|
Nolambas
The Nolamba dynasty the area they held sway over is referred to as ''Nolambasa-37'' of Henjeru (Hemavathi), ''Nolambalige'' (''Nolambavadi''-32000), etc. R. Narasimhacharya states that the Nolambas were a native Kannada dynasty. Officers and kings belonging to the Nolamba dynasty *Simhapota, a Nolamba chief, subordinate to the Ganga kings. *Mahendra I, Ayyapadeva who probably ruled around the period of Krishna II of the Rastrakutas. *Anniga or Annayya with the title Bira-Nolamba ruled in the period of Amoghavarsha of Rastrakutas. *Dilipa or Iriva Nolamba around the period of Krishna III of the Rashtrakutas. According to an inscription from Aimangala, 56 Dilipa's son and successor was Nanni Nolamba. *There are two other names after Nanni Nolamba, namely Polalchora II and Vira Mahendra or Mahendra II as per Kolar district inscriptions. As long as the Rastrakutas were strong Nolamba flourished under their influence. But after their collapse Nolamba Dynasty lost its influence and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Ganga Dynasty
Western Ganga was an important ruling dynasty of ancient Karnataka in India which lasted from about 350 to 1000 CE. They are known as "Western Gangas" to distinguish them from the Eastern Ganga Dynasty, Eastern Gangas who in later centuries ruled over Kalinga (historical region), Kalinga (modern Odisha and Northern Andhra Pradesh). The general belief is that the Western Gangas began their rule during a time when multiple native clans asserted their freedom due to the weakening of the Pallava empire in South India, a geo-political event sometimes attributed to the southern conquests of Samudra Gupta. The Western Ganga sovereignty lasted from about 350 to 550 CE, initially ruling from Kolar and later, moving their capital to Talakadu on the banks of the Kaveri River in modern Mysore district. After the rise of the imperial Chalukya dynasty, Chalukyas of Badami, the Gangas accepted Chalukya overlordship and fought for the cause of their overlords against the Pallavas of Kanchi. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avani
Avani is a small village in Mulabaagilu taluk, Kolara district in Karnataka, India, about ten miles from Kolar Gold Fields. The village is located at 32 km from Kolara, the district centre and 13 km from Mulabaagilu, the Taluk headquarters. It is a popular location for rock climbing. Legend Avani is known for the Sita temple situated on a hill. This temple is one of the few temples dedicated to Sitadevi in India. There is a belief that the sage Valmiki, the author of the epic Ramayana, was residing here during the period of Ramayana. Sitadevi lived here in his ashram while in exile. Sitadevi gave birth to her twin children Lava-Kusha here. Even today the room where Sita gave birth to her children exists. The war between Sri Rama and his sons Lava and Kusha happened in this village. The Temple is also visited by lot of childless couple, it is believed that , the childless women has to take bath in the lakshmana thirtha, then in the wet clothes she has go to the templ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion In Western Ganga Kingdom
The Western Ganga Dynasty (350 - 1000 CE) ( kn, ಪಶ್ಚಿಮ ಗಂಗ ಸಂಸ್ಥಾನ) was an important ruling dynasty of ancient Karnataka. Its members are known as Western Gangas to distinguish them from the Eastern Gangas who in later centuries ruled over modern Orissa. The Western Gangas ruled as a sovereign power from the middle of fourth century to middle of sixth century, initially from Kolar, later moving their capital to Talakad on the banks of the Kaveri River in modern Mysore district. Though territorially a small kingdom, the Western Ganga contribution to polity, culture and literature of the modern south Karnataka region is considered noteworthy. The Ganga kings showed benevolent tolerance to all faiths but are most famous for their patronage towards Jainism resulting in the construction of fine monuments in such places as Shravanabelagola and Kambadahalli. Religion The Western Gangas gave patronage to all the major religious faiths of the time; Jainism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
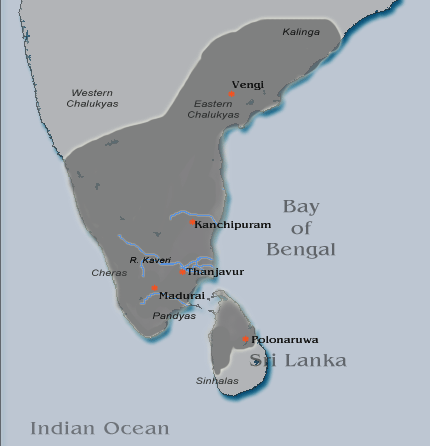
Rajaraja I
Rajaraja I (947 CE – 1014 CE), born Arunmozhi Varman or Arulmozhi Varman and often described as Raja Raja the Great or Raja Raja Chozhan was a Chola emperor who reigned from 985 CE to 1014 CE. He was the most powerful Tamil king in South India during his reign and is remembered for reinstating the Chola influence and ensuring its supremacy across the Indian Ocean. His extensive empire included vast regions of the Pandya country, the Chera country and northern Sri Lanka. He also acquired Lakshadweep and Thiladhunmadulu atoll, and part of the northern-most islands of the Maldives in the Indian Ocean. Campaigns against the Western Gangas and the Chalukyas extended the Chola authority as far as the Tungabhadra River. On the eastern coast, he battled with the Chalukyas for the possession of Vengi.A Journey through India's Past by Chandra Mauli Mani p.51 Rajaraja I, being an able administrator, also built the great Rajarajeshwaram Temple at the Chola capital Thanjavur. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalleshvara Temple, Aralaguppe
The Kalleshvara temple (also spelt "Kallesvara" or "Kalleshwara") is located in Aralaguppe, a village in the Tiptur taluk of Tumkur district, in the Indian state of Karnataka. History According to historian I. K. Sarma, the temple is a fine example of native Western Ganga art of the 9th century, with influences from the Badami Chalukya and Nolamba architectural idioms.Sarma (1992), p. 88 It is dedicated to the Hindu god Shiva (also called "Ishvara") and was commissioned by a vassal king of the Nolamba dynasty. Historians I.K. Sarma, B.S. Ali and K.V. Soundara Rajan date the temple to the late 9th century to early 10th-century period. B.S. Ali calls this temple one of the finest examples of Western Ganga art while Aschwin Lippe and Soundara Rajan feel the temple is more consistent with contemporary Nolamba style.Ali and Soundara Rajana in Sarma (1992), p. 88, p. 90 The dating of the temple is confirmed by two inscriptions. One inscription in the temple dated 895 C.E. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannada
Kannada (; ಕನ್ನಡ, ), originally romanised Canarese, is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by the people of Karnataka in southwestern India, with minorities in all neighbouring states. It has around 47 million native speakers, and was additionally a second or third language for around 13 million non-native speakers in Karnataka. Kannada was the court language of some of the most powerful dynasties of south and central India, namely the Kadambas, Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas, Yadava Dynasty or Seunas, Western Ganga dynasty, Wodeyars of Mysore, Nayakas of Keladi Hoysalas and the Vijayanagara empire. The official and administrative language of the state of Karnataka, it also has scheduled status in India and has been included among the country's designated classical languages.Kuiper (2011), p. 74R Zydenbos in Cushman S, Cavanagh C, Ramazani J, Rouzer P, ''The Princeton Encyclopedia of Poetry and Poetics: Fourth Edition'', p. 767, Princeton Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Karnataka'' in 1973. The state corresponds to the Carnatic region. Its capital and largest city is Bengaluru. Karnataka is bordered by the Lakshadweep Sea to the west, Goa to the northwest, Maharashtra to the north, Telangana to the northeast, Andhra Pradesh to the east, Tamil Nadu to the southeast, and Kerala to the southwest. It is the only southern state to have land borders with all of the other four southern Indian sister states. The state covers an area of , or 5.83 percent of the total geographical area of India. It is the sixth-largest Indian state by area. With 61,130,704 inhabitants at the 2011 census, Karnataka is the eighth-largest state by population, comprising 31 districts. Kannada, one of the classical languages of In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitradurga
Chitradurga is a city and the headquarters of Chitradurga district, which is located on the valley of the Vedavati river in the central part of the Indian state of Karnataka. Chitradurga is a place with historical significance which is located to the North West about 200 km from the state capital Bengaluru. Chitradurga is a major tourist hub in Karnataka. The city is famous for its 15th-century fort, which is locally known as Kallina Kote or Stone Fortress. This is formed of two Kannada words: ‘Kallina’ means "Stone's" and Kote means "Fort". Other names used in Kannada are ‘Ukkina Kote": "Steel Fort" (metaphorically used to mean an impregnable fort) and ‘Yelusuttina Kote’: "Seven Circles Fort". Etymology Chitradurga gets its name from ''Chitrakaldurga (meaning picturesque fort)'', an umbrella-shaped lofty hill found here. Chitradurga was also known by the names Chitradurg, Chitrakaladurga, and Chittaldurg. Chittaldrug (or Chitaldrug or Chittledroog) was the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Challakere
Challakere is a city municipality (taluk) in Chitradurga district in the state of Karnataka, India. It is called Oil City with numerous edible oil mills around the city and also Science City as several science and research organizations such as IISc, DRDO, BARC and ISRO have set up their establishments here. Geography Challakere is located at . It has an average elevation of 585 metres (1919 ft). Demographics Challakere is the largest taluk of Chitradurga District. India census, Challakere has a population of 55,194. Science and research organizations Challakere is 200 km from Bangalore where an integrated township spread over has been set up by Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO), Indian Institute of Science (IISc) and Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC). Oil industry Challakere is also known as the 'oil city' or "second mumbai" of India because it is the second largest producer/supplier of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the north-west, Chhattisgarh to the north, Odisha to the north-east, Tamil Nadu to the south, Karnataka to the west and the Bay of Bengal to the east. It has the second longest coastline in India after Gujarat, of about . Andhra State was the first state to be formed on a linguistic basis in India on 1 October 1953. On 1 November 1956, Andhra State was merged with the Telugu-speaking areas (ten districts) of the Hyderabad State to form United Andhra Pradesh. ln 2014 these merged areas of Hyderabad State are bifurcated from United Andhra Pradesh to form new state Telangana . Present form of Andhra similar to Andhra state.but some mandalas like Bhadrachalam still with Telangana. Visakhapatnam, Guntur, Kurnool is People Capital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandavapura
Pandavapura is a Municipality Town in Mandya district in the Indian state of Karnataka. Geography Pandavapura is located at . It has an average elevation of 709 metres (2326 feet). Demographics India census, Pandavapura had a population of 18,236. Males constitute 51% of the population and females 49%. Pandavapura has an average literacy rate of 67%, higher than the national average of 59.5%: male literacy is 72%, and female literacy is 62%. In Pandavapura, 12% of the population is under 6 years of age. History The name Pandavapura means "Town of Pandavas". Mythology states that the Pandavas during their period of exile stayed here for some time, and Kunti, mother of the Pandavas, liked the hillock so much that it became one of her favorite haunts. The town is also named after the Pandavas because of their brief stay in this region. The name "French Rock" dates back to India's Pre-Independence days, the place was used as the camping ground by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |