|
Nauny
Nauny or Nany (earlier reading: ''Entiuny'') was an ancient Egyptian princess during the Twenty-first Dynasty, probably a daughter of High Priest, later Pharaoh Pinedjem I. The name of her mother, Tentnabekhenu is known only from Nauny's funerary papyrus., p. 207 Life Her titles, known from her tomb are ''King's Daughter of His Body, Singer of Amun, Lady of the House.'' This title is mentioned on an Osiris figure from her burial.Kitchen, Kenneth A. The Third Intermediate Period in Egypt, 1100-650 B.C. (Book & Supplement) Aris & Phillips. 1986, p 67, She is likely to have been Pinedjem's daughter because she was buried at Deir el-Bahri, a popular burial place for the royal family of this period, close to Bab el-Gasus, which was also a popular burial place, for priests; also, Pinedjem's daughter Henuttawy and his probable daughter-in-law Djedmutesankh were buried nearby and Henuttawy's mummy and coffins show similarities with those of Nauny. Nauny's mother, Tentnabekhenu, is also c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinedjem I
Pinedjem I was the High Priest of Amun at Thebes in Ancient Egypt from 1070 to 1032 BC and the ''de facto'' ruler of the south of the country from 1054 BC. He was the son of the High Priest Piankh. However, many Egyptologists today believe that the succession in the Amun priesthood actually ran from Piankh to Herihor to Pinedjem I. Reign According to the new hypothesis regarding the succession of the Amun priesthood, Pinedjem I was too young to succeed to the High Priesthood of Amun after the death of Piankh. Herihor instead intervened to assume this office. After Herihor's death, Pinedjem I finally claimed this office which had once been held by his father Piankh. This interpretation is supported by the decorations from the Temple of Khonsu at Karnak where Herihor's wall reliefs here are immediately followed by those of Pinedjem I with no intervening phase for Piankh and also by the long career of Pinedjem I who served as High Priest of Amun and later as king at Thebes. He inh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TT358
The Theban Tomb TT358 is located in Deir el-Bahari, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. The tomb belongs to the ''king's wife'' Ahmose-Meritamun, the sister and the wife of Pharaoh Amenhotep I.Aidan Dodson & Dyan Hilton: The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt. Thames & Hudson, 2004, , p.123, 127, 129 The tomb was later used for the additional burial of the King's daughter Nany, who was a daughter of Pharaoh Pinedjem I. The tomb was excavated by Winlock during the 1929–30 excavations on behalf of the Metropolitan Museum of Arts. The tomb was discovered in the Court of the Temple of Queen Hatshepsut.H. E. Winlock, The Egyptian Expedition 1928-1929: The Museum's Excavations at Thebes, The Metropolitan Museum of Art Bulletin, Vol. 25, No. 11, Part 2: The EgyptianExpedition 1928-1929 (Nov., 1930), pp. 14-34 Ahmose Meritamun After excavating the outer corridor a large well was encountered. Planks and a board were brought into the tom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
11th-century BC Women
The 11th century is the period from 1001 ( MI) through 1100 ( MC) in accordance with the Julian calendar, and the 1st century of the 2nd millennium. In the history of Europe, this period is considered the early part of the High Middle Ages. There was, after a brief ascendancy, a sudden decline of Byzantine power and a rise of Norman domination over much of Europe, along with the prominent role in Europe of notably influential popes. Christendom experienced a formal schism in this century which had been developing over previous centuries between the Latin West and Byzantine East, causing a split in its two largest denominations to this day: Roman Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy. In Song dynasty China and the classical Islamic world, this century marked the high point for both classical Chinese civilization, science and technology, and classical Islamic science, philosophy, technology and literature. Rival political factions at the Song dynasty court created strife amongs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
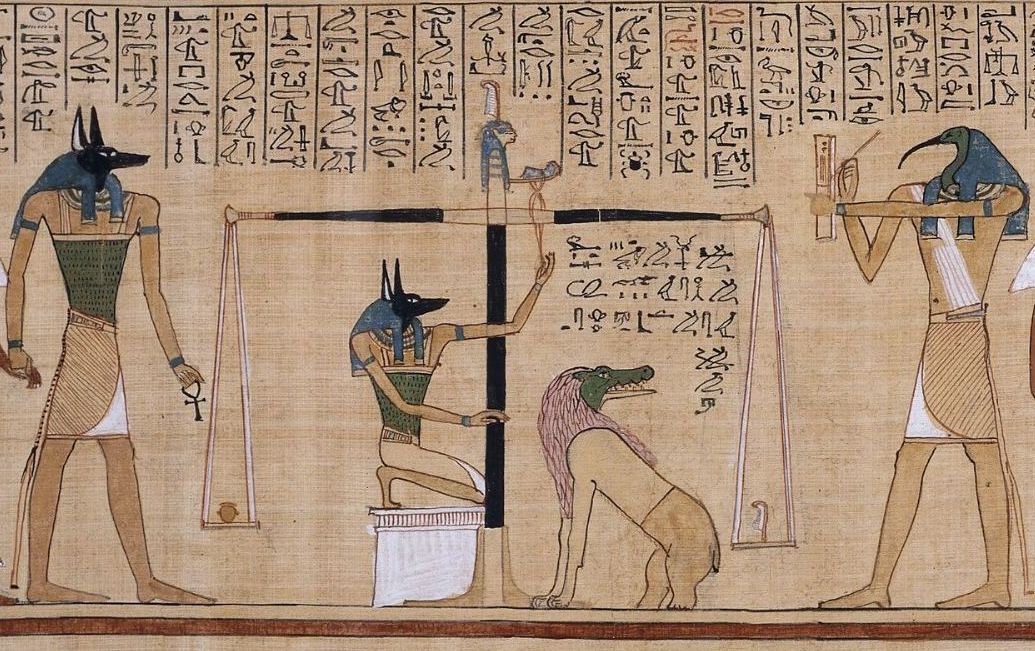
Book Of The Dead
The ''Book of the Dead'' ( egy, 𓂋𓏤𓈒𓈒𓈒𓏌𓏤𓉐𓂋𓏏𓂻𓅓𓉔𓂋𓅱𓇳𓏤, ''rw n(y)w prt m hrw(w)'') is an ancient Egyptian funerary text generally written on papyrus and used from the beginning of the New Kingdom (around 1550 BCE) to around 50 BCE. The original Egyptian name for the text, transliterated ''rw nw prt m hrw'', is translated as ''Book of Coming Forth by Day'' or ''Book of Emerging Forth into the Light''. "Book" is the closest term to describe the loose collection of texts consisting of a number of magic spells intended to assist a dead person's journey through the ''Duat'', or underworld, and into the afterlife and written by many priests over a period of about 1,000 years. Karl Richard Lepsius introduced for these texts the German name ''Todtenbuch'' (modern spelling ''Totenbuch''), translated to English as Book of the Dead. The ''Book of the Dead'', which was placed in the coffin or burial chamber of the deceased, was part of a trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osiris
Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wsjr'', cop, ⲟⲩⲥⲓⲣⲉ , ; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎𐤓, romanized: ʾsr) is the god of fertility, agriculture, the afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He was classically depicted as a green-skinned deity with a pharaoh's beard, partially mummy-wrapped at the legs, wearing a distinctive atef crown, and holding a symbolic crook and flail. He was one of the first to be associated with the mummy wrap. When his brother, Set cut him up into pieces after killing him, Osiris' wife Isis found all the pieces and wrapped his body up, enabling him to return to life. Osiris was widely worshipped until the decline of ancient Egyptian religion during the rise of Christianity in the Roman Empire. Osiris was at times considered the eldest son of the earth god Geb and the sky goddess Nut, as well as being brother and husband of Isis, and brother of Set, Nephthys, and Horus the Elder, with Horus the Younger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ushabti
The ushabti (also called shabti or shawabti, with a number of variant spellings) was a funerary figurine used in ancient Egyptian funerary practices. The Egyptological term is derived from , which replaced earlier , perhaps the nisba of "'' Persea'' tree". Ushabtis were placed in tombs among the grave goods and were intended to act as servants or minions for the deceased, should they be called upon to do manual labor in the afterlife. The figurines frequently carried a hoe on their shoulder and a basket on their backs, implying they were intended to farm for the deceased. They were usually written on by the use of hieroglyphs typically found on the legs. They carried inscriptions asserting their readiness to answer the gods' summons to work. The practice of using ushabtis originated in the Old Kingdom of Egypt (c. 2600 to 2100 BCE), with the use of life-sized reserve heads made from limestone, which were buried with the mummy. Most ushabtis were of minor size, and many pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amenhotep I
Amenhotep I () ( egy, jmn-ḥtp(w) /jaˌmanuwˈħatpaw/ " Amun is satisfied"; Amarna cuneiform ''a-ma-an-ha-at-pe'' or ''-at-pa''), Amenôthes I, or Amenophis I, (,) from Ancient Greek Ἀμένωφις ,Dodson & Hilton (2004) p.126 additionally ''King Djeserkare'' (transliteration: ''Ḏsr-k3-R`''), was the second Pharaoh of the 18th Dynasty of Egypt. His reign is generally dated from 1526 to 1506 BC. He was a son of Ahmose I and Ahmose-Nefertari, but had at least two elder brothers, Ahmose-ankh and Ahmose Sapair, and was not expected to inherit the throne. However, sometime in the eight years between Ahmose I's 17th regnal year and his death, his heir apparent died and Amenhotep became crown prince. He then acceded to the throne and ruled for about 21 years.Manetho - translated by W.G. Waddell, Loeb Classical Library, 1940, p.109 Although his reign is poorly documented, it is possible to piece together a basic history from available evidence. He inherited the kingdom formed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmose-Meritamen
Ahmose-Meritamun (or Ahmose-Meritamon) was a Queen of Egypt during the early Eighteenth Dynasty. She was both the older sister and the wife of Pharaoh Amenhotep I. She died fairly young and was buried in tomb TT358 in Deir el-Bahari. Biography Ahmose-Meritamun was the royal daughter of Ahmose I and Ahmose Nefertari, and became the Great Royal Wife of her younger brother Amenhotep I, pharaoh of Ancient Egypt in the Eighteenth Dynasty.Aidan Dodson & Dyan Hilton: The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt. Thames & Hudson, 2004, , p.123, 127, 129 Meritamun took over the role of God's Wife of Amun from her mother Ahmose Nefertari. Other titles recorded for Meritamun include: lady of the two lands (''nbt-t3wy''), (Great) King's Wife (''ḥmt-nswt(-wrt)''), mistress of the entire two lands (''ḥnwt-tꜣwy-tm''), god's wife (''ḥmt-ntr''), united with the white crown (''ẖnmt-nfr-ḥḏt''), king's daughter (''sꜣt-nswt''), and king's sister (''snt-niswt''). The title king's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masaharta
Masaharta or Masaherta was the High Priest of Amun at Thebes between 1054 and 1045 BC. Biography His father was Pinedjem I, who was the Theban High Priest of Amun and de facto ruler of Upper Egypt from 1070 BC, then declared himself pharaoh in 1054 BC and Masaharta succeeded him as high priest. His mother was probably Duathathor-Henuttawy, the daughter of Ramesses XI, last ruler of the 20th dynasty. His aunt Tentamun, another daughter of Ramesses married Pharaoh Smendes I, who ruled Lower Egypt. One of Masaharta's brothers was Psusennes I, who followed Smendes's successor, the short-lived Amenemnisu as pharaoh. His wife is likely to have been the Singer of Amun Tayuheret, whose mummy was found in the Deir el-Bahri cachette. It is possible that he had a daughter called Isetemkheb, since a lady by this name is called the daughter of a high priest on her funerary objects; it is also possible, though, that she was Menkheperre's daughter. The God's Wife of Amun during Masaharta's re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twenty-first Dynasty Of Egypt
The Twenty-first Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XXI, alternatively 21st Dynasty or Dynasty 21) is usually classified as the first Dynasty of the Ancient Egyptian Third Intermediate Period, lasting from 1077 BC to 943 BC. History After the reign of Ramesses III, a long, slow decline of royal power in Egypt followed. The pharaohs of the Twenty-first Dynasty ruled from Tanis, but were mostly active only in Lower Egypt, which they controlled. This dynasty is described as 'Tanite' because its political capital was based at Tanis. Meanwhile, the High Priests of Amun at Thebes effectively ruled Middle and Upper Egypt in all but name. The later Egyptian Priest Manetho of Sebennytos states in his Epitome on Egyptian royal history that "the 21st Dynasty of Egypt lasted for 130 years".Kenneth A. Kitchen, The Third Intermediate Period in Egypt (1100–650 BC), 3rd edition, 1986, Warminster: Aris & Phillips Ltd, p.531 Pharaohs of the 21st Dynasty Timeline of the 21st Dynasty ImageS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
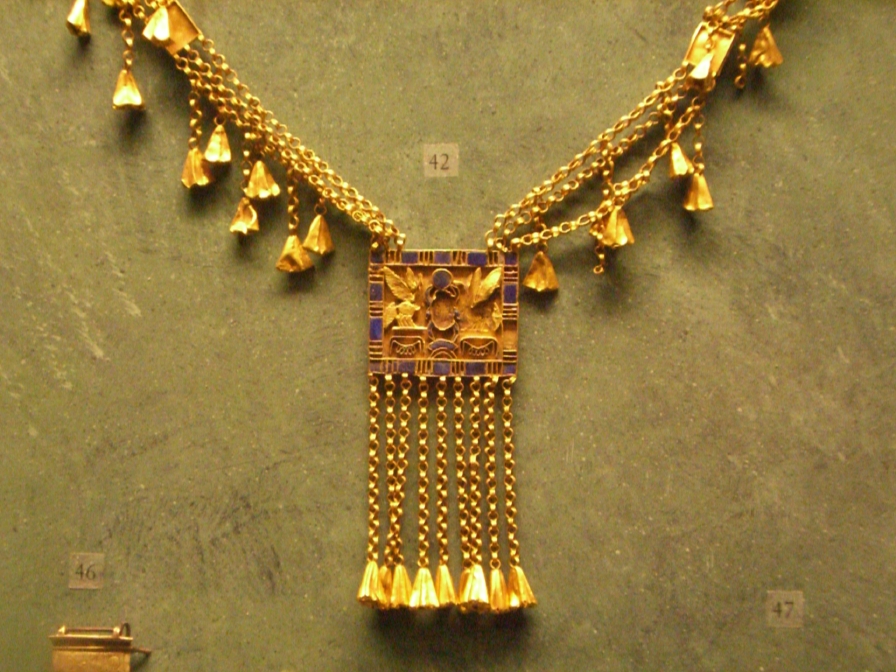
Winged Scarab Pectoral Of Nany MET 30
A wing is a type of fin that produces lift while moving through air or some other fluid. Accordingly, wings have streamlined cross-sections that are subject to aerodynamic forces and act as airfoils. A wing's aerodynamic efficiency is expressed as its lift-to-drag ratio. The lift a wing generates at a given speed and angle of attack can be one to two orders of magnitude greater than the total drag on the wing. A high lift-to-drag ratio requires a significantly smaller thrust to propel the wings through the air at sufficient lift. Lifting structures used in water include various foils, such as hydrofoils. Hydrodynamics is the governing science, rather than aerodynamics. Applications of underwater foils occur in hydroplanes, sailboats and submarines. Etymology and usage For many centuries, the word "wing", from the Old Norse ''vængr'', referred mainly to the foremost limbs of birds (in addition to the architectural aisle). But in recent centuries the word's meaning has exten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |