|
Nasutoceratops Holotype
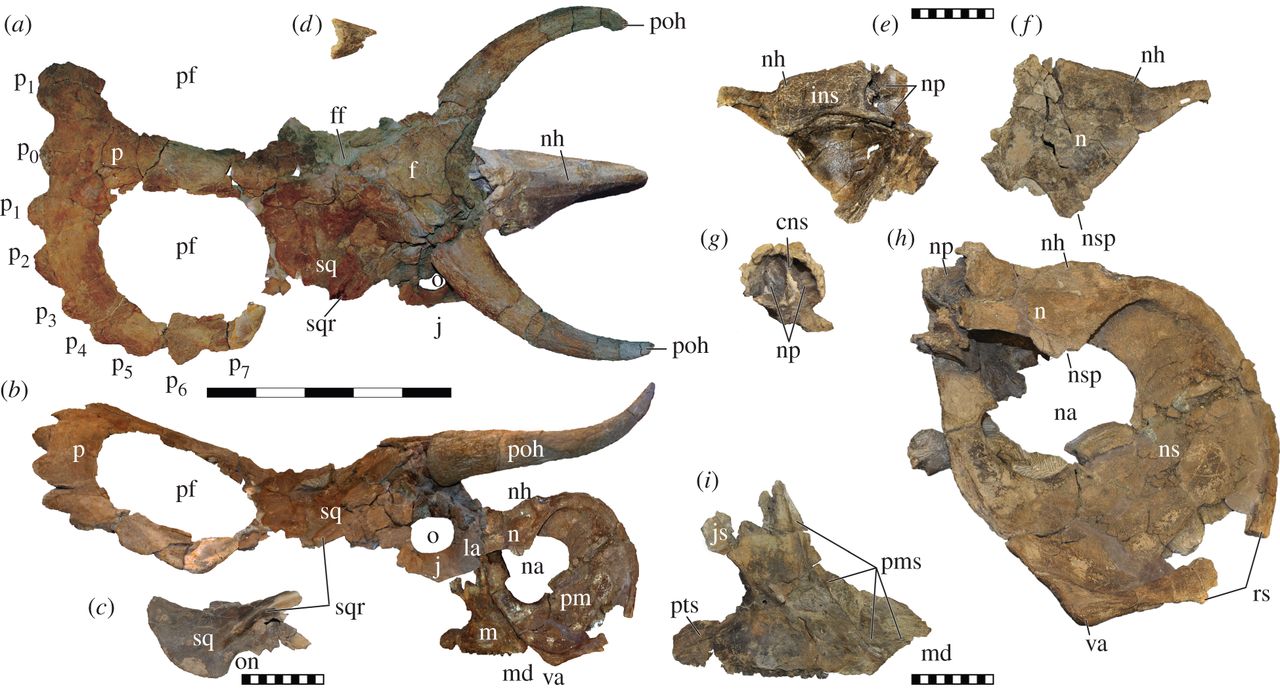
''Nasutoceratops'' is an extinct genus of ceratopsian dinosaur. It is a basal centrosaurine which lived during the Late Cretaceous Period (late Campanian, about 76.0-75.5 Ma). Fossils have been found in southern Utah, United States. ''Nasutoceratops'' was a large, ground-dwelling, quadrupedal herbivore with a short snout and unique rounded horns above its eyes that have been likened to those of modern cattle. Extending almost to the tip of its snout, these horns are the longest of all the members of the centrosaurine subfamily. The presence of pneumatic elements in the nasal bones of ''Nasutoceratops'' are a unique trait and are unknown in any other ceratopsid. Discovery and naming ''Nasutoceratops'' is known from the holotype UMNH VP 16800, a partially associated nearly complete skull, a coronoid process, a syncervical, three partial anterior dorsal vertebrae, a shoulder girdle, an associated left forelimb, parts of the right forelimb and skin impressions. Two spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campanian spans the time from 83.6 (± 0.2) to 72.1 (± 0.2) million years ago. It is preceded by the Santonian and it is followed by the Maastrichtian. The Campanian was an age when a worldwide sea level rise covered many coastal areas. The morphology of some of these areas has been preserved: it is an unconformity beneath a cover of marine sedimentary rocks. Etymology The Campanian was introduced in scientific literature by Henri Coquand in 1857. It is named after the French village of Champagne in the department of Charente-Maritime. The original type locality was a series of outcrop near the village of Aubeterre-sur-Dronne in the same region. Definition The base of the Campanian Stage is defined as a place in the stratigraphic column wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium and the viscerocranium ( facial skeleton) that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to enable sound localisation of the direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, such as horned ungulates (mammals with hooves), the skull also has a defensive function by providing the mount (on the front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Name (zoology)
In zoological nomenclature, the specific name (also specific epithet or species epithet) is the second part (the second name) within the scientific name of a species (a binomen). The first part of the name of a species is the name of the genus or the generic name. The rules and regulations governing the giving of a new species name are explained in the article species description. For example, the scientific name for humans is ''Homo sapiens'', which is the species name, consisting of two names: ''Homo'' is the " generic name" (the name of the genus) and ''sapiens'' is the "specific name". Historically, ''specific name'' referred to the combination of what are now called the generic and specific names. Carl Linnaeus, who formalized binomial nomenclature, made explicit distinctions between specific, generic, and trivial names. The generic name was that of the genus, the first in the binomial, the trivial name was the second name in the binomial, and the specific the proper term for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label=Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Name Of A Biological Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should clearly demonstr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name that has that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have such types. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric Karl Lund
The given name Eric, Erich, Erikk, Erik, Erick, or Eirik is derived from the Old Norse name ''Eiríkr'' (or ''Eríkr'' in Old East Norse due to monophthongization). The first element, ''ei-'' may be derived from the older Proto-Norse ''* aina(z)'', meaning "one, alone, unique", ''as in the form'' ''Æ∆inrikr'' explicitly, but it could also be from ''* aiwa(z)'' "everlasting, eternity", as in the Gothic form ''Euric''. The second element ''- ríkr'' stems either from Proto-Germanic ''* ríks'' "king, ruler" (cf. Gothic ''reiks'') or the therefrom derived ''* ríkijaz'' "kingly, powerful, rich, prince"; from the common Proto-Indo-European root * h₃rḗǵs. The name is thus usually taken to mean "sole ruler, autocrat" or "eternal ruler, ever powerful". ''Eric'' used in the sense of a proper noun meaning "one ruler" may be the origin of ''Eriksgata'', and if so it would have meant "one ruler's journey". The tour was the medieval Swedish king's journey, when newly elected, to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now- extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Earth b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stage (stratigraphy)
In chronostratigraphy, a stage is a succession of rock strata laid down in a single age on the geologic timescale, which usually represents millions of years of deposition. A given stage of rock and the corresponding age of time will by convention have the same name, and the same boundaries. Rock series are divided into stages, just as geological epochs are divided into ages. Stages can be divided into smaller stratigraphic units called chronozones. (See chart at right for full terminology hierarchy.) Stages may also be divided into substages or indeed grouped as superstages. The term faunal stage is sometimes used, referring to the fact that the same fauna (animals) are found throughout the layer (by definition). Definition Stages are primarily defined by a consistent set of fossils (biostratigraphy) or a consistent magnetic polarity (see paleomagnetism) in the rock. Usually one or more index fossils that are common, found worldwide, easily recognized, and limited to a sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Staircase–Escalante National Monument
The Grand Staircase–Escalante National Monument (GSENM) is a United States national monument protecting the Grand Staircase, the Kaiparowits Plateau, and the Canyons of the Escalante (Escalante River) in southern Utah. It was established in 1996 by President of the United States, President Bill Clinton under the authority of the Antiquities Act with 1.7 million acres of land, later expanded to ."National Landscape Conservation System National Monuments" (archive). ''blm.gov''. Bureau of Land Management. April 2012. Retrieved December 10, 2017. In 2017, the monument's size was reduced by half in a succeeding Presidential proclamation (United States), presidential proclamation, and it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaiparowits Formation
The Kaiparowits Formation is a sedimentary rock formation found in the Kaiparowits Plateau in Grand Staircase–Escalante National Monument, in the southern part of Utah in the western United States. It is over 2800 feet (850 m) thick, and is Campanian in age. This Upper Cretaceous formation was formed from alluvial floodplains of large rivers in coastal southern Laramidia; sandstone beds are the deposit of rivers, and mudstone beds represent floodplain deposits. It is fossiliferous, with most specimens from the lower half of the formation, but exploration is only comparatively recent, with most work being done since 1982. It has been estimated that less than 10% of the Kaiparowits formation has been explored for fossils. Most fieldwork has been conducted by The Natural History Museum of Utah. Age Traditionally, the Kaiparowits Formation has been considered to be roughly equivalent in age to the northern Dinosaur Park Formation. This, combined with the differences in fauna betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_(2).jpg)

