|
Nahum Slouschz
Nahum Slouschz ( he, נחום סלושץ, links=no) (November 1872 – December 1966) was a Russian-born Israeli writer, translator and archaeologist. He was known for his studies of the "secret" Jews of Portugal and the history of the Jewish communities in North Africa, mostly, in Libya and Tunisia. Biography Nahum Slouschz was born in Smarhon’ and raised in Odessa. He studied at a local school and was tutored in Jewish studies by his father. At nineteen, he was sent to Palestine by the Hovevei Zion Society of Odessa to explore possibilities of founding a colony in the Holy Land. He was not successful and returned home. In 1896 he traveled through Austria and Lithuania, and then went to Egypt and again to Palestine. Slouschz was a devoted follower of Herzl and the Zionist movement. Slouschz established branches of the movement in Odessa and wrote at length about the Jewish question. He attended the Second Zionist Congress at Basel as a delegate and correspondent. In 1898 h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barash Shalom
Barash is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Brandon Barash *David P. Barash *Joshua Barash *Amanuel Barash See also *Blush (2015 film), originally titled "Barash" *Barash(Wally), the hero of the animated series Kikoriki *Sy Barash Regatta *Barasch {{surname, Barash ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Zionist Congress
The Second World Zionist Congress (Hebrew: הקונגרס הציוני השני) met in Basel, Switzerland on 28 August 1898. and was the second meeting of the Zionist Organisation. The World Zionist Congress brought together delegates from across the world to raise funds, lobby support and create the institutions that would one day form the modern day Jewish State known as Israel, which was established in 1948. The Congress met every year from 1897 to 1901 (after which it met every two years, except during the years of the Second World War). The main focus of the Second Congress, as set out by its chair, Theodor Herzl, was to engage with Jewish communities in the diaspora and encourage them to adopt Political Zionism. The three day congress established the Jewish Colonial Fund (later called the Anglo-Palestine Bank) whose aim was to fund the successful migration of Jews to Palestine, as well as the establishment of a Committee on Culture. Other notable events of the congress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
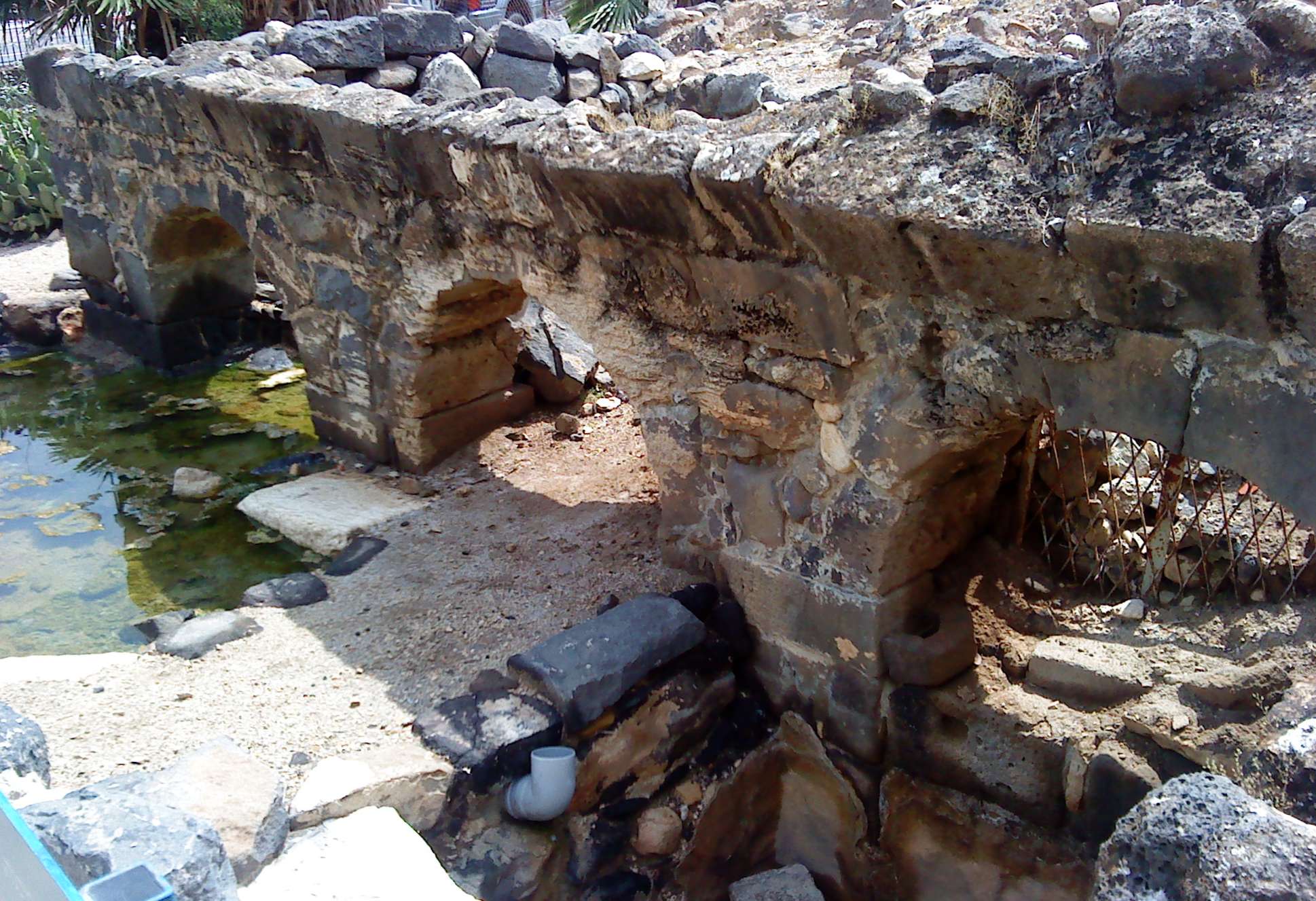
Hamat Tiberias
Hammath Tiberias or Hammat Tiberias is an ancient archaeological site and an Israeli national park known as Hamat Tverya National Park, which is located on the adjacent to Tiberias on the road to Zemach that runs along the shore of the Sea of Galilee. Name ''Hammath'' or ''Hamma'' is the Hebrew and Semitic word for "hot spring." Hammat Tiberias is adjacent to the ancient city of Tiberias, which was established in the first century CE and is called in Hebrew "Tveriya," thus the springs and the resort are called Hammei Tveriya. Since several places bore the name "Hammath", the distinction was made here by adding Tiberias/Tveriya to the name. Spelling varies for both parts of the Hebrew name. The Arabic name uses the cognate word: '' Al-Hammam''. History The 17 springs of Hamat Tiberias have been known since antiquity for their curative properties. According to the Jerusalem Talmud, a village once rested upon the site and was distinct from Tiberias. The site was rediscovered i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aliyah
Aliyah (, ; he, עֲלִיָּה ''ʿălīyyā'', ) is the immigration of Jews from Jewish diaspora, the diaspora to, historically, the geographical Land of Israel, which is in the modern era chiefly represented by the Israel, State of Israel. Traditionally described as "the act of going up" (towards the Jerusalem in Judaism, Jewish holy city of Jerusalem), moving to the Land of Israel or "making aliyah" is one of the most basic tenets of Zionism. The opposite action—emigration by Jews from the Land of Israel—is referred to in the Hebrew language as ''yerida'' (). The Law of Return that was passed by the Knesset, Israeli parliament in 1950 gives all diaspora Jews, as well as their children and grandchildren, the right to relocate to Israel and acquire Israeli citizenship on the basis of connecting to their Jewish identity. For much of Jewish history, their history, most Jews have lived in the diaspora outside of the Land of Israel due to Jewish military history, various hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Language
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved throughout history as the main liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. Hebrew is the only Canaanite language still spoken today, and serves as the only truly successful example of a dead language that has been revived. It is also one of only two Northwest Semitic languages still in use, with the other being Aramaic. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, during the time of the Babylonian captivity. For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as '' Lashon Hakodesh'' (, ) since an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Literature
Hebrew literature consists of ancient, medieval, and modern writings in the Hebrew language. It is one of the primary forms of Jewish literature, though there have been cases of literature written in Hebrew by non-Jews. Hebrew literature was produced in many different parts of the world throughout the medieval and modern eras, while contemporary Hebrew literature is largely Israeli literature. In 1966, Agnon won the Nobel Prize for Literature for novels and short stories that employ a unique blend of biblical, Talmudic and modern Hebrew, making him the first Hebrew writer to receive this award. Ancient era Literature in Hebrew begins with the oral literature of the ' (), "The Holy Language", since ancient times and with the teachings of Abraham, the first of the biblical patriarchs of Israel, c. 2000 BCE . Beyond comparison, the most important work of ancient Hebrew literature is the Hebrew Bible (Tanakh). The Mishna, compiled around 200 CE, is the primary rabbinic codifica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Paris
, image_name = Coat of arms of the University of Paris.svg , image_size = 150px , caption = Coat of Arms , latin_name = Universitas magistrorum et scholarium Parisiensis , motto = ''Hic et ubique terrarum'' (Latin) , mottoeng = Here and anywhere on Earth , established = Founded: c. 1150Suppressed: 1793Faculties reestablished: 1806University reestablished: 1896Divided: 1970 , type = Corporative then public university , city = Paris , country = France , campus = Urban The University of Paris (french: link=no, Université de Paris), metonymically known as the Sorbonne (), was the leading university in Paris, France, active from 1150 to 1970, with the exception between 1793 and 1806 under the French Revolution. Emerging around 1150 as a corporation associated with the cathedral school of Notre Dame de Paris, it was considered the second-oldest university in Europe. Haskins, C. H.: ''The Rise of Universities'', Henry Holt and Company, 1923, p. 292. Officially chartered i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auteuil-Neuilly-Passy
Neuilly-Auteuil-Passy, sometimes also referred to just as Passy-Auteuil, refers to an area covering the westernmost part of the city of Paris and a neighbouring suburban community. This area is commonly known as one of the richest in Paris, with calm, select and very expensive neighbourhoods. Neuilly-Auteuil-Passy is sometimes abbreviated as NAP. Auteuil (pronounced ) and Passy are part of the 16th arrondissement of Paris, while Neuilly-sur-Seine is a suburb located immediately to their west. The three communities border the Bois de Boulogne park. The area has been described as "the wealthiest, the most cocksure and, in many ways, the most irritating part of the city." Passy Benjamin Franklin lived in Passy from 1777 to 1785. When he left, Thomas Jefferson said, "When he left Passy, it seemed as if the village had lost its patriarch." Honoré de Balzac lived in Passy for over six years. Passy is home to the Musée Marmottan Monet, housed in the Château de la Muette, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ha-Tsefirah
''Ha-Tsfira'' ( he, הצפירה) was a Hebrew-language newspaper published in Poland in 1862 and 1874–1931. History The first issue of ''Ha-Tsfira'' appeared in Warsaw, Congress Poland, in 1862, edited by Chaim Selig Slonimski. ''Ha-Tsfira'' was the first Hebrew paper with an emphasis on the sciences. The paper closed down after six months when Slonimski became principal of the rabbinical seminary in Zhytomyr, and the government began censorship of Hebrew books. It reopened in 1874 in Berlin, and began to be published in Warsaw in September 1875. Coverage of news and politics was introduced after the First Zionist Congress. From 1886, the paper began to appear as a daily. The driving spirit behind this change was Slonimski's assistant, Nachum Sokolov, who was later appointed editor-in-chief. ''Ha-Tsfira'' became part of a network of important Hebrew periodicals, among them '' Ha-Shahar'', '' Ha-Asif'', ''Ha-Shiloaḥ''. Some of the greatest names in early modern Hebrew liter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ha-Melitz
''Ha-Melitz'' or ''HaMelitz'' (Hebrew: ) was the first Hebrew newspaper in the Russian Empire. It was founded by Alexander Zederbaum in Odessa in 1860. History ''Ha-Melitz'' first appeared as a weekly, and it began to appear daily in 1886. From 1871, it was published in Saint Petersburg. Publication was suspended several times for lack of support or by order of the authorities. In 1893, Leon Rabinowitz succeeded Zederbaum as the editor. ''Ha-Melitz'' was a representative of the progressive or ''haskalah'' movement, and even so severe a critic as Abraham Kovner admitted that it had been "more useful to the Jews than have the other Hebrew newspapers" (''Ḥeḳer Dabar,'' p. 52 ff., Warsaw, 1866). While it was not so literary or scientific as some of its contemporaries, ''Ha-Melitz'' usually had more news and debates of interest, and was consequently more popular. J. A. Goldenblum was for many years associated with Zederbaum in its publication. Abraham Shalom Friedberg and Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
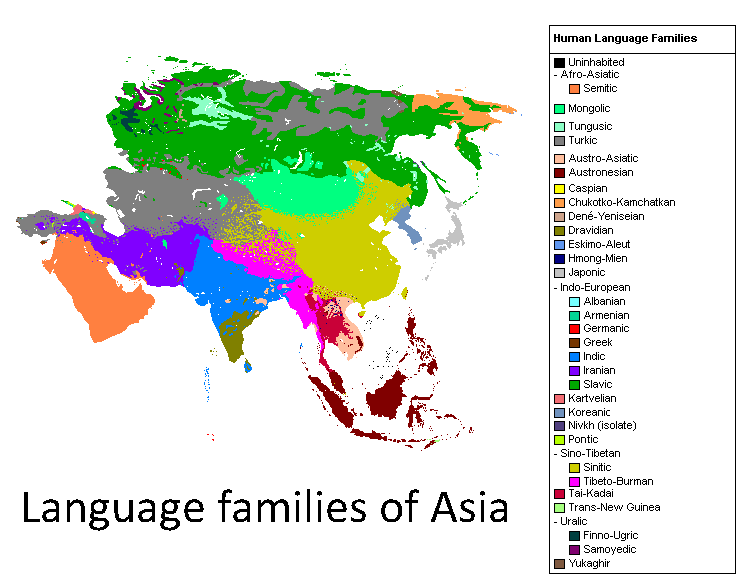
Oriental Language
A wide variety of languages are spoken throughout Asia, comprising different language families and some unrelated isolates. The major language families include Austroasiatic, Austronesian, Caucasian, Dravidian, Indo-European, Afroasiatic, Turkic, Sino-Tibetan and Kra–Dai. Most, but not all, have a long history as a written language. Language groups The major families in terms of numbers are Indo-European and Indo-Aryan languages and Dravidian languages in South Asia and Sino-Tibetan in East Asia. Several other families are regionally dominant. Sino-Tibetan Sino-Tibetan includes Chinese, Tibetan, Burmese, Karen, Boro and numerous languages of the Tibetan Plateau, southern China, Burma, and North east India. Indo-European The Indo-European languages are primarily represented by the Indo-Iranian branch. The family includes both Indic languages (Hindi, Urdu, Bengali, Odia, Assamese, Punjabi, Sindhi, Kashmiri, Marathi, Gujarati, Sinhala and other languages spoken prim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Geneva
The University of Geneva (French: ''Université de Genève'') is a public research university located in Geneva, Switzerland. It was founded in 1559 by John Calvin as a theological seminary. It remained focused on theology until the 17th century, when it became a center for enlightenment scholarship. Today, it is the third largest university in Switzerland by number of students. In 1873, it dropped its religious affiliations and became officially secular. In 2009, the University of Geneva celebrated the 450th anniversary of its founding. Almost 40% of the students come from foreign countries. The university holds and actively pursues teaching, research, and community service as its primary objectives. In 2016, it was ranked 53rd worldwide by the Shanghai Academic Ranking of World Universities, 89th by the QS World University Rankings, and 131st in the Times Higher Education World University Ranking. UNIGE is a member of the League of European Research Universities (includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |