|
Neozygitomycetes
Entomophthoromycota is a division of kingdom fungi. In 2007, it was placed at the taxonomic rank of subphylum in the most recent revision of the entire fungus kingdom. In 2012, it was raised to the rank of phylum as "Entomophthoromycota" in a scientific paper by Richard A. Humber 2012. Divided into three classes and six families (Ancylistaceae, Basidiobolaceae, Completoriaceae, Entomophthoraceae, Meristacraceae, and Neozygitaceae), it contains over 250 species that are mostly arthropod pathogens or soil- and litter-borne saprobes. Taxonomy Circumscribed by mycologist Richard Humber in 2012, it contains species formerly classified in the division Zygomycota. Humber's reorganization divides the division into three classes while retaining the previously defined family structure: Division Entomophthoromycota Humber 2012 ntomophthoromycotina Humber 2007:Class Basidiobolomycetes Humber 2012 olomycetes Cavalier-Smith 1998; Bolomycetidae Cavalier-Smith 2012; Basidiobolomycota Dowe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neozygitomycetes
Entomophthoromycota is a division of kingdom fungi. In 2007, it was placed at the taxonomic rank of subphylum in the most recent revision of the entire fungus kingdom. In 2012, it was raised to the rank of phylum as "Entomophthoromycota" in a scientific paper by Richard A. Humber 2012. Divided into three classes and six families (Ancylistaceae, Basidiobolaceae, Completoriaceae, Entomophthoraceae, Meristacraceae, and Neozygitaceae), it contains over 250 species that are mostly arthropod pathogens or soil- and litter-borne saprobes. Taxonomy Circumscribed by mycologist Richard Humber in 2012, it contains species formerly classified in the division Zygomycota. Humber's reorganization divides the division into three classes while retaining the previously defined family structure: Division Entomophthoromycota Humber 2012 ntomophthoromycotina Humber 2007:Class Basidiobolomycetes Humber 2012 olomycetes Cavalier-Smith 1998; Bolomycetidae Cavalier-Smith 2012; Basidiobolomycota Dowe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
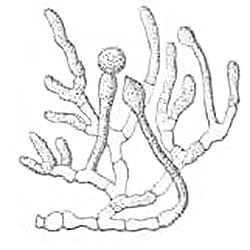
Conidiobolus Firmipilleus
''Conidiobolus'' is a genus of fungi in order Entomophthorales. Some species were defined in ''Conidiobolus'' but then moved into other genera such as ''Capillidium'' and ''Batkoa''. This genus can cause a human infection known as conidiobolomycosis. Species There are 54 species of ''Conidiobolus''. *''Conidiobolus adieretus'' Drechsler, 1953 (= '' Capillidium adiaeretum'' (Drechsler) B. Huang & Y. Nie (2020)) *'' Conidiobolus antarcticus'' S. Tosi, Caretta & Humber, 2004 *'' Conidiobolus apiculatus'' *'' Conidiobolus bangalorensis'' Sriniv. & Thirum., 1967 *'' Conidiobolus batkoi'' *'' Conidiobolus brefeldianus'' Couch, 1939 *'' Conidiobolus caecilius'' S. Keller, 2007 *'' Conidiobolus carpentieri'' (Giard) Remaud. & S. Keller, 1980 *'' Conidiobolus cercopidis'' *'' Conidiobolus cercopidis'' *'' Conidiobolus chlamydosporus'' Drechsler, 1955 *'' Conidiobolus chlapowskii'' Bałazy, J. Wiśn. & S. Kaczm., 1987 *'' Conidiobolus conglomeratus'' *''Conidiobolus coronatus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entomophthoraceae
Entomophthoraceae is a family of fungi in the order Entomophthorales The Entomophthorales are an order of fungi that were previously classified in the class Zygomycetes. A new subdivision, Entomophthoromycotina, has recently been circumscribed for them. Most species of the Entomophthorales are pathogens of ins .... This has been supported by molecular phylogenetic analysis (Gryganskyi et al. 2012).Gryganskyi AP, Humber RA, Smith ME et al (2012) Molecular phylogeny of the Entomophthoromycota. Mol Phylogenet Evol 65:682–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2012.07.026 Most species in the family are obligately entomopathogenic. There are two subfamilies, Erynioideae and Entomophthoroideae, which were proposed in 2005. Genera *'' Batkoa'' – 10 spp. *'' Entomophaga'' – 22 spp. *'' Entomophthora'' – 63 spp. *'' Erynia'' – 27 spp. *'' Eryniopsis'' – 5 spp. *'' Furia'' – 16 spp. *'' Massospora'' – 5 spp. *'' Orthomyces'' – 1 sp. *'' Pandora'' Humber 2005 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basidiobolus
''Basidiobolus ranarum'' is a filamentous fungus with worldwide distribution. The fungus was first isolated by Eidam in 1886. It can saprophytically live in the intestines of mainly cold-blooded vertebrates and on decaying fruits and soil. The fungus prefers glucose as a carbon source and grows rapidly at room temperature. ''Basidiobolus ranarum'' is also known as a cause of subcutaneous zygomycosis, usually causing granulomatous infections on a host's limbs. Infections are generally geographically limited to tropical and subtropical regions such as East and West Africa. Subcutaneous zygomycosis caused by ''B. ranarum'' is a rare disease and predominantly affects children and males. Common subcutaneous zygomycosis shows characteristic features and is relatively easy to be diagnosed; while, certain rare cases might show non-specific clinical features that might pose a difficulty on its identification. Although disease caused by this fungus is known to resolve spontaneously on its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygomycota
Zygomycota, or zygote fungi, is a former division or phylum of the kingdom Fungi. The members are now part of two phyla: the Mucoromycota and Zoopagomycota. Approximately 1060 species are known. They are mostly terrestrial in habitat, living in soil or on decaying plant or animal material. Some are parasites of plants, insects, and small animals, while others form symbiotic relationships with plants. Zygomycete hyphae may be coenocytic, forming septa only where gametes are formed or to wall off dead hyphae. Zygomycota is no longer recognised as it was not believed to be truly monophyletic. Etymology The name ''Zygomycota'' refers to the zygosporangia characteristically formed by the members of this clade, in which resistant spherical spores are formed during sexual reproduction. ''Zygos'' is Greek for "joining" or "a yoke", referring to the fusion of two hyphal strands which produces these spores, and ''-mycota'' is a suffix referring to a division of fungi. Spores The ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classification (biology)
In biology, taxonomy () is the science, scientific study of naming, defining (Circumscription (taxonomy), circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxon, taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain (biology), domain, kingdom (biology), kingdom, phylum (''division'' is sometimes used in botany in place of ''phylum''), class (biology), class, order (biology), order, family (biology), family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, as he developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms and binomial nomenclature for naming organisms. With advances in the theory, data and analytical technology of biologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saprobic
Saprotrophic nutrition or lysotrophic nutrition is a process of chemoheterotrophic extracellular digestion involved in the processing of decayed (dead or waste) organic matter. It occurs in saprotrophs, and is most often associated with fungi (for example ''Mucor'') and soil bacteria. Saprotrophic microscopic fungi are sometimes called saprobes; saprotrophic plants or bacterial flora are called saprophytes ( sapro- 'rotten material' + -phyte 'plant'), although it is now believed that all plants previously thought to be saprotrophic are in fact parasites of microscopic fungi or other plants. The process is most often facilitated through the active transport of such materials through endocytosis within the internal mycelium and its constituent hyphae. states the purpose of saprotrophs and their internal nutrition, as well as the main two types of fungi that are most often referred to, as well as describes, visually, the process of saprotrophic nutrition through a diagram of hyph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |