty itself to refer to their homeland.
According to the Japanese scholar Junko Miyawaki-Okada, the Japanese geographer Takahashi Kageyasu was the first to use the term ''Manshū'' as a place name in 1809 in the ''Nippon Henkai Ryakuzu'', and it was from that work that Westerners adopted the name..
. According to Mark C. Elliott, the term ''Manshū'' first appeared as a place name in Katsuragawa Hoshū's 1794 work ''Hokusa Bunryaku'' in two maps, "Ashia zenzu" and "Chikyū hankyū sōzu", which were also created by Katsuragawa. ''Manshū'' then began to appear as a place name in more maps created by Japanese like Kondi Jūzō, Takahashi Kageyasu, Baba Sadayoshi and Yamada Ren, and these maps were brought to Europe by the Dutch Philipp von Siebold. According to Nakami Tatsuo, Philip Franz von Siebold was the one who brought the usage of the term ''Manchuria'' to Europeans after borrowing it from the Japanese, who were the first to use it in a geographic manner in the 18th century.ed. Wolff & Steinberg 2007
, p. 514. According to Bill Sewell, it was Europeans who first started using the name Manchuria to refer to the location and it is "not a genuine geographic term". The historian Gavan McCormack agreed with Robert H. G. Lee's statement that "The term Manchuria or Man-chou is a modern creation used mainly by westerners and Japanese", with McCormack writing that the term Manchuria is imperialistic in nature and has no "precise meaning" since the Japanese deliberately promoted the use of "Manchuria" as a geographic name to promote its separation from China at the time they were setting up their puppet state of Manchukuo. The Japanese had their own motive for deliberately spreading the usage of the term Manchuria. The historian Norman Smith wrote that "The term 'Manchuria' is controversial". Professor Mariko Asano Tamanoi said that she "should use the term in quotation marks" when referring to Manchuria. In 18th-century Europe, the region later known as "Manchuria", was most commonly referred to as " hinese Tartary". However, the term Manchuria (''Mantchourie'', in French) started appearing by the end of the century; French missionaries used it as early as 1800. The French-based geographers Conrad Malte-Brun and
Edme Mentelle
Edme Mentelle (11 October 1730 - 28 April 1816) was a French geographer.
Biography
Student of Jean-Baptiste Louis Crévier at the Collège de Beauvais (at the time a constituent college of the University of Paris), he found employment with the ...
promoted the use of the term Manchuria (''Mantchourie'', in French), along with "Mongolia", "Kalmykia", etc., as more precise terms than Tartary, in their world geography work published in 1804.
In present-day Chinese, an inhabitant of the Northeast is a "Northeasterner" (). "The Northeast" is a term that expresses the entire region, encompassing its history and various cultures. It's usually restricted to the "Three East Provinces" or "Three Northeast Provinces", however, to the exclusion of northeastern Inner Mongolia. In China, the term Manchuria () is rarely used today, and the term is often negatively associated with the Japanese imperial legacy and the puppet state of Manchukuo
Manchukuo, officially the State of Manchuria prior to 1934 and the Empire of (Great) Manchuria after 1934, was a puppet state of the Empire of Japan in Northeast China, Manchuria from 1932 until 1945. It was founded as a republic in 1932 afte ...
.
Manchuria has been referred to as Guandong (), which literally means "east of the pass", and similarly Guanwai (), a reference to Shanhai Pass
Shanhai Pass or Shanhaiguan () is one of the major passes in the Great Wall of China, being the easternmost stronghold along the Ming Great Wall, and commands the narrowest choke point in the Liaoxi Corridor. It is located in Shanhaiguan Di ...
in Qinhuangdao in today's Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and ...
, at the eastern end of the Great Wall of China. This usage is seen in the expression ''Chuǎng Guāndōng
''Chuang Guandong'' (; IPA: ; literally "Crashing into Guandong" with ''Guandong'' being an older name for Manchuria) is descriptive of the rush of Han people into Manchuria, mainly from the Shandong Peninsula and Zhili, during the hundred-year per ...
'' (literally "Rushing into Guandong") referring to the mass migration of Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive v ...
to Manchuria in the 19th and 20th centuries. The name Guandong later came to be used more narrowly for the area of the Kwantung Leased Territory
The Kwantung Leased Territory ( ja, 關東州, ''Kantō-shū''; ) was a leased territory of the Empire of Japan in the Liaodong Peninsula from 1905 to 1945.
Japan first acquired Kwantung from the Qing Empire in perpetuity in 1895 in the Trea ...
on the Liaodong Peninsula. It is not to be confused with the southern province of Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020 ...
.
During the Qing dynasty, the region was known as the "three eastern provinces" (; Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
, ''Dergi Ilan Golo'')Clausen 1995, p. 7. since 1683 when Jilin and Heilongjiang were separated even though it was not until 1907 that they were turned into actual provinces. The administrators of the three areas were the General of Heilongjiang (Sahaliyan Ula i Jiyanggiyūn), General of Jilin (Girin i Jiyanggiyūn), and General of Shengjing (Mukden i Jiyanggiyūn). The area of Manchuria was then converted into three provinces by the late
Qing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaki ...
government in 1907. Since then, the phrase "Three Northeast Provinces" was officially used by the Qing government in China to refer to this region, and the post of Viceroy of the Three Northeast Provinces (dergi ilan goloi uheri kadalara amban) was established to take charge of these provinces. After the 1911 revolution, which resulted in the collapse of the Manchu-established Qing dynasty, the name of the region where the Manchus originated was known as "the Northeast" in official documents in the newly founded Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
, in addition to the "Three Northeast Provinces".
During the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
the area where the Jurchens lived was referred to as Nurgan
The Nurgan Regional Military Commission () was a Chinese administrative seat established in Manchuria during the Ming dynasty, located on the banks of the Amur River, about 100 km from the sea, at Nurgan city (modern Tyr, Russia). Nurgan ( ...
. Nurgan was the area of modern Jilin in Manchuria.
Geography and climate
 Manchuria consists mainly of the northern side of the funnel-shaped North China Craton, a large area of tilled and overlaid
Manchuria consists mainly of the northern side of the funnel-shaped North China Craton, a large area of tilled and overlaid Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of the ...
rocks spanning . The North China Craton was an independent continent before the Triassic period and is known to have been the northernmost piece of land in the world during the Carboniferous. The Khingan Mountains in the west are a Jurassic mountain range formed by the collision of the North China Craton with the Siberian Craton, which marked the final stage of the formation of the supercontinent Pangaea.
 No part of Manchuria was glaciated during the
No part of Manchuria was glaciated during the Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three period (geology), periods of the Cenozoic era (geology), Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spa ...
, but the surface geology of most of the lower-lying and more fertile parts of Manchuria consists of very deep layers of loess
Loess (, ; from german: Löss ) is a clastic, predominantly silt-sized sediment that is formed by the accumulation of wind-blown dust. Ten percent of Earth's land area is covered by loess or similar deposits.
Loess is a periglacial or aeol ...
, which have been formed by the wind-borne movement of dust
Dust is made of fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian process), volcanic eruptions, and pollution. Dust in ...
and till particles formed in glaciated parts of the Himalayas, Kunlun Shan
The Kunlun Mountains ( zh, s=昆仑山, t=崑崙山, p=Kūnlún Shān, ; ug, كۇئېنلۇن تاغ تىزمىسى / قۇرۇم تاغ تىزمىسى ) constitute one of the longest mountain chains in Asia, extending for more than . In the bro ...
and Tien Shan, as well as the Gobi and Taklamakan Deserts. Soils are mostly fertile mollisols and fluvents except in the more mountainous parts where they have poorly developed orthent
Orthents are soils defined in USDA soil taxonomy as entisols that lack due to either steep slopes or parent materials that contain no permanent weatherable minerals (such as ironstone).
Typically, Orthents are exceedingly shallow soils. They ar ...
s, as well as in the extreme north where permafrost
Permafrost is ground that continuously remains below 0 °C (32 °F) for two or more years, located on land or under the ocean. Most common in the Northern Hemisphere, around 15% of the Northern Hemisphere or 11% of the global surface ...
occurs and orthels dominate.
The climate of Manchuria has extreme seasonal contrasts, ranging from humid, almost tropical heat in summer to windy, dry, Arctic cold in winter. This pattern occurs because the position of Manchuria on the boundary between the great Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelag ...
n continental landmass and the huge Pacific Ocean causes complete monsoonal wind reversal.
In summer, when the land heats faster than the ocean, low-pressure forms over Asia and warm, moist south to southeasterly winds bring heavy, thundery rain, yielding annual rainfall ranging from , or less in the west, to over in the Changbai Mountains. Temperatures in summer are very warm to hot, with July average maxima ranging from in the south to in the extreme north.
In winter, however, the vast Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part o ...
n High
High may refer to:
Science and technology
* Height
* High (atmospheric), a high-pressure area
* High (computability), a quality of a Turing degree, in computability theory
* High (tectonics), in geology an area where relative tectonic uplift ...
causes very cold, north-to-northwesterly winds that bring temperatures as low as in the extreme south and in the north where the zone of discontinuous permafrost reaches northern Heilongjiang. However, because the winds from Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part o ...
are exceedingly dry, snow falls only on a few days every winter, and it is never heavy. This explains why corresponding latitudes of North America were fully glaciated during glacial periods of the Quaternary while Manchuria, though even colder, always remained too dry to form glaciers – a state of affairs enhanced by stronger westerly winds from the surface of the ice sheet in Europe.
History
Early history

 Manchuria was the homeland of several ethnic groups, including
Manchuria was the homeland of several ethnic groups, including Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
, Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
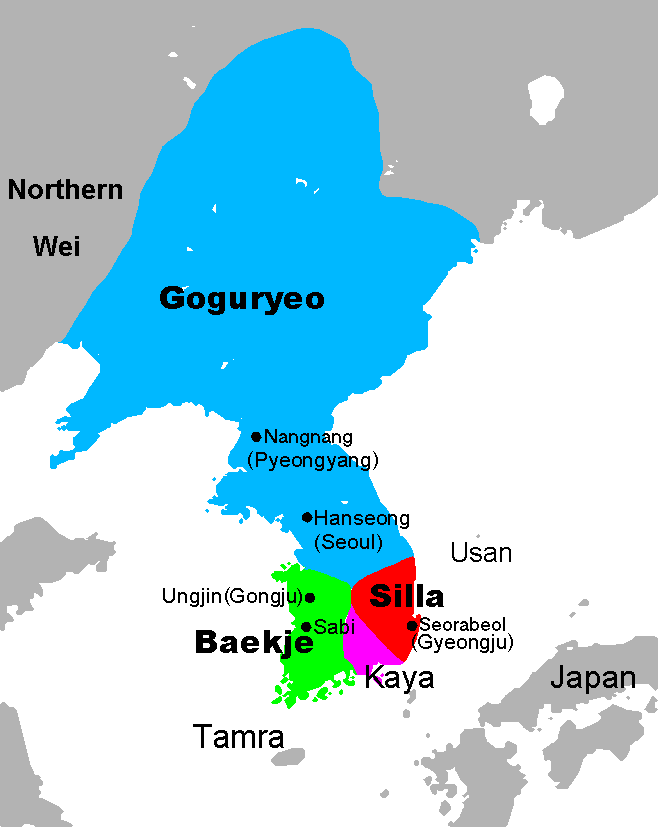
, Koreans, Nanai, Nivkhs, Ulchs, Hui and possibly Turkic peoples and ethnic Han Chinese in southern Manchuria. Various ethnic groups and their respective kingdoms, including the Sushen, Donghu, Xianbei, Wuhuan, Mohe, Khitan and Jurchens, have risen to power in Manchuria. Various Koreanic kingdoms such as Gojoseon (before 108 BCE), Buyeo (2nd century BCE to 494 CE) and Goguryeo
Goguryeo (37 BC–668 AD) ( ) also called Goryeo (), was a Korean kingdom located in the northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula and the southern and central parts of Northeast China. At its peak of power, Goguryeo controlled mos ...
(37 BCE to 688 CE) also became established in large parts of this area. The Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
(202 BCE to 9 CE and 25 to 220 CE), the Cao Wei dynasty (220–266), the Western Jin dynasty (266–316), the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdo ...
(618–690 and 705–907) and some other minor kingdoms of China established control in parts of Manchuria and in some cases tributary relations with peoples in the area. Parts of northwestern Manchuria came under the control of the First Turkic Khaganate of 552–603 and of the Eastern Turkic Khaganate of 581–630. Early Manchuria had a mixed economy of hunting, fishing, livestock, and agriculture.
With the Song dynasty (960-1269) to the south, the Khitan people
The Khitan people (Khitan small script: ; ) were a historical nomadic people from Northeast Asia who, from the 4th century, inhabited an area corresponding to parts of modern Mongolia, Northeast China and the Russian Far East.
As a people desce ...
of Inner Mongolia created the Liao dynasty (916-1125) and conquered Outer Mongolia and Manchuria, going on to control the adjacent part of the Sixteen Prefectures
The Sixteen Prefectures () comprise a historical region in northern China along the Great Wall in present-day Beijing, Tianjin, and northern Hebei and Shanxi.
Name
It is more specifically called the Sixteen Prefectures of Yan and Yun or the Six ...
in Northern China
Northern China () and Southern China () are two approximate regions within China. The exact boundary between these two regions is not precisely defined and only serve to depict where there appears to be regional differences between the climate ...
as well. The Liao dynasty became the first state to control all of Manchuria.

 In the early 12th century the
In the early 12th century the Tungusic Tungusic may refer to:
*The Tungusic languages
*The Tungusic peoples, people who speak a Tungusic language
{{dab ...
Jurchen people, who were Liao's tributaries, overthrew the Liao and formed the Jin dynasty (1115–1234)
The Jin dynasty (,
; ) or Jin State (; Jurchen: Anchun Gurun), officially known as the Great Jin (), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed between 1115 and 1234. Its name is sometimes written as Kin, Jurchen Jin, Jinn, or Chin
in ...
, which went on to control parts of Northern China and Mongolia after a series of successful military campaigns. During the Mongol Yuan dynasty rule of China (1271–1368), Manchuria was administered as Liaoyang province. In 1375 Naghachu, a Mongol official of the Mongolia-based Northern Yuan dynasty
The Northern Yuan () was a dynastic regime ruled by the Mongol Borjigin clan based in the Mongolian Plateau. It existed as a rump state after the collapse of the Yuan dynasty in 1368 and lasted until its conquest by the Jurchen-led Later ...
of 1368–1635 in Liaoyang province invaded Liaodong, but later surrendered to the Ming dynasty in 1387. In order to protect the northern border areas, the Ming dynasty decided to "pacify" the Jurchens in order to deal with its problems with Yuan remnants along its northern border. The Ming solidified control over Manchuria under the Yongle Emperor (), establishing the Nurgan Regional Military Commission of 1409–1435. Starting in the 1580s, a Jianzhou Jurchen chieftain, Nurhaci (1558–1626), started to unify Jurchen tribes of the region. Over the next several decades, the Jurchen took control of most of Manchuria. In 1616 Nurhaci founded the Later Jin dynasty, which later became known as the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
. The Qing defeated the Evenk- Daur federation led by the Evenki chief Bombogor and beheaded Bombogor in 1640, with Qing armies massacring and deporting Evenkis and absorbing the survivors into the Banners.
 Chinese cultural and religious influence such as Chinese New Year, the " Chinese god", motifs such as the dragon, spirals, and scrolls, agriculture, husbandry, methods of heating, and material goods such as iron cooking-pots, silk, and cotton spread among the Amur natives including the
Chinese cultural and religious influence such as Chinese New Year, the " Chinese god", motifs such as the dragon, spirals, and scrolls, agriculture, husbandry, methods of heating, and material goods such as iron cooking-pots, silk, and cotton spread among the Amur natives including the Udeghes
Udege (russian: Удэгейцы; ude, удиэ or , or Udihe, Udekhe, and Udeghe correspondingly) are a native people of the Primorsky Krai and Khabarovsk Krai regions in Russia. They live along the tributaries of the Ussuri, Amur, Khu ...
, Ulchis, and Nanais.
In 1644, after peasant rebels sacked the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
's capital of Beijing, the Jurchens (now called Manchus) allied with Ming general Wu Sangui
Wu Sangui (; 8 June 1612 – 2 October 1678), courtesy name Changbai () or Changbo (), was a notorious Ming Dynasty military officer who played a key role in the fall of the Ming dynasty and the founding of the Qing dynasty in China. In Chinese ...
and seized control of Beijing, overthrowing the short-lived Shun dynasty (1644–1649) and establishing Qing-dynasty rule (1644–1912) over all of China. The Manchu conquest of China involved the deaths of over 25 million people. The Qing dynasty built the Willow Palisade – a system of ditches and embankments – during the later 17th century to restrict the movement of Han civilians into Jilin and Heilongjiang. Only bannermen, including Chinese bannermen, were allowed to settle in Jilin and Heilongjiang.
 After conquering the Ming, the Qing often identified their state as "China" (中國, ''Zhongguo''; "Middle Kingdom"), and referred to it as ''Dulimbai Gurun'' ("Middle Kingdom") in Manchu. In the ''
After conquering the Ming, the Qing often identified their state as "China" (中國, ''Zhongguo''; "Middle Kingdom"), and referred to it as ''Dulimbai Gurun'' ("Middle Kingdom") in Manchu. In the ''Qing shilu
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu people, Manchu-led Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin (1616–1636), La ...
'' the lands of the Qing state (including Manchuria and present-day Xinjiang, Mongolia, and Tibet) are thus identified as "the Middle Kingdom" in both the Chinese and Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
languages in roughly two-thirds of the cases, while the term refers to the traditional Chinese provinces populated by the Han in roughly one third of the cases. It was also common to use "China" (''Zhongguo'', ''Dulimbai gurun'') to refer to the Qing in official documents, international treaties, and foreign affairs. In diplomatic documents, the term "Chinese language" (''Dulimbai gurun i bithe'') referred to the Chinese, Manchu, and Mongol languages, and the term "Chinese people" (中國人 Zhongguo ren; Manchu: Dulimbai gurun i niyalma) referred to all Han, Manchus, and Mongol subjects of the Qing. The Qing explicitly stated that the lands in Manchuria belonged to "China" (Zhongguo, Dulimbai gurun) in Qing edicts and in the 1689 Treaty of Nerchinsk.
Despite migration restrictions, Qing rule saw massively increasing numbers of Han Chinese both illegally and legally streaming into Manchuria and settling down to cultivate land – Manchu landlords desired Han Chinese peasants to rent their land and to grow grain; most Han Chinese migrants were not evicted as they crossed the Great Wall and Willow Palisade. During the eighteenth century Han Chinese farmed 500,000 hectares of privately owned land in Manchuria and 203,583 hectares of lands which were part of courier stations, noble estates, and Banner lands; in garrisons and towns in Manchuria Han Chinese made up 80% of the population.
The Qing resettled Han Chinese farmers from north China to the area along the Liao River
The Liao River () is the principal river in southern Northeast China, and one of the seven main river systems in China. Its name derived from the Liao region, a historical name for southern Manchuria, from which the Liaoning province, Liaodong P ...
in order to restore the land to cultivation. Han Chinese squatters reclaimed wasteland, and other Han rented land from Manchu landlords.
By the 18th century, despite officially prohibiting Han Chinese settlement on Manchu and Mongol lands, the Qing decided to settle Han refugees from northern China – who were suffering from famine, floods, and drought – into Manchuria and Inner Mongolia, so that Han Chinese farmed 500,000 hectares in Manchuria and tens of thousands of hectares in Inner Mongolia by the 1780s. The Qianlong Emperor
The Qianlong Emperor (25 September 17117 February 1799), also known by his temple name Emperor Gaozong of Qing, born Hongli, was the fifth Emperor of the Qing dynasty and the fourth Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1735 t ...
() allowed Han Chinese peasants suffering from drought to move into Manchuria despite his having issued edicts in favor of banning them from 1740 to 1776. Han Chinese then streamed into Manchuria, both illegally and legally, over the Great Wall of China and the Willow Palisade. Chinese tenant farmers rented or even claimed title to land from the "imperial estates" and Manchu Bannerlands in the area. Besides moving into the Liao area in southern Manchuria, Han Chinese settled the path linking Jinzhou, Fengtian Fengtian (; postal: Fengtien; Manchu: ''Abkai imiyangga fu'') is:
* Shenyang, largest city and provincial capital of Liaoning province, which was formerly administered under Fengtian Fu, which was abolished in 1910
* Liaoning, the province formerl ...
, Tieling, Changchun, Hulun, and Ningguta
Ning'an () is a city located approximately southwest of Mudanjiang, in the southeast of Heilongjiang province, China, bordering Jilin province to the south. It is located on the Mudanjiang River (formerly known as Hurka River), which flows north, ...
during the Qianlong Emperor's reign, and Han Chinese had become the majority in urban areas of Manchuria by 1800. To increase the Imperial Treasury's revenue, the Qing sold formerly Manchu-only lands along the Sungari to Han Chinese at the beginning of the Daoguang Emperor's 1820–1850 reign, and Han Chinese filled up most of Manchuria's towns by the 1840s, according to Abbé Huc
''Abbé'' (from Latin ''abbas'', in turn from Greek , ''abbas'', from Aramaic ''abba'', a title of honour, literally meaning "the father, my father", emphatic state of ''abh'', "father") is the French word for an abbot. It is the title for ...
.
 The Russian conquest of Siberia was met with indigenous resistance to colonization, but
The Russian conquest of Siberia was met with indigenous resistance to colonization, but Russian Cossacks
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
crushed the natives. The conquest of Siberia and Manchuria also resulted in the spread of infectious diseases
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
. Historian John F. Richards wrote: "... New diseases weakened and demoralized the indigenous peoples of Siberia. The worst of these was smallpox "because of its swift spread, the high death rates, and the permanent disfigurement of survivors." ... In the 1690s, smallpox epidemics reduced Yukagir numbers by an estimated 44 percent." At the behest of people like Vasilii Poyarkov
Vassili Danilovich Poyarkov (Василий Данилович Поярков in Russian, ? - after 1668) was the first Russian explorer of the Amur region.
The Russian expansion into Siberia began with the conquest of the Khanate of Sibir in 158 ...
in 1645 and Yerofei Khabarov in 1650, Russian Cossacks killed some peoples like the Daur people of Inner Mongolia and Xinjiang to the extent that some authors speak of genocide.
The Daurs initially deserted their villages since they had heard about the cruelty of the Russians the first time Khabarov came. The second time he came, the Daurs decided to do battle against the Russians instead, but were slaughtered by Russian guns. The Russians came to be known as "red-beards". The Amur natives called Russian Cossacks ''luocha'' (羅剎), after demons in Buddhist mythology, because of their cruelty towards the Amur tribespeople, who were subjects of the Qing. The Qing viewed Russian proselytization of Eastern Orthodox Christianity to the indigenous peoples along the Amur River as a threat.
In 1858 Russian diplomacy forced a weakening Qing dynasty to cede Manchuria north of the Amur to Russia under the Treaty of Aigun. In 1860, with the Treaty of Peking, the Russians managed to obtain a further large slice of Manchuria, east of the Ussuri River. As a result, Manchuria became divided into a Russian half (known as " Outer Manchuria", and a remaining Chinese half (known as "Inner Manchuria"). In modern literature, "Manchuria" usually refers to Inner (Chinese) Manchuria. As a result of the Treaties of Aigun and Peking, Qing China lost access to the Sea of Japan.
History after 1860
 Inner Manchuria also came under strong Russian influence with the building of the
Inner Manchuria also came under strong Russian influence with the building of the Chinese Eastern Railway
The Chinese Eastern Railway or CER (, russian: Китайско-Восточная железная дорога, or , ''Kitaysko-Vostochnaya Zheleznaya Doroga'' or ''KVZhD''), is the historical name for a railway system in Northeast China (al ...
through Harbin
Harbin (; mnc, , v=Halbin; ) is a sub-provincial city and the provincial capital and the largest city of Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China, as well as the second largest city by urban population after Shenyang and largest ...
to Vladivostok. In the '' Chuang Guandong'' movement, many Han farmers, mostly from the Shandong peninsula moved there. By 1921, Harbin, northern Manchuria's largest city, had a population of 300,000, including 100,000 Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
. Japan replaced Russian influence in the southern half of Inner Manchuria as a result of the Russo-Japanese War in 1904–1905. Most of the southern branch of the Chinese Eastern Railway was transferred from Russia to Japan, and became the South Manchurian Railway. Japanese influence extended into Outer Manchuria in the wake of the Russian Revolution of 1917, but Outer Manchuria had reverted to Soviet control by 1925. Manchuria was an important region due to its rich natural resources including coal, fertile soil, and various minerals. For pre–World War II Japan, Manchuria was an essential source of raw materials. Without occupying Manchuria, the Japanese probably could not have carried out their plan for conquest over Southeast Asia or taken the risk of attacking the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
and the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading post ...
in 1941.
There was a major epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time.
Epidemics of infectious d ...
known as the Manchurian plague in 1910–1911, likely caused by the inexperienced hunting of marmots
Marmots are large ground squirrels in the genus ''Marmota'', with 15 species living in Asia, Europe, and North America. These herbivores are active during the summer, when they can often be found in groups, but are not seen during the winter, w ...
, many of whom are diseased. The cheap railway transport and the harsh winters, where the hunters sheltered in close confinement, helped to propagate the disease. The response required close coordination between the Chinese, Russian and Japanese authorities and international disease experts held an 'International Plague Conference' in the northern city of Shenyang after the disease was under control to learn the lessons.
It was reported that among Banner people, both Manchu and Chinese (Hanjun) in Aihun, Heilongjiang in the 1920s, would seldom marry with Han civilians, but they (Manchu and Chinese Bannermen) would mostly intermarry with each other. Owen Lattimore reported that during his January 1930 visit to Manchuria, he studied a community in Jilin (Kirin), where both Manchu and Chinese Bannermen were settled at a town called Wulakai, and eventually the Chinese Bannermen there could not be differentiated from Manchus since they were effectively Manchufied (assimilated). The Han civilian population was in the process of absorbing and mixing with them when Lattimore wrote his article.
 Around the time of
Around the time of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, Zhang Zuolin established himself as a powerful warlord
A warlord is a person who exercises military, economic, and political control over a region in a country without a strong national government; largely because of coercive control over the armed forces. Warlords have existed throughout much of h ...
with influence over most of Manchuria. During his rule, the Manchurian economy grew tremendously, backed by the immigration of Chinese from other parts of China. The Japanese assassinated him on 2 June 1928, in what is known as the Huanggutun Incident. Following the Mukden Incident
The Mukden Incident, or Manchurian Incident, known in Chinese as the 9.18 Incident (九・一八), was a false flag event staged by Japanese military personnel as a pretext for the 1931 Japanese invasion of Manchuria.
On September 18, 1931, L ...
in 1931 and the subsequent Japanese invasion of Manchuria
The Empire of Japan's Kwantung Army invaded Manchuria on 18 September 1931, immediately following the Mukden Incident. At the war's end in February 1932, the Japanese established the puppet state of Manchukuo. Their occupation lasted until t ...
, the Japanese declared Inner Manchuria an "independent state", and appointed the deposed Qing emperor Puyi as puppet emperor of Manchukuo
Manchukuo, officially the State of Manchuria prior to 1934 and the Empire of (Great) Manchuria after 1934, was a puppet state of the Empire of Japan in Northeast China, Manchuria from 1932 until 1945. It was founded as a republic in 1932 afte ...
. Under Japanese control, Manchuria was brutally run, with a systematic campaign of terror and intimidation against the local populations including arrests, organised riots and other forms of subjugation.Edward Behr, ''ibid'', p. 202 Manchukuo was used by Japan as a base to invade the rest of China. At that time, hundreds of thousands of Japanese settlers arrived in Manchuria.
After the atomic bombing of Hiroshima
is the capital of Hiroshima Prefecture in Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 1,199,391. The gross domestic product (GDP) in Greater Hiroshima, Hiroshima Urban Employment Area, was US$61.3 billion as of 2010. Kazumi Matsui h ...
, Japan in 1945, the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
invaded from Soviet Outer Manchuria as part of its declaration of war against Japan. Soon afterwards, the Chinese Communist Party
The Chinese Communist Party (CCP), officially the Communist Party of China (CPC), is the founding and sole ruling party of the People's Republic of China (PRC). Under the leadership of Mao Zedong, the CCP emerged victorious in the Chinese Ci ...
and Chinese Nationalist Party (Kuomintang) started fighting for control over Manchuria. The communists won in the Liaoshen Campaign and took complete control over Manchuria. With the encouragement of the Soviet Union, Manchuria was then used as a staging ground
A staging area (otherwise staging point, staging base, or staging post) is a location in which organisms, people, vehicles, equipment, or material are assembled before use. It may refer to:
* In construction, a designated area in which vehicles, ...
during the Chinese Civil War for the Chinese Communist Party
The Chinese Communist Party (CCP), officially the Communist Party of China (CPC), is the founding and sole ruling party of the People's Republic of China (PRC). Under the leadership of Mao Zedong, the CCP emerged victorious in the Chinese Ci ...
, which emerged victorious in 1949. Ambiguities in the treaties that ceded Outer Manchuria to Russia led to disputes over the political status of several islands. The Kuomintang government in Taiwan (Formosa) complained to the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ...
, which passed resolution 505 on February 1, 1952, denouncing Soviet actions over the violations of the 1945 Sino-Soviet Treaty of Friendship and Alliance.
As part of the Sino-Soviet split, this ambiguity led to armed conflict in 1969, called the Sino-Soviet border conflict, resulting in an agreement. In 2004, Russia agreed to transfer Yinlong Island
Bolshoi Ussuriysky Island (russian: Большо́й Уссури́йский о́стров Bol'shoy Ussuriyskiy Ostrov), or Heixiazi Island (; lit. "black blind island"), is a sedimentary island at the confluence of the Ussuri and ...
and one half of Heixiazi Island
Bolshoi Ussuriysky Island (russian: Большо́й Уссури́йский о́стров Bol'shoy Ussuriyskiy Ostrov), or Heixiazi Island (; lit. "black blind island"), is a sedimentary island at the confluence of the Ussuri and ...
to China, ending an enduring border dispute.
See also
*Indigenous peoples of Siberia
Siberia, including the Russian Far East, is a vast region spanning the northern part of the Asian continent, and forming the Asiatic portion of Russia. As a result of the Russian conquest of Siberia (17th to 19th centuries) and of the subs ...
*Religion in Northeast China
The predominant religions in Northeast China (including the provinces of Liaoning, Jilin and Heilongjiang, historically also known as Manchuria) are Chinese folk religions led by local shamans. Taoism and Chinese Buddhism were never well establi ...
* Tungusic peoples
References
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * *Elliott, Mark C. "The Limits of Tartary: Manchuria in Imperial and National Geographies." ''Journal of Asian Studies'' 59, no. 3 (2000): 603–46. * * Gamsa, Mark, "Manchuria: A Concise History", Bloomsbury Academic, 2020. * * * Hata, Ikuhiro. "Continental Expansion: 1905–1941". In ''The Cambridge History of Japan''. Vol. 6. Cambridge University Press. 1988. * *Jones, Francis Clifford, ''Manchuria Since 1931'', London, Royal Institute of International Affairs, 1949 * * * Kwong, Chi Man. ''War and Geopolitics in Interwar Manchuria'' (2017). * * * Masafumi, Asada. "The China-Russia-Japan Military Balance in Manchuria, 1906–1918." ''Modern Asian Studies'' 44.6 (2010): 1283–1311. * Nish, Ian. ''The History of Manchuria, 1840-1948: A Sino-Russo-Japanese Triangle'' (2016) * * * * * * Tamanoi, Mariko Asano. ''Crossed Histories: Manchuria in the Age of Empire'' (2005) * * * * *Tao, Jing-shen, ''The Jurchen in Twelfth-Century China''. University of Washington Press, 1976, . *KISHI Toshihiko, MATSUSHIGE Mitsuhiro and MATSUMURA Fuminori eds, 20 Seiki Manshu Rekishi Jiten ncyclopedia of 20th Century Manchuria History Tokyo: Yoshikawa Kobunkan, 2012, * * *External links
* {{Regions of the world Inner Asia Northeast Asia Regions of China Historical regions in Russia Historical regions