|
Nikolaos Kylafis
Nikolaos Kylafis ( el, Νικόλαος Κυλάφης) is a Greek Theoretical Astrophysicist, who is professor emeritus at the Department of Physics of the University of Crete, Greece. Kylafis contributed to the founding of the Astrophysics Group of the University of Crete and the Foundation for Research & Technology – Hellas, Foundation for Research & Technology - Helas (FORTH) in 1985 and led, together with his colleague Ioannis Papamastorakis, the effort to create the Institute of Astrophysics at FORTH in 2018. He has been teaching undergraduate and graduate courses in the Department of Physics since 1985. He has published research works in refereed journals. Education Nikolaos (Nick) Kylafis was born in Nea Avorani, Greece, on 1 January 1949, where he grew up. In 1966 he was admitted at the Department of Physics of the University of Patras and graduated in 1971. The next year he started his graduate studies in the US at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
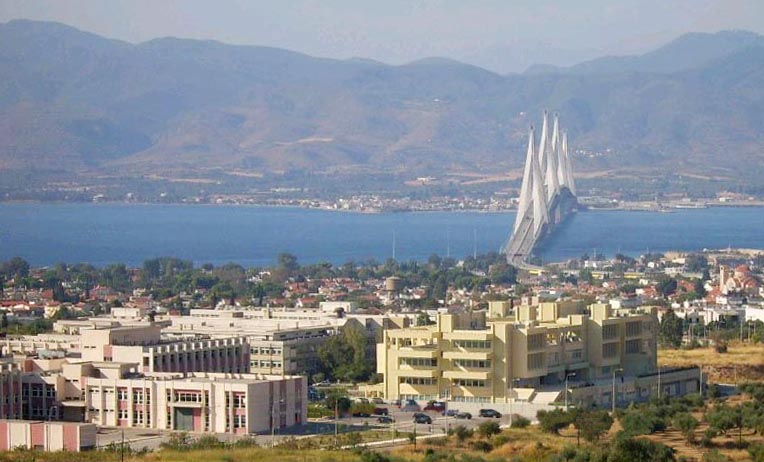
University Of Patras
The University of Patras (UPatras; el, Πανεπιστήμιο Πατρών, ''Panepistímio Patrón'') is a public university in Patras, Greece. It is the third-largest university in Greece with respect to the size of the student body, the staff, and the number of departments."''The EEC recommends that the Institution should develop and implement a pragmatic strategic planning process to set priorities for the university as a whole and for each School with an explicitly defined set of targets and timelines. The EEC evaluated and scored according to our estimate of where UPatras stands in relation to our understanding of an international norm of excellence. Although we are conscious of the severe constraints imposed by the Greek State, we have not used them as an excuse for not identifying areas of improvement. Please note that an EEC member gave a worthy of merit vote by taking into account with a heavier weight the negative influence of the external environment on UPatras's a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ewine Van Dishoeck
Ewine Fleur van Dishoeck (born 13 June 1955, in Leiden) is a Dutch astronomer and chemist. She is Professor of Molecular Astrophysics at Leiden Observatory, and served as the President of the International Astronomical Union (2018–2021) and a co-editor of the '' Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics'' (2012–present). She is one of the pioneers of astrochemistry, and her research is aimed at determination of the structure of cosmic objects using their molecular spectra. Early life Ewine Fleur van Dishoeck was born on June 13, 1955, in Leiden, Netherlands. With her father being a professor of ear, nose, and throat medicine, her love of science was inspired at the young age of 12. During this time, her father was invited to spend six months in San Diego, CA. Her first science class ever was through the San Diego Public School system. She fondly remembers that her science teacher, a female and African-American in the 1960s, was forced to overcome many obstacles to reach t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, and are created by electric currents such as those used in electromagnets, and by electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function assigning a vector to each point of space, cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Polarization
In electrodynamics, linear polarization or plane polarization of electromagnetic radiation is a confinement of the electric field vector or magnetic field vector to a given plane along the direction of propagation. The term ''linear polarization'' (French: ''polarisation rectiligne'') was coined by Augustin-Jean Fresnel in 1822.A. Fresnel, "Mémoire sur la double réfraction que les rayons lumineux éprouvent en traversant les aiguilles de cristal de roche suivant les directions parallèles à l'axe", read 9 December 1822; printed in H. de Senarmont, E. Verdet, and L. Fresnel (eds.), ''Oeuvres complètes d'Augustin Fresnel'', vol. 1 (1866), pp.731–51; translated as "Memoir on the double refraction that light rays undergo in traversing the needles of quartz in the directions parallel to the axis", , 2021 (open access); §9. See '' polarization'' and ''plane of polarization'' for more information. The orientation of a linearly polarized electromagn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstellar Molecules
This is a list of molecules that have been detected in the interstellar medium and circumstellar envelopes, grouped by the number of component atoms. The chemical formula is listed for each detected compound, along with any ionized form that has also been observed. Background The molecules listed below were detected through astronomical spectroscopy. Their spectral features arise because molecules either absorb or emit a photon of light when they transition between two molecular energy levels. The energy (and thus the wavelength) of the photon matches the energy difference between the levels involved. Molecular electronic transitions occur when one of the molecule's electrons moves between molecular orbitals, producing a spectral line in the ultraviolet, optical or near-infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. Alternatively, a vibrational transition transfers quanta of energy to (or from) vibrations of molecular bonds, producing signatures in the mid- or far-infrared. G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectral Line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used to identify atoms and molecules. These "fingerprints" can be compared to the previously collected ones of atoms and molecules, and are thus used to identify the atomic and molecular components of stars and planets, which would otherwise be impossible. Types of line spectra Spectral lines are the result of interaction between a quantum system (usually atoms, but sometimes molecules or atomic nuclei) and a single photon. When a photon has about the right amount of energy (which is connected to its frequency) to allow a change in the energy state of the system (in the case of an atom this is usually an electron changing orbitals), the photon is absorbed. Then the energy will be spontaneously re-emitted, either as one photon at the same frequenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Holes
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can deform spacetime to form a black hole. The boundary of no escape is called the event horizon. Although it has a great effect on the fate and circumstances of an object crossing it, it has no locally detectable features according to general relativity. In many ways, a black hole acts like an ideal black body, as it reflects no light. Moreover, quantum field theory in curved spacetime predicts that event horizons emit Hawking radiation, with the same spectrum as a black body of a temperature inversely proportional to its mass. This temperature is of the order of billionths of a kelvin for stellar black holes, making it essentially impossible to observe directly. Objects whose gravitational fields are too strong for light to escape were first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Stars
A neutron star is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star, which had a total mass of between 10 and 25 solar masses, possibly more if the star was especially metal-rich. Except for black holes and some hypothetical objects (e.g. white holes, quark stars, and strange stars), neutron stars are the smallest and densest currently known class of stellar objects. Neutron stars have a radius on the order of and a mass of about 1.4 solar masses. They result from the supernova explosion of a massive star, combined with gravitational collapse, that compresses the core past white dwarf star density to that of atomic nuclei. Once formed, they no longer actively generate heat, and cool over time; however, they may still evolve further through collision or accretion. Most of the basic models for these objects imply that neutron stars are composed almost entirely of neutrons (subatomic particles with no net electrical charge and with slightly larger mass than protons); the electron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accretion Disks
An accretion disk is a structure (often a circumstellar disk) formed by diffuse material in orbital motion around a massive central body. The central body is typically a star. Friction, uneven irradiance, magnetohydrodynamic effects, and other forces induce instabilities causing orbiting material in the disk to spiral inward towards the central body. Gravitational and frictional forces compress and raise the temperature of the material, causing the emission of electromagnetic radiation. The frequency range of that radiation depends on the central object's mass. Accretion disks of young stars and protostars radiate in the infrared; those around neutron stars and black holes in the X-ray part of the Electromagnetic spectrum, spectrum. The study of oscillation modes in accretion disks is referred to as diskoseismology. Manifestations Accretion disks are a ubiquitous phenomenon in astrophysics; active galactic nuclei, protoplanetary disks, and gamma ray bursts all involve accretio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savilian Professor Of Astronomy
The position of Savilian Professor of Astronomy was established at the University of Oxford in 1619. It was founded (at the same time as the Savilian Professor of Geometry, Savilian Professorship of Geometry) by Henry Savile (Bible translator), Sir Henry Savile, a mathematician and classical scholar who was Warden of Merton College, Oxford, and Provost of Eton College. He appointed John Bainbridge (astronomer), John Bainbridge as the first professor, who took up his duties in 1620 or 1621. There have been 21 astronomy professors in all; Steven Balbus, the professor , was appointed in 2012. Past professors include Christopher Wren (1661–73), architect of St Paul's Cathedral in London and the Sheldonian Theatre in Oxford; he held the professorship at the time of his commission to rebuild the cathedral after it was destroyed by the Great Fire of London in 1666. Three professors have been awarded the Gold Medal of the Royal Astronomical Society: Charles Pritchard (1870–93), Harry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steven Balbus
Steven Andrew Balbus FRS (born 23 November 1953) is an American-born astrophysicist who is the Savilian Professor of Astronomy at the University of Oxford and a professorial fellow at New College, Oxford. In 2013, he shared the Shaw Prize for Astronomy with John F. Hawley. Early life and education Balbus was born in 1953 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He attended the William Penn Charter School, received S.B. degrees in mathematics and in physics from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1975, and a PhD in theoretical astrophysics from the University of California, Berkeley in 1981. Research and career Following his PhD, Balbus held postdoctoral research appointments at MIT and Princeton University. In 1985, Balbus joined the faculty of the University of Virginia. In 2004, he was appointed Professeur des Universités in the Physics Department of the École Normale Supérieure de Paris. He remained in Paris until 2012, when he moved to Oxford as the Savilia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
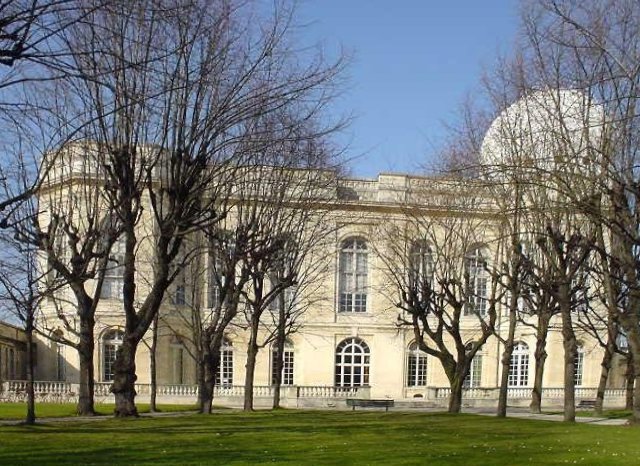
Observatoire De Paris
The Paris Observatory (french: Observatoire de Paris ), a research institution of the Paris Sciences et Lettres University, is the foremost astronomical observatory of France, and one of the largest astronomical centers in the world. Its historic building is on the Left Bank of the Seine in central Paris, but most of the staff work on a satellite campus in Meudon, a suburb southwest of Paris. The Paris Observatory was founded in 1667. Construction was completed by the early 1670s and coincided with a major push for increased science, and the founding of the Royal Academy of Sciences. King Louis XIV's minister of finance organized a "scientific powerhouse" to increase understanding of astronomy, maritime navigation, and science in general. Through the centuries the Paris Observatory has continued in support of astronomical activities, and in the 21st century connects multiple sites and organizations, supporting astronomy and science, past and present. Constitution Administrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |