|
Nicoya (canton)
Nicoya is a Cantons of Costa Rica, canton in the Guanacaste Province, Guanacaste province of Costa Rica. The head city is in Nicoya District, Nicoya district. History Proto-historical Nicoya When conquistador Pedrarias Dávila, Gil Gonzalez Dávila entered Nicoya in 1523, it was the largest ''Cacique, cacicazgo'' (chiefdom) on the Pacific coast of Costa Rica. Though it is often surmised that the city and peninsula of Nicoya derive their name from a ''cacique'' Nicoa (or Nicoya) who welcomed Dávila and his men, actually Nicoya took its name from the Nahuatl appellation ''Necoc Īāuh'', literally "on both sides its water(s)", as Nicoya is in fact situated between two major rivers. Nicoya Peninsula, The Peninsula de Nicoya is itself named for the city, Nicoya being the most important town in that area. The treasurer on Dávila's expedition, Andrés de Cereceda, reported a population of 6,063 inhabitants under Nicoya's leadership, almost five and a half times larger than the next ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantons Of Costa Rica
Costa Rica Costa Rica (, ; ; literally "Rich Coast"), officially the Republic of Costa Rica ( es, República de Costa Rica), is a country in the Central American region of North America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the no ... is administratively divided into seven provinces which are subdivided into 83 Canton (country subdivision), cantons, and these are further subdivided into Districts of Costa Rica, districts. Cantons are the only administrative division in Costa Rica that possess local government in the form of Municipality, municipalities. Each municipality has its own mayor and several representatives, all of them chosen via municipal elections every four years. The original 14 cantons were established in 1848, and the number has risen gradually by the division of existing cantons. Law no. 4366 of 19 August 1969, which outlines the creation of administrative divisions of Costa Rica, states that new cantons may only be created if they h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cacique
A ''cacique'' (Latin American ; ; feminine form: ''cacica'') was a tribal chieftain of the Taíno people, the indigenous inhabitants at European contact of the Bahamas, the Greater Antilles, and the northern Lesser Antilles. The term is a Spanish transliteration of the Taíno word ''kasike''. Cacique was initially translated as "king" or "prince" for the Spanish. In the colonial era the conquistadors and the administrators who followed them used the word generically, to refer to any leader of practically any indigenous group they encountered in the Western Hemisphere. In Hispanic and Lusophone countries, the term also has come to mean a political boss, similar to ''caudillo,'' exercising power in a system of ''caciquismo''. Spanish colonial-era caciques The Taíno word ''kasike'' descends from the Taíno word ''kassiquan'', which means "to keep house". In 1555 the word first entered the English language, defined as "prince". In Taíno culture, the ''kasike'' rank was her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polychrome
Polychrome is the "practice of decorating architectural elements, sculpture, etc., in a variety of colors." The term is used to refer to certain styles of architecture, pottery or sculpture in multiple colors. Ancient Egypt Colossal statue of Tutankhamun Paris 2019 A.jpg, Polychrome quartzite colossal statue of Tutankhamun, 1355-1315 BC Nofretete Neues Museum.jpg, Polychrome limestone and plaster ''Bust of Nefertiti'', 1352–1336 BC Composite Papyrus Capital MET 10.177.2 EGDP018080.jpg, Polychrome sandstone Composite papyrus capital, 380–343 BC Medinet Habu 2016-03-23g.jpg, Polychrome winged sun on a cavetto from the Medinet Habu temple complex, unknown date Classical world Some very early polychrome pottery has been excavated on Minoan Crete such as at the Bronze Age site of Phaistos. In ancient Greece sculptures were painted in strong colors. The paint was frequently limited to parts depicting clothing, hair, and so on, with the skin left in the natural co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mound
A mound is a heaped pile of earth, gravel, sand, rocks, or debris. Most commonly, mounds are earthen formations such as hills and mountains, particularly if they appear artificial. A mound may be any rounded area of topographically higher elevation on any surface. Artificial mounds have been created for a variety of reasons throughout history, including habitation (see Tell and Terp), ceremonial (platform mound), burial (tumulus), and commemorative purposes (e.g. Kościuszko Mound). Archaeology North American archaeology In the archaeology of the United States and Canada, a mound is a deliberately constructed elevated earthen structure or earthwork, intended for a range of potential uses. In European and Asian archaeology, the word "tumulus" may be used as a synonym for an artificial hill, particularly if the hill is related to particular burial customs. While the term "mound" may be applied to historic constructions, most mounds in the United States are pre-Columbian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabana Grande, Costa Rica
Sabana may refer to: Places * Sabana, Orocovis, Puerto Rico, a barrio in Puerto Rico * Sabana, Vega Alta, Puerto Rico, a barrio in Puerto Rico * Sabana, Luquillo, Puerto Rico Sabana is a barrio in the municipality of Luquillo, Puerto Rico. Its population in 2010 was 2,352. History Puerto Rico was ceded by Spain in the aftermath of the Spanish–American War under the terms of the Treaty of Paris of 1898 and became an ..., a barrio in Puerto Rico * Sabana, Boven Saramacca, Suriname, a village or town in Boven Saramacca municipality (resort) in Sipaliwini District in Suriname * Sabana, Para, Suriname, a village or town in Para, Suriname {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rio Chipanzé
Rio or Río is the Portuguese, Spanish, Italian, and Maltese word for "river". When spoken on its own, the word often means Rio de Janeiro, a major city in Brazil. Rio or Río may also refer to: Geography Brazil * Rio de Janeiro * Rio do Sul, a town in the state of Santa Catarina, Brazil Mexico * Río Bec, a Mayan archaeological site in Mexico * Río Bravo, Tamaulipas, a city in Mexico United States * Rio, a location in Deerpark, New York, US * Rio, Florida, a census-designated place in Martin County, US * Rio, Georgia, an unincorporated community in Spalding County, US * Rio, Illinois, a village in Knox County, US * Rio, Virginia, a community in Albemarle County, US * Rio, West Virginia, a village in Hampshire County, US * Rio, Wisconsin, a village in Columbia County, US * El Río, Las Piedras, Puerto Rico, a barrio * Río Arriba, Añasco, Puerto Rico, a barrio * Río Arriba, Arecibo, Puerto Rico, a barrio * Río Arriba, Fajardo, Puerto Rico, a barrio * Río Arriba, Vega Baja, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
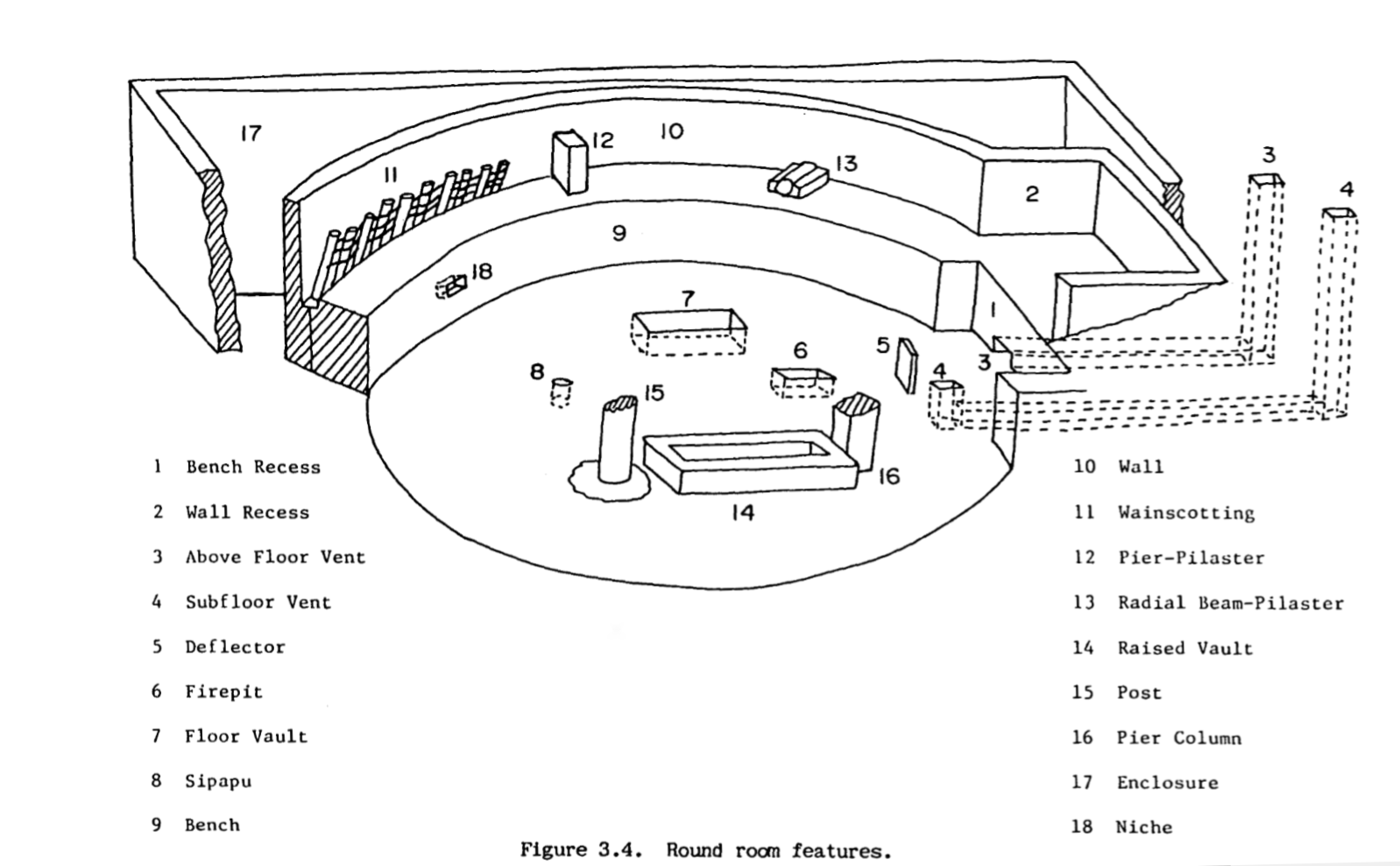
Kiva
A kiva is a space used by Puebloans for rites and political meetings, many of them associated with the kachina belief system. Among the modern Hopi and most other Pueblo peoples, "kiva" means a large room that is circular and underground, and used for spiritual ceremonies. Similar subterranean rooms are found among ruins in the North-American South-West, indicating uses by the ancient peoples of the region including the ancestral Puebloans, the Mogollon, and the Hohokam. Those used by the ancient Pueblos of the Pueblo I Period and following, designated by the Pecos Classification system developed by archaeologists, were usually round and evolved from simpler pit-houses. For the Ancestral Puebloans, these rooms are believed to have had a variety of functions, including domestic residence along with social and ceremonial purposes. Evolution During the late 8th century, Mesa Verdeans started building square pit structures that archeologists call protokivas. They were typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramids
A pyramid (from el, πυραμίς ') is a structure whose outer surfaces are triangular and converge to a single step at the top, making the shape roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be trilateral, quadrilateral, or of any polygon shape. As such, a pyramid has at least three outer triangular surfaces (at least four faces including the base). The square pyramid, with a square base and four triangular outer surfaces, is a common version. A pyramid's design, with the majority of the weight closer to the ground and with the pyramidion at the apex, means that less material higher up on the pyramid will be pushing down from above. This distribution of weight allowed early civilizations to create stable monumental structures. Civilizations in many parts of the world have built pyramids. The largest pyramid by volume is the Great Pyramid of Cholula, in the Mexican state of Puebla. For thousands of years, the largest structures on Earth were pyramid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlos Meléndez Chaverri
Carlos Meléndez Chaverri (23 June 1926 – 12 June 2000) was a Costa Rican historian. Meléndez was the son of Saturnino Lizano and Chaverri Orfilia Chacon. He married María Lourdes Doubles Umaña, who bore him five children: Silvia María, Lucia, Diego, Alberto and Pablo Meléndez Doubles. He won the Magón National Prize for Culture in 1993. Education He began his primary studies at the Escuela Argentina, and continued them at the Central School of Puntarenas. His father Don Saturnino moved the Meléndez family then moved to Limon, where he finished his primary education at the School Tomás Guardia. After spending a year in that province, the family returned to Hall where he entered the Ecole Normale de Costa Rica, being a student of renowned professors such as Fernando Vargas Fernández Gámez Solano Uladislaus "Don Lalo" and Marco Tulio Salazar Salazar. On 13 December 1946, Carlos Meléndez concluded secondary education, having passed exams in high school. He earned a BA i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Within this region pre-Columbian societies flourished for more than 3,000 years before the Spanish colonization of the Americas. Mesoamerica was the site of two of the most profound historical transformations in world history: primary urban generation, and the formation of New World cultures out of the long encounters among indigenous, European, African and Asian cultures. In the 16th century, Eurasian diseases such as smallpox and measles, which were endemic among the colonists but new to North America, caused the deaths of upwards of 90% of the indigenous people, resulting in great losses to their societies and cultures. Mesoamerica is one of the five areas in the world where ancient civilization arose independently (see cradle of civ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the country's capital and largest city. , it was estimated to be the second largest city in Central America. Nicaragua's multiethnic population of six million includes people of mestizo, indigenous, European and African heritage. The main language is Spanish. Indigenous tribes on the Mosquito Coast speak their own languages and English. Originally inhabited by various indigenous cultures since ancient times, the region was conquered by the Spanish Empire in the 16th century. Nicaragua gained independence from Spain in 1821. The Mosquito Coast followed a different historical path, being colonized by the English in the 17th century and later coming under British rule. It became an autonomous territory of Nicaragua in 1860 and its northernmost part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |