|
Nicholas De Graham
Sir Nicholas de Graham of Dalkeith and Abercorn, was a 13th-14th century Scottish noble. Nicholas was the son of Henry de Graham. He was part of the Treaty of Salisbury The Treaty of Birgham, also referred to as the Treaty of Salisbury, comprised two treaties in 1289 and 1290 intended to secure the independence of Scotland after the death of Alexander III of Scotland and accession of his three-year-old granddaugh ... in 1289. He was one of Robert de Brus, 5th Lord of Annandale, Robert de Brus, Lord of Annandale's auditors during the Competitors for the Crown of Scotland, arbitration for the Crown of Scotland between 1291 and 1292. He performed homage to King Edward I of England at Berwick-upon-Tweed on 28 August 1296. Nicholas died in 1306. His escutcheon is described as "On a chief, three escallops". Family and issue He married Mary de Strathearn, daughter of Malise II, Earl of Strathearn, Malise, Earl of Strathearn, and Marjory de Muschamp, and is known to have had at least t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. It also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt—the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands—in the Scottish Lowlands. Scotland is divided into 32 administrative subdivisions or local authorities, known as council areas. Glasgow City is the largest council area in terms of population, with Highland being the largest in terms of area. Limited self-governing power, covering matters such as education, social services and roads and transportation, is devolved from the Scott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Birgham
The Treaty of Birgham, also referred to as the Treaty of Salisbury, comprised two treaties in 1289 and 1290 intended to secure the independence of Scotland after the death of Alexander III of Scotland and accession of his three-year-old granddaughter Margaret, Maid of Norway in 1286. They were negotiated and signed by the Guardians of Scotland, who were ruling in Margaret's name due to her age. The first treaty was concluded in Salisbury in November 1289 and relates to the arrangements by which Edward I of England would secure the transport of the Maid of Norway from her homeland to Edward's own custody until Scotland was made safe for her to take up her right as queen. The Maid's father, Eric II of Norway, while keen for his daughter to take up her right in Scotland, had been concerned for her safety given the political instability in Scotland. Edward I was able to broker her transfer from Norway, assuaging Eric's fears with his own personal guarantees for the infant girl's safet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert De Brus, 5th Lord Of Annandale
Robert V de Brus (Robert de Brus), 5th Lord of Annandale (ca. 1215 – 31 March or 3 May 1295), was a feudal lord, justice and constable of Scotland and England, a regent of Scotland, and a competitor for the Scottish throne in 1290/92 in the Great Cause. He is commonly known as "Robert the Competitor". His grandson Robert the Bruce eventually became King of Scots. Life Early life Robert was son of Robert Bruce, 4th Lord of Annandale and Isobel of Huntingdon. Widely known as Robert the Noble, he was also grandson of David of Scotland, 8th Earl of Huntingdon, and Matilda de Kevilloc of Chester, great-grandson of Henry of Scotland, Earl of Huntingdon and Northumberland, and Ada de Warenne, and great-great-grandson of King David I of Scotland and Maud, Countess of Huntingdon. In addition to Annandale, Robert was Lord of Hartlepool (otherwise known as Hartness) in county Durham, and Writtle and Hatfield Broadoak in Essex, England. His first wife brought to him the village of Ripe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
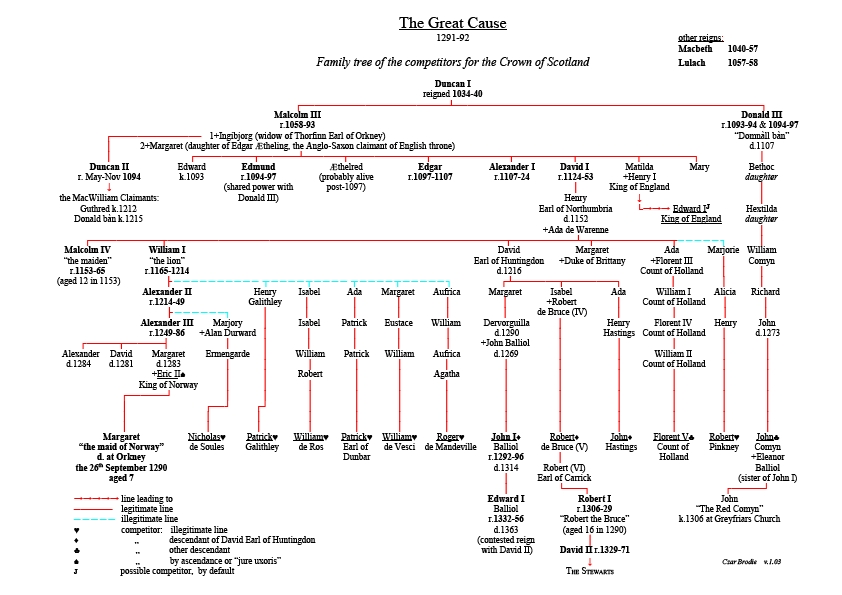
Competitors For The Crown Of Scotland
When the crown of Scotland became vacant in September 1290 on the death of the seven-year-old Queen Margaret, 13 claimants to the throne came forward. Those with the most credible claims were John Balliol, Robert de Brus, 5th Lord of Annandale, John Hastings and Floris V, Count of Holland. Fearing civil war, the Guardians of Scotland asked Edward I of England to arbitrate. Before agreeing, he obtained concessions going some way to revive English overlordship over the Scots. A commission of 104 "auditors" was then appointed—24 by Edward himself, acting as president; and the rest by Bruce and Balliol, in equal numbers. In November 1292, the body decided in favour of John Balliol, whose claim was based on the traditional criterion of primogeniture—inheritance through a line of firstborn sons. The decision was accepted by the majority of the powerful in Scotland, and John ruled as King of Scots from then until 1296. Background With the death of King Alexander III in 1286, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward I Of England
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony as a vassal of the French king. Before his accession to the throne, he was commonly referred to as the Lord Edward. The eldest son of Henry III, Edward was involved from an early age in the political intrigues of his father's reign, which included a rebellion by the English barons. In 1259, he briefly sided with a baronial reform movement, supporting the Provisions of Oxford. After reconciliation with his father, however, he remained loyal throughout the subsequent armed conflict, known as the Second Barons' War. After the Battle of Lewes, Edward was held hostage by the rebellious barons, but escaped after a few months and defeated the baronial leader Simon de Montfort at the Battle of Evesham in 1265. Within two years the rebellion was extin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berwick-upon-Tweed
Berwick-upon-Tweed (), sometimes known as Berwick-on-Tweed or simply Berwick, is a town and civil parish in Northumberland, England, south of the Anglo-Scottish border, and the northernmost town in England. The 2011 United Kingdom census recorded Berwick's population as 12,043. The town is at the mouth of the River Tweed on the east coast, south east of Edinburgh, north of Newcastle upon Tyne, and north of London. Uniquely for England, the town is slightly further north than Denmark's capital Copenhagen and the southern tip of Sweden further east of the North Sea, which Berwick borders. Berwick was founded as an Anglo-Saxon settlement in the Kingdom of Northumbria, which was annexed by England in the 10th century. A civil parish and town council were formed in 2008 comprising the communities of Berwick, Spittal and Tweedmouth. It is the northernmost civil parish in England. The area was for more than 400 years central to historic border wars between the Kingdoms of Engla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malise II, Earl Of Strathearn
Máel Ísu or Malise II (Modern Gaelic: ''Maol Íosa''; died 1271) is the fifth known mormaer, or earl, of the Scottish region of Strathearn. He was the son of Robert, 4th Earl of Strathearn. Biography Malise first appears on record in 1244, when he promised to observe the Treaty of York, the signing of which had been witnessed by his father. By this treaty, the King of Scots had dropped his claims to the northern shires of England. He was present in parliament from 1244 to 1245, and took part in the coronation of King Alexander in 1249. He was a friend of King Henry of England, and was tasked by him to attend his daughter Margaret, when she became Queen of Scots as the wife of Alexander. In 1259 he obtained safe conduct from King Henry to go abroad, and had returned the following year. Malise was an intelligent figure who managed to retain the favor of both the Scottish and English kings. Said to have been "munificent above all his compatriots", he was also much noted for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John De Graham (died 1337)
Sir John de Graham of Dalkeith, Abercorn & Eskdale (1278–1337) was a 13th-14th century Scottish noble. John, born in 1278, was the son of Nicholas de Graham of Dalkeith and Abercorn and Mary de Strathearn. He fought at the Battle of Bannockburn against the English on 23–24 June 1314 and as a result had his Northumberland estates confiscated. King Edward II of England denounced John as an enemy and rebel, and granted his Scottish lands to Hugh le Despenser. He signed the Declaration of Arbroath in 1320. John died on 25 April 1337. Family and issue John married Isabella, and had the following known issue: *Sir John de Graham, last of Dalkeith, Abercorn, and Eskdale, died without issue; resigned Dalkeith in favor of William Douglas of Laudonia 6 Jan 1343 *Sybilla de Graham, married Reginald de Mure, had issue. Abercorn passed to the Mure family. *Isabel de Graham, married Walter Stewart, 6th High Steward of Scotland Walter Stewart (G. W. S. Barrow, ‘Stewart fami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Death Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year (the mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Soldiers
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including: *Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland *Scottish English *Scottish national identity, the Scottish identity and common culture *Scottish people, a nation and ethnic group native to Scotland *Scots language, a West Germanic language spoken in lowland Scotland *Symphony No. 3 (Mendelssohn), a symphony by Felix Mendelssohn known as ''the Scottish'' See also *Scotch (other) *Scotland (other) *Scots (other) *Scottian (other) *Schottische The schottische is a partnered country dance that apparently originated in Bohemia. It was popular in Victorian era ballrooms as a part of the Bohemian folk-dance craze and left its traces in folk music of countries such as Argentina ("chotis"Span ... * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ca:Escocès ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish People Of The Wars Of Scottish Independence
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including: *Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland *Scottish English *Scottish national identity, the Scottish identity and common culture *Scottish people, a nation and ethnic group native to Scotland *Scots language, a West Germanic language spoken in lowland Scotland *Symphony No. 3 (Mendelssohn), a symphony by Felix Mendelssohn known as ''the Scottish'' See also *Scotch (other) *Scotland (other) *Scots (other) *Scottian (other) *Schottische The schottische is a partnered country dance that apparently originated in Bohemia. It was popular in Victorian era ballrooms as a part of the Bohemian folk-dance craze and left its traces in folk music of countries such as Argentina ("chotis"Span ... * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ca:Escocès ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |