|
Natashquan River
The Natashquan is a river in the Canadian provinces of Quebec and Newfoundland and Labrador. It flows south into the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. Geography The river has its source just south of the boundary between the Atlantic and Saint Lawrence river watersheds. It flows south-east to the Labrador–Quebec border from where it flows southward to the Gulf. The river basin covers . It lies between the basins of the Aguanish River to the west and the Kegaska River to the east. About 39.8% of the basin is in Labrador north of the provincial boundary. The river is about , of which about is in Labrador. The river has a Strahler number of 7. In Quebec, the river forms the boundary between the Minganie and Golfe-du-Saint-Laurent Regional County Municipalities before draining into the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, about east from Sept-Îles. The name is of Innu origin, who call it ''Nutahquaniu Hipu'', meaning "river where black bear is hunted". Together with the Moisie River, the Nata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
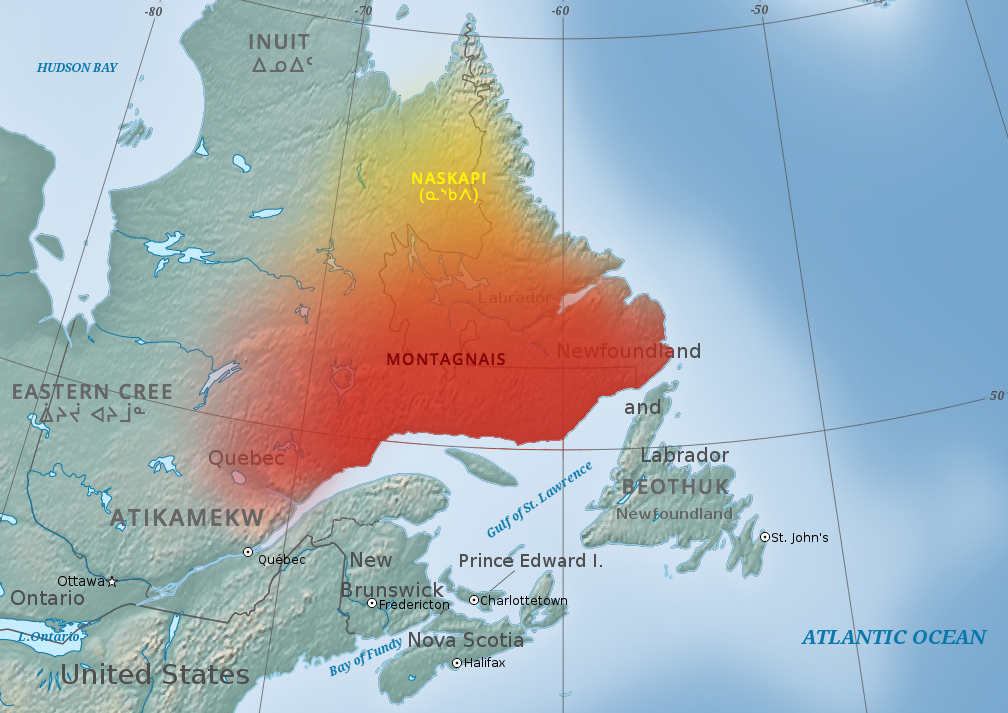
Innu
The Innu / Ilnu ("man", "person") or Innut / Innuat / Ilnuatsh ("people"), formerly called Montagnais from the French colonial period (French for "mountain people", English pronunciation: ), are the Indigenous inhabitants of territory in the northeastern portion of the present-day province of Labrador and some portions of Quebec. They refer to their traditional homeland as ''Nitassinan'' ("Our Land", ᓂᑕᔅᓯᓇᓐ) or ''Innu-assi'' ("Innu Land"). The Innu are divided into several bands, with the Montagnais being the southernmost group and the Naskapi being the northernmost. Their ancestors were known to have lived on these lands as hunter-gatherers for several thousand years. To support their seasonal hunting migrations, they created portable tents made of animal skins. Their subsistence activities were historically centred on hunting and trapping caribou, moose, deer, and small game. Their language, Ilnu-Aimun or Innu-Aimun (popularly known since the French colonial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quebec Route 138
Route 138 is a major highway in the Canadian province of Quebec, following the entire north shore of the Saint Lawrence River past Montreal to the temporary eastern terminus in Kegashka on the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. The western terminus is in Elgin, at the border with New York State south-west of Montreal (connecting with New York State Route 30 at the Trout River Border Crossing). Part of this highway is known as the ''Chemin du Roy'', or King's Highway, which is one of the oldest highways in Canada. It passes through the Montérégie, Lanaudière, Mauricie, Capitale-Nationale and Côte-Nord regions of Quebec. In Montreal, Highway 138 runs via Sherbrooke Street, crosses the Pierre Le Gardeur Bridge to Charlemagne and remains a four-lane road until exiting Repentigny. This highway takes a more scenic route than the more direct Autoroute 40 between Montreal and Quebec City. It crosses the Saguenay River via a ferry which travels between Baie-Sainte-Catherine and Tadoussac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trade, fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business division is Hudson's Bay (department store), Hudson's Bay, commonly referred to as The Bay ( in French). After incorporation by Kingdom of England, English royal charter in 1670, the company functioned as the ''de facto'' government in parts of North America for nearly 200 years until the HBC sold the land it owned (the entire Hudson Bay drainage basin, known as Rupert's Land) to Canada in 1869 as part of the Deed of Surrender, authorized by the Rupert's Land Act 1868. At its peak, the company controlled the fur trade throughout much of the English- and later British North America, British-controlled North America. By the mid-19th century, the company evolved into a mercantile business selling a wide variety of products from furs t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques-Nicolas Bellin
Jacques Nicolas Bellin (1703 – 21 March 1772) was a French hydrographer, geographer, and member of the French intellectual group called the philosophes. Bellin was born in Paris. He was hydrographer of France's hydrographic office, member of the ''Académie de Marine'' and of the Royal Society of London. Over a 50-year career, he produced many maps of particular interest to the ''Ministère de la Marine''. His maps of Canada and of French territories in North America ( New France, Acadia, Louisiana) are particularly valuable. He died at Versailles. First ''Ingenieur de la Marine'' In 1721, at age 18, he was appointed hydrographer (chief cartographer) to the French Navy. In August 1741, he became the first ''Ingénieur de la Marine of the Dépot des cartes et plans de la Marine'' (the French Hydrographical Office) and was named Official Hydrographer of the French King. Prodigious work, high standard of excellence During his reign the Depot published a prodigious numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Jolliet
Louis Jolliet (September 21, 1645after May 1700) was a French-Canadian explorer known for his discoveries in North America. In 1673, Jolliet and Jacques Marquette, a Jesuit Catholic priest and missionary, were the first non-Natives to explore and map the Upper Mississippi River. Early life Jolliet was born in 1645 in Beaupré, a French settlement near Quebec City, to Jean Jolliet and Marie D'Abancourt. When he was six years old, his father died; his mother then married a successful merchant, Geoffroy Guillot dit Lavalle, until his death in 1665. Shortly after the passing of his mother's second husband, she was married to Martin Prevost until her death in 1678. Jolliet's stepfather owned land on the Ile d'Orleans, an island in the Saint Lawrence River in Quebec that was home to First Nations. Jolliet spent much time on Ile d'Orleans, so it was likely that he began speaking Indigenous languages of the Americas at a young age. Besides French, he also learned English and Span ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Cartier
Jacques Cartier ( , also , , ; br, Jakez Karter; 31 December 14911 September 1557) was a French- Breton maritime explorer for France. Jacques Cartier was the first European to describe and map the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the shores of the Saint Lawrence River, which he named "The Country of Canadas" after the Iroquoian names for the two big settlements he saw at Stadacona (Quebec City) and at Hochelaga (Montreal Island).. Early life Jacques Cartier was born in 1491 in Saint-Malo, the port on the north-east coast of Brittany. Cartier, who was a respectable mariner, improved his social status in 1520 by marrying Mary Catherine des Granches, member of a leading aristocratic family. His good name in Saint-Malo is recognized by its frequent appearance in baptismal registers as godfather or witness. First voyage (1534) In 1534, two years after the Duchy of Brittany was formally united with France in the Edict of Union, Cartier was introduced to King Francis I by Jean L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humid Continental Climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing cold (sometimes severely cold in the northern areas) winters. Precipitation is usually distributed throughout the year but often do have dry seasons. The definition of this climate regarding temperature is as follows: the mean temperature of the coldest month must be below or depending on the isotherm, and there must be at least four months whose mean temperatures are at or above . In addition, the location in question must not be semi-arid or arid. The cooler ''Dfb'', ''Dwb'', and ''Dsb'' subtypes are also known as hemiboreal climates. Humid continental climates are generally found between latitudes 30° N and 60° N, within the central and northeastern portions of North America, Europe, and Asia. They are rare and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subarctic Climate
The subarctic climate (also called subpolar climate, or boreal climate) is a climate with long, cold (often very cold) winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, generally at latitudes from 50° to 70°N, poleward of the humid continental climates. Subarctic or boreal climates are the source regions for the cold air that affects temperate latitudes to the south in winter. These climates represent Köppen climate classification ''Dfc'', ''Dwc'', ''Dsc'', ''Dfd'', ''Dwd'' and ''Dsd''. Description This type of climate offers some of the most extreme seasonal temperature variations found on the planet: in winter, temperatures can drop to below and in summer, the temperature may exceed . However, the summers are short; no more than three months of the year (but at least one month) must have a 24-hour average temperature of at least to fall into this category of climate, and the coldest month should a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mafic
A mafic mineral or rock is a silicate mineral or igneous rock rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Common mafic rocks include basalt, diabase and gabbro. Mafic rocks often also contain calcium-rich varieties of plagioclase feldspar. Mafic materials can also be described as ferromagnesian. History The term ''mafic'' is a portmanteau of "magnesium" and "ferric" and was coined by Charles Whitman Cross, Joseph P. Iddings, Louis Valentine Pirsson, and Henry Stephens Washington in 1912. Cross' group had previously divided the major rock-forming minerals found in igneous rocks into ''salic'' minerals, such as quartz, feldspars, or feldspathoids, and ''femic'' minerals, such as olivine and pyroxene. However, micas and aluminium-rich amphiboles were excluded, while some calcium minerals containing little iron or magnesium, such as wollastonite or apatite, were incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clastic Rock
Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus,Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak, p. G-3 chunks, and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak, p. G-5 Geologists use the term clastic to refer to sedimentary rocks and particles in sediment transport, whether in suspension or as bed load, and in sediment deposits. Sedimentary clastic rocks Clastic sedimentary rocks are rocks composed predominantly of broken pieces or ''clasts'' of older weathered and eroded rocks. Clastic sediments or sedimentary rocks are classified based on grain size, clast and cementing material (matrix) composition, and texture. The classification factors are often useful in determining a sample's environment of deposition. An example of clastic environment would be a river system in which the full range of grains being transpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphic Rock
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock ( protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causing profound physical or chemical changes. During this process, the rock remains mostly in the solid state, but gradually recrystallizes to a new texture or mineral composition. The protolith may be an igneous, sedimentary, or existing metamorphic rock. Metamorphic rocks make up a large part of the Earth's crust and form 12% of the Earth's land surface. They are classified by their protolith, their chemical and mineral makeup, and their texture. They may be formed simply by being deeply buried beneath the Earth's surface, where they are subject to high temperatures and the great pressure of the rock layers above. They can also form from tectonic processes such as continental collisions, which cause horizontal pressure, friction, and di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |