|
Nicobar Islands Rain Forests
The Nicobar Islands rain forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in the Nicobar Islands. The Nicobar Islands are in the Indian Ocean, lying north of Sumatra and south of the Andaman Islands. The islands are politically part of India, although physically closer to Southeast Asia. Millions of years of isolation from the mainland has given rise to a distinct flora and fauna, including many endemic species. Geography The Nicobar Islands consist of 22 islands, of which 13 are inhabited. The islands extend about 260 km from north and south, and form three groups. The northern group is composed of Car Nicobar, the northernmost island, and Batti Malv. The central group includes Nancowry, Katchal, Kamorta, Teressa, Chowra, Tillangchong, and several smaller islets. The southern group includes Great Nicobar, Little Nicobar and several smaller islets. Great Nicobar is the largest (), highest (Mount Thullier, 670 m), and southernmost island. The Andaman Sea lies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teressa Island
Teressa (Teressa language: ''Luroo'', hi, ÓżżÓźćÓż░ÓźćÓżĖÓźŹÓżĖÓżŠ, also called Tarasa Dwip) is one of the Nicobar Islands, India. History When Austria claimed Nicobar Islands as a colony (1778-1784) on the assumption that Denmark had ababdoned its claim (1754/56-1868), they named Teressa after the Austrian Arch-duchess Maria Theresia. Extensive damage to the island's flora and fauna occurred following the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami. Geography Teressa lies west of the neighboring island of Camorta Island, Camorta and northwest of Katchal Island, Katchal. The smaller island known as Chowra is to the north and Bompoka lies to the east. The northern portion of the island has elevations reaching 87 meters. The island has a surface area of 101.26 km2. Demography The Indian National Census of 2011 showed the island to have a population of 1,934, and the largest settlements were: Bengali, Nancowry, Bengali (354), Kalasi (335), and Minyuk (305). Administration The i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Nicobar
Great Nicobar is the southernmost and largest of the Nicobar Islands of India, north of Sumatra. History The Nicobar Island has been well known to Indian mariners since the time of the seafaring Cholas https://www.britannica.com/place/Nicobar-Islands In the 15th century, Great Nicobar Island was recorded as "Cui Lan island" (ń┐ĀĶśŁÕČ╝) during the voyages of Zheng He in the Mao Kun map of the Wu Bei Zhi. Great Nicobar Island was severely affected by the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake tsunami with many deaths, and was cut off from all outside contact for more than a day. Geography The island of Sumatra is located to the south of Great Nicobar. The island covers but is sparsely inhabited, with a population of 8067, largely being covered by rainforest and known for its diverse wildlife. Topography The island has several rivers, including the Alexandra, Amrit Kaur, Dogmar and Galathea. Virtually all rivers flow in a southern or southwesterly direction, which is indicative of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serpentinite
Serpentinite is a rock composed predominantly of one or more serpentine group minerals, the name originating from the similarity of the texture of the rock to that of the skin of a snake. Serpentinite has been called ''serpentine'' or ''serpentine rock'', particularly in older geological texts and in wider cultural settings.California Government Code ┬¦ 425.2; ''see'' Formation and mineralogy Serpentinite is formed by near to complete serpentinization of mafic to ultramafic rocks. Serpentinite can be formed wherever ultramafic rock is infiltrated by water poor in carbon dioxide. This occurs at mid-ocean ridges and in the forearc mantle of subduction zones. The final mineral composition of serpentinite is usually dominated by lizardite, chrysotile, and magnetite. Brucite and antigorite are less commonly present. Lizardite, chrysotile, and antigorite all have approximately the formula or , but differ in minor components and in form. Accessory minerals, present in smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrabasic
Ultramafic rocks (also referred to as ultrabasic rocks, although the terms are not wholly equivalent) are igneous and meta-igneous rocks with a very low silica content (less than 45%), generally >18% MgO, high FeO, low potassium, and are composed of usually greater than 90% mafic minerals (dark colored, high magnesium and iron content). The Earth's mantle is composed of ultramafic rocks. Ultrabasic is a more inclusive term that includes igneous rocks with low silica content that may not be extremely enriched in Fe and Mg, such as carbonatites and ultrapotassic igneous rocks. Intrusive ultramafic rocks Intrusive ultramafic rocks are often found in large, layered ultramafic intrusions where differentiated rock types often occur in layers. Such cumulate rock types do not represent the chemistry of the magma from which they crystallized. The ultramafic intrusives include the dunites, peridotites and pyroxenites. Other rare varieties include troctolite which has a greater perc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake
An earthquake and a tsunami, known as the Boxing Day Tsunami and, by the scientific community, the SumatraŌĆōAndaman earthquake, occurred at 07:58:53 local time (UTC+7) on 26 December 2004, with an epicentre off the west coast of northern Sumatra, Indonesia. It was an undersea megathrust earthquake that registered a magnitude of 9.1ŌĆō9.3 , reaching a Mercalli intensity up to IX in certain areas. The earthquake was caused by a rupture along the fault between the Burma Plate and the Indian Plate. A series of massive tsunami waves grew up to high once heading inland, after being created by the underwater seismic activity offshore. Communities along the surrounding coasts of the Indian Ocean were devastated, and the tsunamis killed an estimated 227,898 people in 14 countries, making it one of the deadliest natural disasters in recorded history. The direct results caused major disruptions to living conditions and commerce in coastal provinces of surrounded countries, including Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1881 Nicobar Islands Earthquake
The 1881 Nicobar Islands earthquake occurred at about 07:49 local time (01:49 UTC) on 31 December, with an epicentre beneath Car Nicobar. It occurred as two separate ruptures, the largest of which had an estimated magnitude of 7.9 on the moment magnitude scale and triggered a tsunami that was observed around the Bay of Bengal. It is probably the earliest earthquake for which rupture parameters have been estimated instrumentally. Tectonic setting The Nicobar Islands are a series of volcanic islands that are part of an active volcanic arc, formed above the subduction zone where the Indo-Australian Plate passes beneath the Burma Plate. The convergence along this plate boundary is highly oblique, with the plate vector running at a low angle to the boundary. Most of the strike-slip component of the convergence is accommodated by the Great Sumatran fault, which passes northwards into the Andaman Sea spreading centre. This plate boundary has been the location of many historical meg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
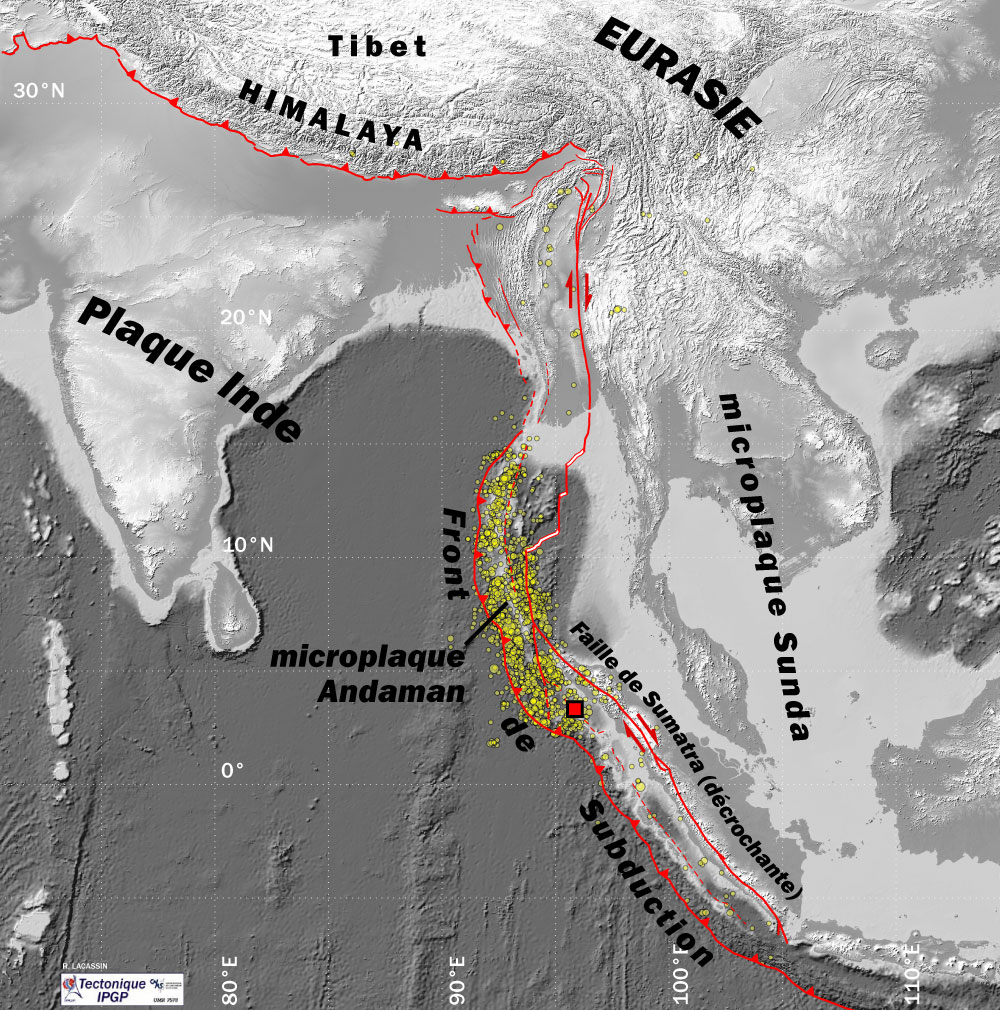
Burma Plate
The Burma Plate is a minor tectonic plate or microplate located in Southeast Asia, sometimes considered a part of the larger Eurasian Plate. The Andaman Islands, Nicobar Islands, and northwestern Sumatra are located on the plate. This island arc separates the Andaman Sea from the main Indian Ocean to the west. To its east lies the Sunda Plate, from which it is separated along a transform boundary, running in a rough north-south line through the Andaman Sea. This boundary between the Burma and Sunda plates is a marginal seafloor spreading centre, which has led to the opening up of the Andaman Sea (from a southerly direction) by "pushing out" the Andaman-Nicobar-Sumatra island arc from mainland Asia, a process which began in earnest approximately 4 million years ago. To the west is the much larger India Plate, which is subducting beneath the western facet of the Burma Plate. This extensive subduction zone has formed the Sunda Trench. Tectonic history In models of the reconst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Plate
The Indian Plate (or India Plate) is a minor tectonic plate straddling the equator in the Eastern Hemisphere. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, the Indian Plate broke away from the other fragments of Gondwana , began moving north and carried Insular India with it. It was once fused with the adjacent Australian Plate to form a single Indo-Australian Plate, and recent studies suggest that India and Australia have been separate plates for at least 3 million years and likely longer. The Indian Plate includes most of modern South Asia (the Indian subcontinent) and a portion of the basin under the Indian Ocean, including parts of South China and western Indonesia, and extending up to but not including Ladakh, Kohistan and Balochistan. Plate movements Until roughly , the Indian Plate formed part of the supercontinent Gondwana together with modern Africa, Australia, Antarctica, and South America. Gondwana broke up as these continents drifted apart at different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the second plate and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with the average rate of convergence being approximately two to eight centimeters per year along most plate boundaries. Subduction is possible because the cold oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle underlying the cold, rigid lithosphere. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Arc
Island arcs are long chains of active volcanoes with intense seismic activity found along convergent tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have resulted from the descent of the lithosphere into the mantle along the subduction, subduction zone. They are the principal way by which continental growth is achieved. Island arcs can either be active or inactive based on their seismicity and presence of volcanoes. Active arcs are ridges of recent volcanoes with an associated deep seismic zone. They also possess a distinct curved form, a chain of active or recently extinct volcanoes, a Oceanic trench, deep-sea trench, and a large negative Bouguer anomaly on the convex side of the volcanic arc. The small positive gravity anomaly associated with volcanic arcs has been interpreted by many authors as due to the presence of dense volcanic rocks beneath the arc. Inactive arcs are a chain of islands which contains older volcanic and volcaniclastic rocks. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ten Degree Channel
The Ten Degree Channel is a channel that separates the Andaman Islands and Nicobar Islands from each other in the Bay of Bengal. The two sets of islands together form the Indian Union Territory (UT) of Andaman and Nicobar Islands. This channel is wide from north to south, and approximately long from east to west. It has minimum depth of 7.3m and lies from east to west on the 10-degree line of latitude north of the equator,Ten degrees channel (India) Sea-Seek] hence the name. See also * |
Bay Of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between Sangaman Kanda, Sri Lanka, and the north westernmost point of Sumatra, Indonesia. It is the largest water region called a bay in the world. There are countries dependent on the Bay of Bengal in South Asia and Southeast Asia. During the existence of British India, it was named as the Bay of Bengal after the historic Bengal region. At the time, the Port of Kolkata served as the gateway to the Crown rule in India. Cox's Bazar, the longest sea beach in the world and Sundarbans, the largest mangrove forest and the natural habitat of the Bengal tiger, are located along the bay. The Bay of Bengal occupies an area of . A number of large rivers flow into the Bay of Bengal: the GangesŌĆō Hooghly, the Padma, the BrahmaputraŌĆōYamuna, the BarakŌĆ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |