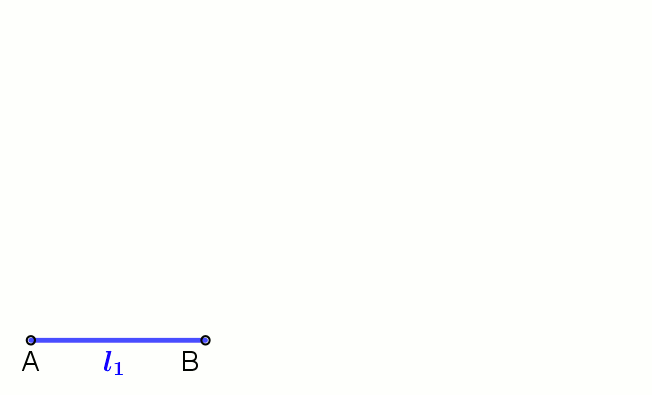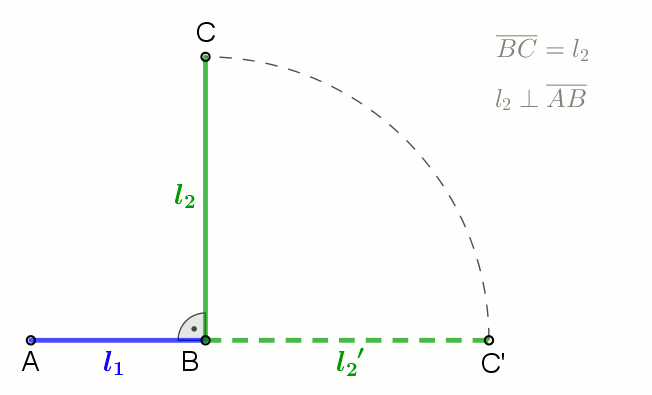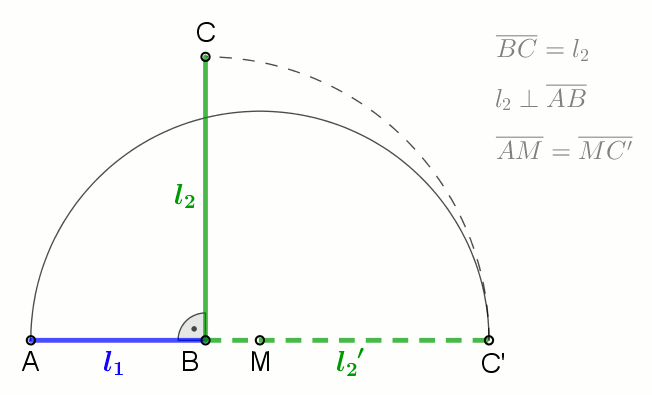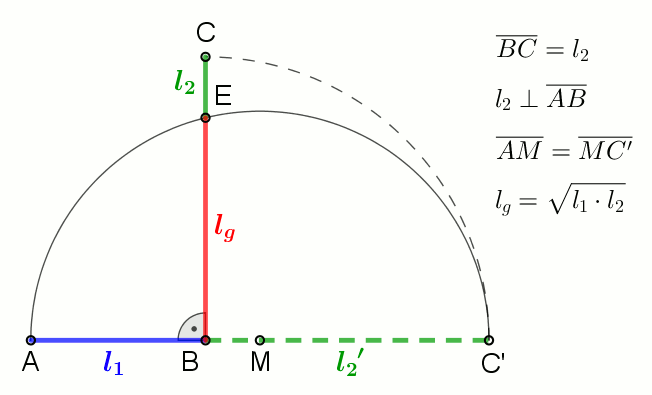|
Neuman–Sándor Mean
In mathematics of special functions, the Neuman–Sándor mean ''M'', of two positive and unequal numbers ''a'' and ''b'', is defined as: : M(a,b) = \frac This mean interpolates the inequality of the unweighted arithmetic mean ''A'' = (''a'' + ''b'')/2) and of the second Seiffert mean ''T'' defined as: : T(a,b)=\frac , so that ''A'' < ''M'' < ''T''. The ''M''(''a'',''b'') mean, introduced by Edward Neuman and József Sándor, has recently been the subject of intensive research and many remarkable inequalities for this mean can be found in the literature. Several authors obtained sharp and optimal bounds for the Neuman–Sándor mean. Neuman and others utilized this mean to study other bivariate means and inequalities. See also * *[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Functions
Special functions are particular mathematical functions that have more or less established names and notations due to their importance in mathematical analysis, functional analysis, geometry, physics, or other applications. The term is defined by consensus, and thus lacks a general formal definition, but the List of mathematical functions contains functions that are commonly accepted as special. Tables of special functions Many special functions appear as solutions of differential equations or integrals of elementary functions. Therefore, tables of integrals usually include descriptions of special functions, and tables of special functions include most important integrals; at least, the integral representation of special functions. Because symmetries of differential equations are essential to both physics and mathematics, the theory of special functions is closely related to the theory of Lie groups and Lie algebras, as well as certain topics in mathematical physics. Symbolic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Neuman
Edward Neuman (born September 19, 1943 in Rydułtowy, Silesian Voivodeship, Poland) is a Polish-American mathematician, currently a professor emeritus of mathematics at Southern Illinois University Carbondale. Academic career Neuman received his Ph.D. in mathematics from the University of Wrocław in 1972 under the supervision of wmpl:Stefan Paszkowski. His dissertation was entitled "Projections in Uniform Polynomial Approximation." He held positions at the Institute of Mathematics and the Institute of Computer Sciences of the University of Wroclaw, and the Institute of Applied Mathematics Bonn in Germany. In 1986, he took a permanent faculty position at Southern Illinois University. Contributions Neuman has contributed 130 journal articles in computational mathematics and mathematical inequalities such as the Ky Fan inequality, on bivariate means, and mathematical approximations and expansions. Neuman also developed software for computing with spline functions and wrote several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean
There are several kinds of mean in mathematics, especially in statistics. Each mean serves to summarize a given group of data, often to better understand the overall value (magnitude and sign) of a given data set. For a data set, the ''arithmetic mean'', also known as "arithmetic average", is a measure of central tendency of a finite set of numbers: specifically, the sum of the values divided by the number of values. The arithmetic mean of a set of numbers ''x''1, ''x''2, ..., x''n'' is typically denoted using an overhead bar, \bar. If the data set were based on a series of observations obtained by sampling from a statistical population, the arithmetic mean is the ''sample mean'' (\bar) to distinguish it from the mean, or expected value, of the underlying distribution, the ''population mean'' (denoted \mu or \mu_x).Underhill, L.G.; Bradfield d. (1998) ''Introstat'', Juta and Company Ltd.p. 181/ref> Outside probability and statistics, a wide range of other notions of mean are o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arithmetic Mean
In mathematics and statistics, the arithmetic mean ( ) or arithmetic average, or just the ''mean'' or the ''average'' (when the context is clear), is the sum of a collection of numbers divided by the count of numbers in the collection. The collection is often a set of results of an experiment or an observational study, or frequently a set of results from a survey. The term "arithmetic mean" is preferred in some contexts in mathematics and statistics, because it helps distinguish it from other means, such as the geometric mean and the harmonic mean. In addition to mathematics and statistics, the arithmetic mean is used frequently in many diverse fields such as economics, anthropology and history, and it is used in almost every academic field to some extent. For example, per capita income is the arithmetic average income of a nation's population. While the arithmetic mean is often used to report central tendencies, it is not a robust statistic, meaning that it is greatly influe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Mean
In mathematics, the geometric mean is a mean or average which indicates a central tendency of a set of numbers by using the product of their values (as opposed to the arithmetic mean which uses their sum). The geometric mean is defined as the th root of the product of numbers, i.e., for a set of numbers , the geometric mean is defined as :\left(\prod_^n a_i\right)^\frac = \sqrt /math> or, equivalently, as the arithmetic mean in logscale: :\exp For instance, the geometric mean of two numbers, say 2 and 8, is just the square root of their product, that is, \sqrt = 4. As another example, the geometric mean of the three numbers 4, 1, and 1/32 is the cube root of their product (1/8), which is 1/2, that is, \sqrt = 1/2. The geometric mean applies only to positive numbers. The geometric mean is often used for a set of numbers whose values are meant to be multiplied together or are exponential in nature, such as a set of growth figures: values of the human population or inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stolarsky Mean
In mathematics, the Stolarsky mean is a generalization of the logarithmic mean. It was introduced by Kenneth B. Stolarsky in 1975. Definition For two positive real numbers ''x'', ''y'' the Stolarsky Mean is defined as: : \begin S_p(x,y) & = \lim_ \left(\right)^ \\0pt& = \begin x & \textx=y \\ \left(\right)^ & \text \end \end Derivation It is derived from the mean value theorem, which states that a secant line, cutting the graph of a differentiable function f at ( x, f(x) ) and ( y, f(y) ), has the same slope as a line tangent to the graph at some point \xi in the interval ,y/math>. : \exists \xi\in ,y f'(\xi) = \frac The Stolarsky mean is obtained by : \xi = f'^\left(\frac\right) when choosing f(x) = x^p. Special cases *\lim_ S_p(x,y) is the minimum. *S_(x,y) is the geometric mean. *\lim_ S_p(x,y) is the logarithmic mean. It can be obtained from the mean value theorem by choosing f(x) = \ln x. *S_(x,y) is the power mean with exponent \frac. *\lim_ S_p(x,y) is the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Identric Mean
The identric mean of two positive real numbers ''x'', ''y'' is defined as: : \begin I(x,y) &= \frac\cdot \lim_ \sqrt xi-\eta\\ pt&= \lim_ \exp\left(\frac-1\right) \\ pt&= \begin x & \textx=y \\ pt\frac \sqrt -y& \text \end \end It can be derived from the mean value theorem by considering the secant of the graph of the function x \mapsto x\cdot \ln x. It can be generalized to more variables according by the mean value theorem for divided differences. The identric mean is a special case of the Stolarsky mean. See also * Mean * Logarithmic mean In mathematics, the logarithmic mean is a function of two non-negative numbers which is equal to their difference divided by the logarithm of their quotient. This calculation is applicable in engineering problems involving heat and mass trans ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Identric Mean Means ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Analysis
Analysis is the branch of mathematics dealing with continuous functions, limit (mathematics), limits, and related theories, such as Derivative, differentiation, Integral, integration, measure (mathematics), measure, infinite sequences, series (mathematics), series, and analytic functions. These theories are usually studied in the context of Real number, real and Complex number, complex numbers and Function (mathematics), functions. Analysis evolved from calculus, which involves the elementary concepts and techniques of analysis. Analysis may be distinguished from geometry; however, it can be applied to any Space (mathematics), space of mathematical objects that has a definition of nearness (a topological space) or specific distances between objects (a metric space). History Ancient Mathematical analysis formally developed in the 17th century during the Scientific Revolution, but many of its ideas can be traced back to earlier mathematicians. Early results in analysis were i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Means
{{disambiguation ...
Means may refer to: * Means LLC, an anti-capitalist media worker cooperative * Means (band), a Christian hardcore band from Regina, Saskatchewan * Means, Kentucky, a town in the US * Means (surname) * Means Johnston Jr. (1916–1989), US Navy admiral * Means, in ethics, something of instrumental value that helps to achieve an end ** Means, an indicator of suspicion in a criminal investigation See also * Ways and means committee, a government body charged with reviewing and making recommendations for government budgets * Mean (other) Mean is a term used in mathematics and statistics. Mean may also refer to: Music * ''Mean'' (album), a 1987 album by Montrose * "Mean" (song), a 2010 country song by Taylor Swift from ''Speak Now'' * "Mean", a song by Pink from '' Funhouse'' * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |