|
Nipawin Hydroelectric Station
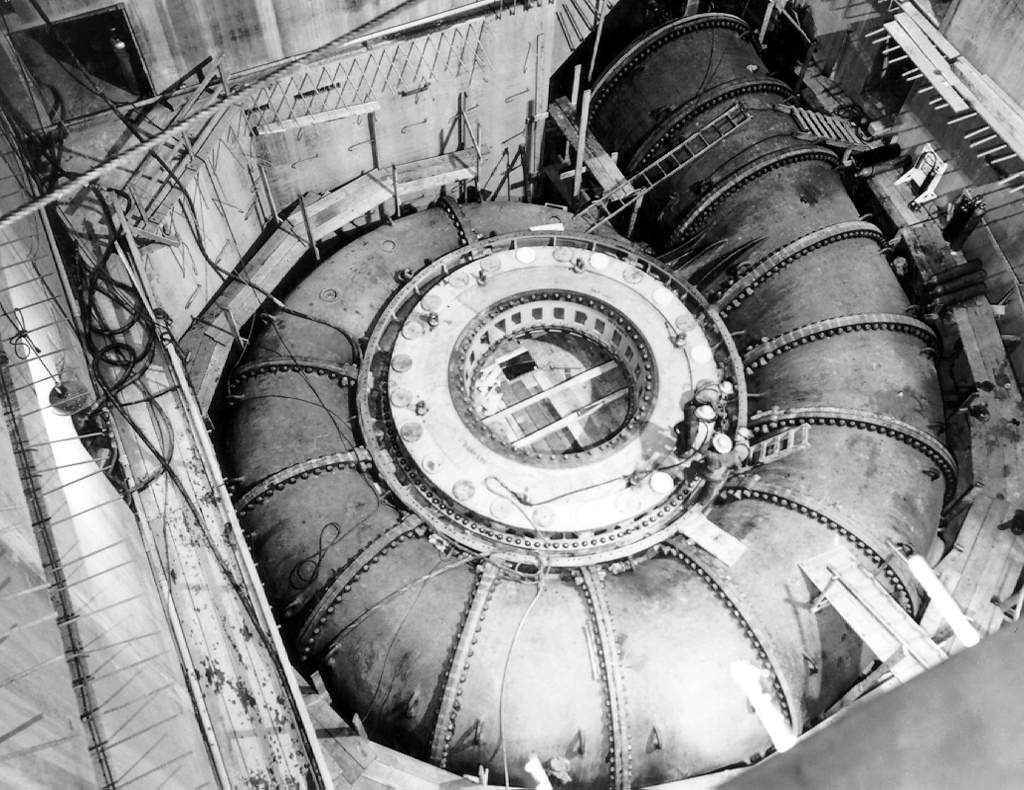
Nipawin Hydroelectric Station is a hydroelectric station owned by SaskPower, located near Nipawin, Saskatchewan, Canada Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot .... Description The Nipawin Hydroelectric Station has a capacity of 255MW, and consists of: *one Hitachi 85 net MW unit (commissioned in 1985) *two Hitachi 85 net MW units (commissioned in 1986) It is possible to expand the station to five generating units, which would keep the baseload capacity at 255MW, but would increase the peak capacity to 420MW. See also * SaskPower * E.B. Campbell Hydroelectric Station References External links SaskPower Station Description Hydroelectric power stations in Saskatchewan Nipawin No. 487, Saskatchewan SaskPower Torch River No. 488, Saskatchewan Dams in the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nipawin No
Nipawin () is a town in Saskatchewan, Canada, on the Saskatchewan River portion of Tobin Lake. The town lies between Codette Lake, created by the Francois-Finlay Dam (built in 1986) and Tobin Lake, created by the E.B. Campbell Dam built in 1963, renamed from Squaw Rapids. The construction of Francois-Finlay Dam earned Nipawin the nickname the "Town of Two Lakes". Nipawin is bordered by the Rural Municipality of Nipawin No. 487 and the Rural Municipality of Torch River No. 488 (the latter across the Saskatchewan River). Highway 35 and Highway 55 intersect in Nipawin. The Nipawin Airport and the Nipawin Water Aerodrome also serve the community. Nipawin is a Cree word meaning "a bed, or resting place" which referred to a low-lying area along the river now flooded by Codette Lake where First Nations women and children would camp and wait for the men to arrive. History The first permanent settlement of Nipawin occurred in 1910 with the establishment of a trading post. In 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torch River No
A torch is a stick with combustible material at one end, which is ignited and used as a light source. Torches have been used throughout history, and are still used in processions, symbolic and religious events, and in juggling entertainment. In some countries "torch" in modern usage is the term for a battery-operated portable light. Etymology From the Old French "''torche''" meaning "twisted thing", hence "torch formed of twisted tow dipped in wax", probably from Vulgar Latin *''torca'', alteration of Late Latin ''torqua'', variant of classical Latin ''torques'' "collar of twisted metal", from ''torquere'' "to twist". Torch construction Torch construction has varied through history depending on the torch's purpose. Torches were usually constructed of a wooden stave with one end wrapped in a material which was soaked in a flammable substance. In the United States, black bear bones may have been used. Modern procession torches are made from coarse hessian rolled into a tube an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nipawin, Saskatchewan
Nipawin () is a town in Saskatchewan, Canada, on the Saskatchewan River portion of Tobin Lake. The town lies between Codette Lake, created by the Francois-Finlay Dam (built in 1986) and Tobin Lake, created by the E.B. Campbell Dam built in 1963, renamed from Squaw Rapids. The construction of Francois-Finlay Dam earned Nipawin the nickname the "Town of Two Lakes". Nipawin is bordered by the Rural Municipality of Nipawin No. 487 and the Rural Municipality of Torch River No. 488 (the latter across the Saskatchewan River). Highway 35 and Highway 55 intersect in Nipawin. The Nipawin Airport and the Nipawin Water Aerodrome also serve the community. Nipawin is a Cree word meaning "a bed, or resting place" which referred to a low-lying area along the river now flooded by Codette Lake where First Nations women and children would camp and wait for the men to arrive. History The first permanent settlement of Nipawin occurred in 1910 with the establishment of a trading post. In 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada, western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on the south by the United States, U.S. states of Montana and North Dakota. Saskatchewan and Alberta are the only landlocked provinces of Canada. In 2022, Saskatchewan's population was estimated at 1,205,119. Nearly 10% of Saskatchewan’s total area of is fresh water, mostly rivers, reservoirs and List of lakes in Saskatchewan, lakes. Residents primarily live in the southern prairie half of the province, while the northern half is mostly forested and sparsely populated. Roughly half live in the province's largest city Saskatoon or the provincial capital Regina, Saskatchewan, Regina. Other notable cities include Prince Albert, Saskatchewan, Prince Albert, Moose Jaw, Yorkton, Swift Current, North Battleford, Melfort, Saskatchewan, Melfort, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SaskPower
Saskatchewan Power Corporation, operating as SaskPower, is the principal electric utility in Saskatchewan, Canada. Established in 1929 by the provincial government, it serves more than 538,000 customers and manages over $11.8 billion in assets. SaskPower is a major employer in the province with over 3,100 permanent full-time staff located in approximately 70 communities.SaskPower 2019, p. 2. Legal status SaskPower was founded as the Saskatchewan Power Commission in 1929, becoming the Saskatchewan Power Corporation in 1949 with the passage of ''The Rural Electrification Act''. The abbreviated name SaskPower was officially adopted as a trade name in 1987. Owned by the government through its holding company, the Crown Investments Corporation, SaskPower is governed by a Board of Directors who are accountable to the provincial government Minister Responsible for Saskatchewan Power Corporation. SaskPower has the exclusive right and the exclusive obligation to supply electricity in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency. The process of arriving at the modern Francis runner design took from 1848 to approximately 1920. It became known as the Francis turbine around 1920, being named after British-American engineer James B. Francis who in 1848 created a new turbine design. Francis turbines are primarily used for producing electricity. The power output of the electric generators generally ranges from just a few kilowatts up to 1000 MW, though mini-hydro installations may be lower. The best performance is seen when the head height is between . Penstock diameters are between . The speeds of different turbine units range from 70 to 1000 rpm. A wicket gate around the outside of the turbine's rotating runner controls the rate of water flow through the turbine for d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroelectric Power Stations In Saskatchewan
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dams In The Saskatchewan River Basin
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aquaculture, and navigability. Hydropower is often used in conjunction with dams to generate electricity. A dam can also be used to collect or store water which can be evenly distributed between locations. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees (also known as dikes) are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions. The earliest known dam is the Jawa Dam in Jordan, dating to 3,000 BC. The word ''dam'' can be traced back to Middle English, and before that, from Middle Dutch, as seen in the names of many old cities, such as Amsterdam and Rotterdam. History Ancient dams Early dam building took place in Mesopotamia and the Middle East. Dams were used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |